迭代器
迭代器广泛使用于容器,用于访问和操纵元素:
for(iterator p=c.begin();p!=c.end();p++){
operations;}
每个容器都有自己的迭代器类型,抽象层隐藏具体实现细节,为所有容器的迭代器的使用提供了一致方法:故知道了一种迭代器使用,就可以知道其他迭代器使用。
1 迭代器的使用
int main(){
vector<int>intvec;
intvec.push_back(10);
intvec.push_back(40);
intvec.push_back(50);
intvec.push_back(20);
intvec.push_back(30);
vector<int>::iterator p1;
cout<<"the inf of vec:"<<endl;
for(p1=intvec.begin();p1!=intvec.end();p1++)
cout<<*p1<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
set<int>s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(40);
s.insert(50);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(30);
set<int>::iterator p2;
cout<<"the inf of set:"<<endl;
for(p2=s.begin();p2!=s.end();p2++)//集合中元素是排序的
cout<<*p2<<" ";
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;}
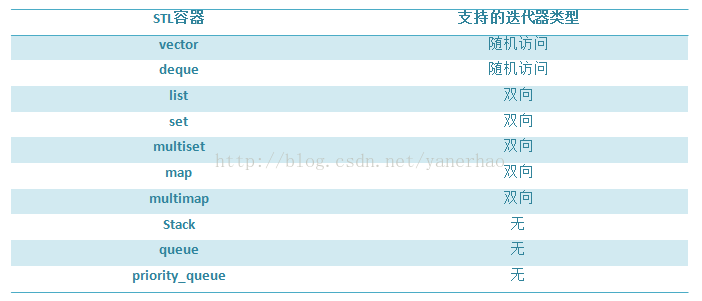
2 迭代器的分类
输入迭代器:用于从容器读取元素,每一步只能沿向前的方向移动一个元素
输出迭代器:用于向容器写入元素,每一步只能沿向前方向移动一个元素
向前迭代器:包括输入输出等所有功能,即支持读写。每一步只能沿向前方向移动一个元素
双向迭代器:包含向前迭代器,但是也可以实现向后,即可以实现每一步向前向后自由选择的移动一个元素
随机访问迭代器:包括双向迭代器,而且可以实现任意访问,向前或者向后跳过多个元素
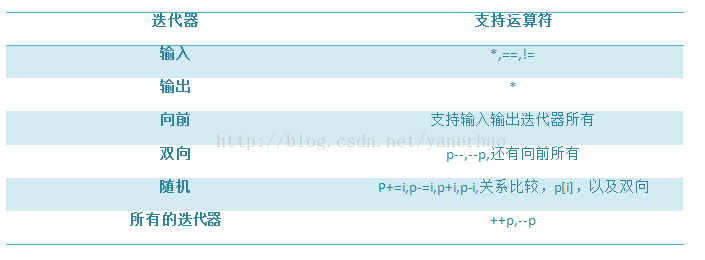
3 迭代器的一些知识
迭代器运算符:
利用运算符重载,对迭代器而言,有++,--,*,==,>=等运算符支持
由于vector支持随机访问迭代器,随机访问迭代器可以使用所有运算符,所以举例:
int main(){
vector<int>intvec;
intvec.push_back(10);
intvec.push_back(20);
intvec.push_back(30);
intvec.push_back(40);
intvec.push_back(50);
intvec.push_back(60);
vector<int>::iterator p1;
cout<<"the inf of vec:"<<endl;
for(p1=intvec.begin();p1!=intvec.end();p1++)
cout<<*p1<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
cout<<*(--p1)<<endl;//p1原来是尾部后一位,先前-,退一位
cout<<*(p1-3)<<endl;//p1原来是尾部,返回p1之前的3位,p1还在尾部
cout<<p1[-3]<<endl;//p1在尾部,返回前向距离p1为3的元素
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;}
预定义的迭代器
有iterator(可读可写)
const_iterator(只可读)
reverse_iterator(反向遍历)
const_reverse_iterator
int main(){
vector<int>intvec;
intvec.push_back(10);
intvec.push_back(20);
intvec.push_back(30);
intvec.push_back(40);
intvec.push_back(50);
intvec.push_back(60);
vector<int>::reverse_iterator p1;
cout<<"the inf of vec:"<<endl;
for(p1=intvec.rbegin();p1!=intvec.rend();p1++)
cout<<*p1<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
cout<<*(--p1)<<endl;//p1原来是尾部后一位,先前-,退一位
cout<<*(p1-3)<<endl;//p1原来是尾部,返回p1之前的3位,p1还在尾部
cout<<p1[-3]<<endl;//p1在尾部,返回前向距离p1为3的元素
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;}
istream_iterator&&ostream_iterator
这两个迭代器用于序列号元素:既可以是容器里的,也可以是输入输出流的元素
#include<iterator>
int main(){
int a[3]={0};
cout<<"enter 3 nums:"<<endl;
istream_iterator<int> in(cin);
ostream_iterator<int> out(cout);
a[0]=*in;
in++;
a[1]=*in;
in++;
a[2]=*in;
cout<<"the inf:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{*out=a[i];
cout<<" ";}
system("pause");
return 0;}