全文检索Lucence(二)——索引
上篇博客中从要解决的数据和系统业务以及内部结构上,大致了解了下Lucence,这里重点从代码层面开始学习Lucence的核心部分——索引
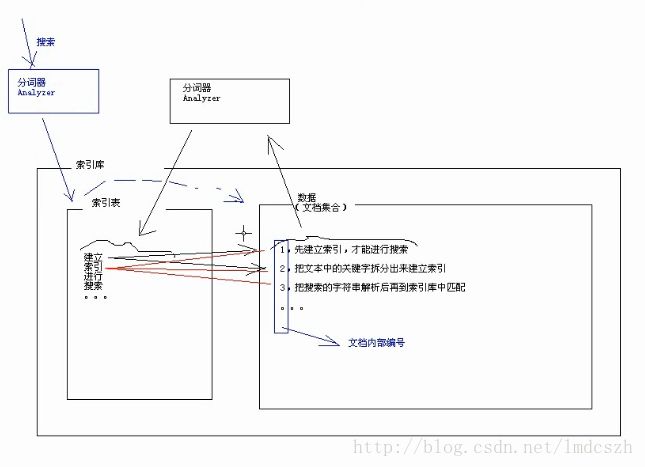
通过这张图可以对索引有个大致的了解:
1、IndexWriter——创建索引的对象:
建立索引的核心对象是IndexWriter,创建索引的实质就是:将一个文本文件转换为一个Lucence可以识别的文档格式,然后使用索引管理对象加入索引库。
<span style="font-size:18px;">//类的成员变量
//创建索引和搜索的使用同一个分词器
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer ();
String filePath= "D:\\Java\\JavaSource\\Lucence\\LucenceDemo\\LucenceDatasource\\IndexWriter addDocument's a javadoc.txt";
String indexPath="D:\\Java\\JavaSource\\Lucence\\LucenceDemo\\lucenceIndex";
/**
* 创建索引
* 索引设计到文件io操作,每次操作完后都需要关闭
* indexWriter 操作(crud)索引库
* @throws IOException
* @throws LockObtainFailedException
* @throws CorruptIndexException
*/
@Test
public void createIndex() throws Exception{
//file---->doc
System.out.println("文件转换成doc执行开始-------");
Document doc = File2DocumentUtils.file2Document(filePath);
System.out.println("文件转换成doc执行成功-------");
//建立索引
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(indexPath, analyzer, true, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
indexWriter.addDocument(doc);
indexWriter.close();
}</span>
2、IndexSearcher——根据索引检索的对象:
根据索引检索的过程和HQL的查询很类似,也都需要将查询参数封装到查询对象(query)中,然后将查询对象传递给indexSearcher对象,按照Lucence内部的机制进行解析,可以返回检索到的数据条数,和sql这样的查询有些区别的是,这里直接查出的是文档编号,如果需要显示文档内容,需要根据文档编号,进行查询,仍然是使用indexSearcher对象。
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* 搜索
* IndexSearcher 在索引库中进行查询
*/
@Test
public void search() throws Exception{
String queryString = "adddocument";
//1、把要搜索的文本解析为query对象
String[] fields= {"name","content"};
QueryParser queryParser= new MultiFieldQueryParser(fields, analyzer);
Query query= queryParser.parse(queryString);
Filter filter= null;
//2、进行查询
IndexSearcher indexSearcher= new IndexSearcher(indexPath);
TopDocs topDocs= indexSearcher.search(query, filter, 1000);
System.out.println("共有【"+topDocs.totalHits+"】条结果");
//3、打印结果
for(ScoreDoc scoreDoc: topDocs.scoreDocs){
//文档内部编号
int docSn = scoreDoc.doc;
//根据编号取出相应的文档
Document doc=indexSearcher.doc(docSn);
System.out.print("开始打印文件信息");
//打印出文档信息
File2DocumentUtils.printDocumentInfo(doc);
}
}</span>
说明:
为了便于复用,封装了将普通的文件转化为Lucence识别的文档格式的方法file2Document和将Lucence识别的文档内容解析成普通的文档信息的方法printDocumentInfo。通常的文档信息,包括四个字段:标题、内容、大小、路径,在建立索引和显示文档信息的时候都根据这四个字段。
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* 读取文件路径,然后将file转换成Document类型
* 文件: name content size path
* key value 形式
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static Document file2Document(String path){
System.out.println(path.trim());
File file = new File(path.trim());
System.out.println("静态方法file2Document-->文件转换成功!");
Document doc = new Document();
doc.add(new Field("name",file.getName(), Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED));
doc.add(new Field("content",readFileContent(file), Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED));
doc.add(new Field("size",NumberTools.longToString(file.length()), Store.YES, Index.NOT_ANALYZED));
doc.add(new Field("path",file.getPath(), Store.YES, Index.NOT_ANALYZED));
return doc;
}
/**
* <pre>
* 方法1:
* Field field = doc.getField("name");
String name= field.stringValue();
方法2:doc.get("name")
</pre>
* @param doc
*/
public static void printDocumentInfo(Document doc){
/* Field field = doc.getField("name");
String name= field.stringValue();*/
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("name-----"+doc.get("name"));
System.out.println("content-----"+doc.get("content"));
System.out.println("size-----"+NumberTools.stringToLong(doc.get("size")));
System.out.println("path-----"+doc.get("path"));
}</span>
3、Directory——索引库的位置:
Directory时索引库的操作对象,可以读取磁盘目录的位置,也可以从内存中读取。因为磁盘的I/O影响性能,通常的操作办法是:启动时读取索引到内存,退出时保存到本地。
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* 根据目录创建索引
* @throws Exception
*
*/
@Test
public void testIndexRamOrFSDir() throws Exception {
Directory dir = FSDirectory.getDirectory(indexPath);
//Directory dir= new RAMDirectory();
Document doc =File2DocumentUtils.file2Document(filePath);
IndexWriter indexWriter= new IndexWriter(dir, analyzer, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
indexWriter.addDocument(doc);
indexWriter.close();
}</span>
启动时读取索引到内存,退出时保存到本地:
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* 启动时读取索引到内存,退出时保存到本地
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testIndexUpdateAndSave() throws Exception{
//根据路径自动创建索引库对象
Directory fsDir= FSDirectory.getDirectory(indexPath);
//启动时读取
Directory ramDir = new RAMDirectory(fsDir);
//运行时操作ramDir
IndexWriter indexWriter= new IndexWriter(ramDir, analyzer, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
Document doc = File2DocumentUtils.file2Document(filePath);
indexWriter.addDocument(doc);
indexWriter.close();
//退出时保存到本地
//如果没有true,那么每次都会在原有的基础上增加,如果原有的是3条,那么这里通过内存中又添加了一条,之后再加上文件中的3条,那么最后将会是7条
//IndexWriter fsIndexWriter= new IndexWriter(fsDir, analyzer, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
//这里添加了true后,就是每次只添加内存中新增的那一条
IndexWriter fsIndexWriter= new IndexWriter(fsDir, analyzer,true, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
fsIndexWriter.addIndexesNoOptimize(new Directory[]{ramDir});
//优化,类似hibernate的缓存
fsIndexWriter.flush();
//fsIndexWriter.commit();
//优化是合并文件,需要先从内存中flush掉后才能合并文件
fsIndexWriter.optimize();
fsIndexWriter.close();
}</span>
4、索引的优化:
优化的实质是合并小的文件,通过indexWriter对象实现,机制很类似hibernate的缓存,从内存中flush的时候会触发合并的动作。
<span style="font-size:18px;">/**
* 对索引库的优化
*/
@Test
public void testIndexOptimize() throws Exception{
Directory dir= FSDirectory.getDirectory(indexPath);
IndexWriter indexWriter= new IndexWriter(dir, analyzer, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);
//合并文件优化
indexWriter.optimize();
indexWriter.close();
}</span>
总结:
索引是全文检索的一个核心,索引的管理,包括索引的建立和根据索引的查询。
维护索引库的常见做法是:启动的时候从磁盘读取到内存,索引经过修改后,再退出的时候再保存到磁盘。