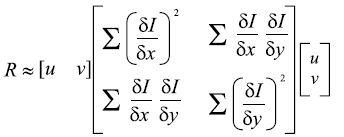角点检测和匹配之Harris与FAST角点检测
这一章主要内容:
1. Harris角点检测
2. FAST特征检测
3. 尺度不变的SURF特征检测
4.SURF检测描述
一、引言
在计算机视觉中,特征点或称兴趣点,角点(即图像的极值点,线段的终点,曲线曲率最大的点或水平、竖直方向上属性最大的点等等)被广泛应用。这些特征点是图像很重要的特征,对图像图形的理解和分析有很重要的作用。特征点在保留图像图形重要特征的同时,可以代替整幅图像的处理,有效地减少信息的数据量,使其信息的含量很高,有效地提高了计算的速度,有利于图像的可靠匹配,使得实时处理成为可能。
特征点检测就是是对有具体定义的、或者是能够具体检测出来的特征点的检测。目前检测方法很多,具体分有三大类基于灰度图像的角点检测、基于二值图像的角点检测、基于轮廓曲线的角点检测。基于灰度图像的角点检测又可分为基于梯度、基于模板和基于模板梯度组合3类方法,其中基于模板的方法主要考虑像素领域点的灰度变化,即图像亮度的变化,将与邻点亮度对比足够大的点定义为角点。常见的基于模板的角点检测算法有Kitchen-Rosenfeld角点检测算法,Harris角点检测算法、KLT角点检测算法及SUSAN角点检测算法。和其他角点检测算法相比,SUSAN角点检测算法具有算法简单、位置准确、抗噪声能力强等特点。
特征点的应用也很广泛,去解决一些重要的图像问题,如目标识别,图像匹配,视觉跟踪,3D重建等等。
二、Harris角点检测
角点是图像局部特征,很方便的在图像中定位(甚至是半像素精确定位),而且经常出现在人造的物体(如墙,门,窗户,桌子等等)中,所以应用广泛。
Harris角点检测是最经典的检测方法,基本原理就是,角点的水平和竖直方向梯度都比较大(经过数学推导,两个特征值即代表水平和垂直方向的强度),边缘点是水平或竖直梯度有一个比较大,平坦点是水平和竖直梯度都比较小。因此主要是计算方向梯度,然后根据特定门限判断是否是最大,确定角点。
opencv中提供两个Harris角点检测的函数,
2.1 cornerHarris
第一个比较简单,直接调用即可
函数头文件:
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>函数定义:
//! computes Harris cornerness criteria at each image pixel
CV_EXPORTS_W void cornerHarris( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int blockSize,
int ksize, double k,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT ); 函数参数说明:
blockSize:角点是两个边缘的连接点,因此在局部范围内,角点是所有方向上梯度最大的点,blockSize就是设置局部检测窗口大小
ksize:在计算个方向变化强度的时候使用了Sobel求其导数,该参数就是设置Sobel滤波器参数。
k: 两个特征值都不大于门限时,该点是普通点;当只有一个特征值大于门限时,是边缘点;当两个特征值都大于门限时,是角点。由于同时判断两个特征值比较麻烦,经过变形,得出下面公式,根据公式的不同值对应不同结果。需要设置K参数,来调节所需要结果的性能,一般K取(0.05--0.5)。
函数使用实例:
// Detect Harris Corners
cv::Mat cornerStrength;
cv::cornerHarris(image,cornerStrength,
3, // neighborhood size
3, // aperture size
0.01); // Harris parameter
// threshold the corner strengths
cv::Mat harrisCorners;
double threshold= 0.0001;
cv::threshold(cornerStrength,harrisCorners,
threshold,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
程序结果显示:
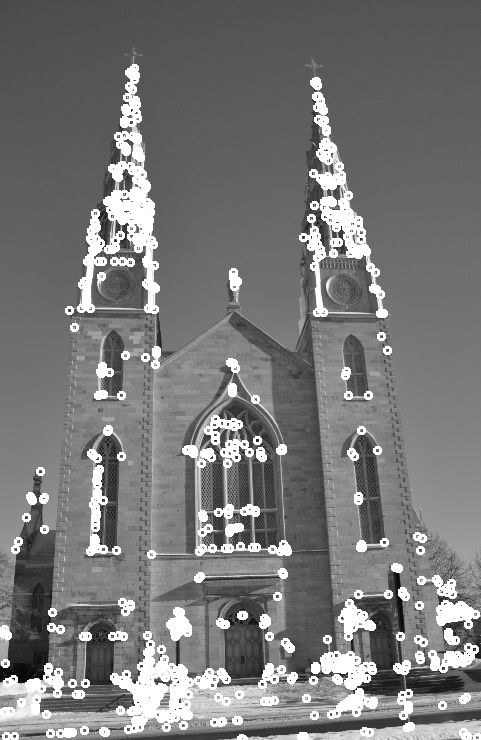
church01.jpg
Harris Corner Map.jpg
可以看出角点检测的图形有很多簇角点,导致很难对角点进行精确定位,所以我们在下面定义个类,检测角点并进行其他处理。
类得设计有两步,第一步计算源图像所有的角点;第二步,1,可设置质量等级(即门限)的值,当大于门限值时,选为候选角点,2 ,再进行非极大值抑制算法,排除一些虽然超过门限,但是不是局部最大的点。实现方法:先膨胀(dilate),把局部小于最大值的点全部膨胀为最大值,然后和原图比较(compare),剩下和原图相同的点,得出局部最大点,存入localMax。通过bitwise_and,将localMax和cornerMap相与,完成非极大值抑制。
#if !defined HARRISD
#define HARRISD
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
class HarrisDetector {
private:
// 32-bit float image of corner strength
cv::Mat cornerStrength;
// 32-bit float image of thresholded corners
cv::Mat cornerTh;
// image of local maxima (internal)
cv::Mat localMax;
// size of neighbourhood for derivatives smoothing
int neighbourhood;
// aperture for gradient computation
int aperture;
// Harris parameter
double k;
// maximum strength for threshold computation
double maxStrength;
// calculated threshold (internal)
double threshold;
// size of neighbourhood for non-max suppression
int nonMaxSize;
// kernel for non-max suppression
cv::Mat kernel;
public:
HarrisDetector() : neighbourhood(3), aperture(3), k(0.1), maxStrength(0.0), threshold(0.01), nonMaxSize(3) {
setLocalMaxWindowSize(nonMaxSize);
}
// Create kernel used in non-maxima suppression
void setLocalMaxWindowSize(int size) {
nonMaxSize= size;
kernel.create(nonMaxSize,nonMaxSize,CV_8U);
}
// Compute Harris corners
void detect(const cv::Mat& image) {
// Harris computation
cv::cornerHarris(image,cornerStrength,
neighbourhood,// neighborhood size
aperture, // aperture size
k); // Harris parameter
// internal threshold computation
double minStrength; // not used
cv::minMaxLoc(cornerStrength,&minStrength,&maxStrength);
// local maxima detection
cv::Mat dilated; // temporary image
cv::dilate(cornerStrength,dilated,cv::Mat());
cv::compare(cornerStrength,dilated,localMax,cv::CMP_EQ);
}
// Get the corner map from the computed Harris values
cv::Mat getCornerMap(double qualityLevel) {
cv::Mat cornerMap;
// thresholding the corner strength
threshold= qualityLevel*maxStrength;
cv::threshold(cornerStrength,cornerTh,threshold,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
// convert to 8-bit image
cornerTh.convertTo(cornerMap,CV_8U);
// non-maxima suppression
cv::bitwise_and(cornerMap,localMax,cornerMap);
return cornerMap;
}
// Get the feature points vector from the computed Harris values
void getCorners(std::vector<cv::Point> &points, double qualityLevel) {
// Get the corner map
cv::Mat cornerMap= getCornerMap(qualityLevel);
// Get the corners
getCorners(points, cornerMap);
}
// Get the feature points vector from the computed corner map
void getCorners(std::vector<cv::Point> &points, const cv::Mat& cornerMap) {
// Iterate over the pixels to obtain all feature points
for( int y = 0; y < cornerMap.rows; y++ ) {
const uchar* rowPtr = cornerMap.ptr<uchar>(y);
for( int x = 0; x < cornerMap.cols; x++ ) {
// if it is a feature point
if (rowPtr[x]) {
points.push_back(cv::Point(x,y));
}
}
}
}
// Draw circles at feature point locations on an image
void drawOnImage(cv::Mat &image, const std::vector<cv::Point> &points, cv::Scalar color= cv::Scalar(255,255,255), int radius=3, int thickness=2) {
std::vector<cv::Point>::const_iterator it= points.begin();
// for all corners
while (it!=points.end()) {
// draw a circle at each corner location
cv::circle(image,*it,radius,color,thickness);
++it;
}
}
};
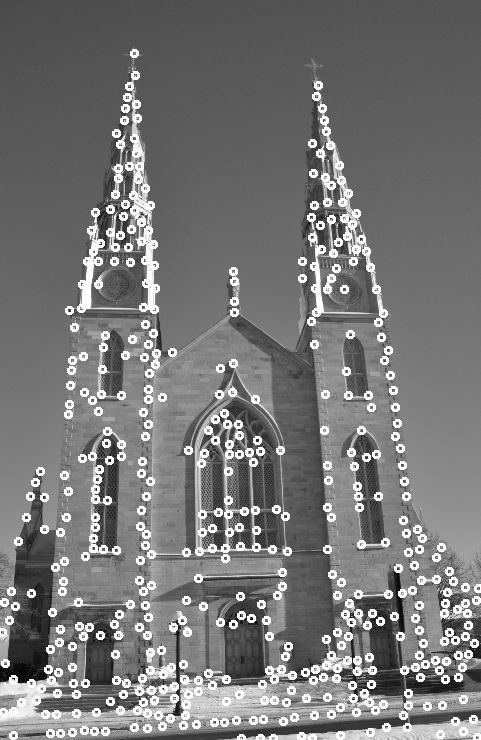
#endif 程序结果:
Harris Corners.jpg
程序结果分析:
可以看出检测出的角点,虽然是最优,但是一簇一簇的,有些地方重复太多。
2.2 goodFeaturesToTrack
由于第一种Harris算法,对K值的选取有很大要求,K值是经验值,对不同图像不好确定,因此提出改进型的Harris算法,只需计算两个特征值,例外也不选用非极大值抑制方法,而选择容忍距离。
函数定义:
//! finds the strong enough corners where the cornerMinEigenVal() or cornerHarris() report the local maxima
CV_EXPORTS_W void goodFeaturesToTrack( InputArray image, OutputArray corners,
int maxCorners, double qualityLevel, double minDistance,
InputArray mask=noArray(), int blockSize=3,
bool useHarrisDetector=false, double k=0.04 ); 函数使用例子:
// Compute good features to track
std::vector<cv::Point2f> corners;
cv::goodFeaturesToTrack(image,corners,
500, // maximum number of corners to be returned 角点总数
0.01, // quality level 质量等级
10); // minimum allowed distance between points 容忍距离
// for all corners
std::vector<cv::Point2f>::const_iterator it= corners.begin();
while (it!=corners.end()) {
// draw a circle at each corner location
cv::circle(image,*it,3,cv::Scalar(255,255,255),2);
++it;
} 程序结果:
2.3 GoodFeaturesToTrackDetector
opencv对goodFeaturesToTrack设置一个接口。
应用实例:
// vector of keypoints std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypoints; // Construction of the Good Feature to Track detector cv::GoodFeaturesToTrackDetector gftt( 500, // maximum number of corners to be returned 0.01, // quality level 10); // minimum allowed distance between points // point detection using FeatureDetector method gftt.detect(image,keypoints); cv::drawKeypoints(image, // original image keypoints, // vector of keypoints image, // the resulting image cv::Scalar(255,255,255), // color of the points cv::DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_OVER_OUTIMG); //drawing flag
三、FAST(Features from Accelerated Segment Test)角点检测
Harris角点检测定义了角点的数学表达式,但是这只是众多定义的一种,而且由于需要计算导数,比较复杂。特别是在实际应用中,角点检测只是很多应用的第一步,所以在这提出了一种FAST角点检测,角点的确定只取决于相邻像素的比较。
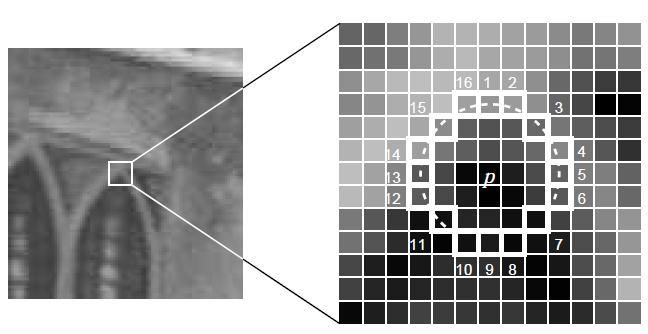
FAST算法检测的角点定义为在像素点的周围邻域内有足够多的像素点与该点处于不同的区域。应用到灰度图像中,即有足够多的像素点的灰度值大于该点的灰度值或者小于该点的灰度值。例如选取半径是3的情况,如下图,如果这1-16个点中,有超过3/4即12个,与圆点的灰度差大于阈值,则确定该点为候选角点,再利用非极大值抑制,从期望角点中选出最佳角点。
为了能利用机器学习的的方法进行加速。对同一类图像,例如同一场景的图像,可以在16个方向上进行训练,得到一棵决策树,从而在判定某一像素点是否为角点时,不再需要对所有方向进行检测,而只需要按照决策树指定的方向进行2-3次判定即可确定该点是否为角点。
另外非极大值抑制,一般是选择原点与相邻节点灰度差之和最大的角点,作为最后保留的最优角点。
opencv中提供的FAST函数如下:
函数举例:
// Read input image
image= cv::imread("church01.jpg",0);
keypoints.clear();
cv::FastFeatureDetector fast(40);
fast.detect(image,keypoints);
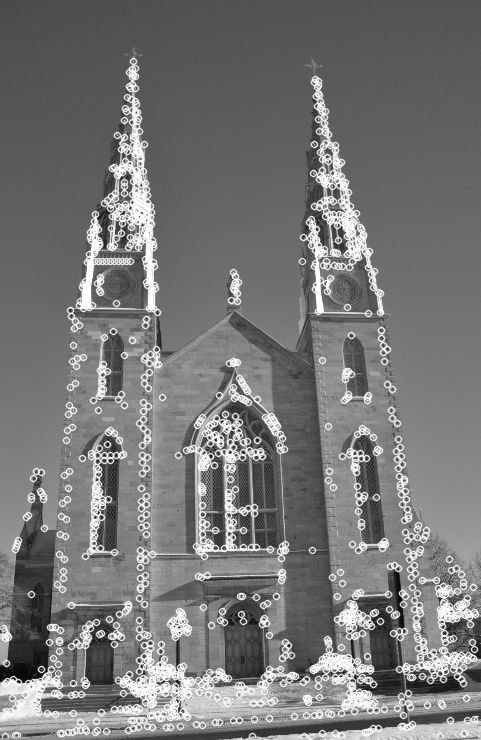
cv::drawKeypoints(image,keypoints,image,cv::Scalar(255,255,255),cv::DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_OVER_OUTIMG); 程序结果:
FAST Features.jpg