队列与栈相互模拟的读书笔记
栈与队列都是比较高级的数据结构,虽然不难,但有时有些问题也比较灵活,在《编程之美》与《剑指offer》上就有一些这样的题目。用队列模拟栈、用站栈模拟队列,以及现实队列与栈的最大值与最小值求解,这些都是基础的,只要理解栈的后进先出与队列的先进先出特点即可解决。
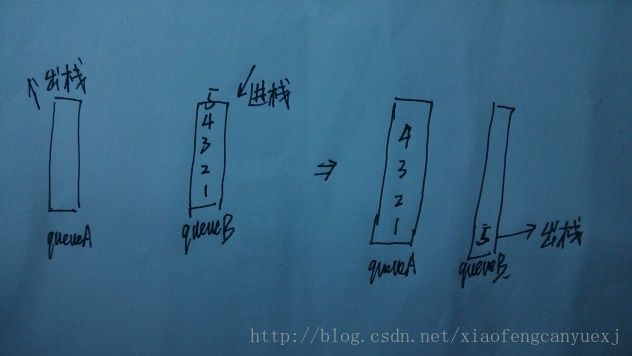
1、栈模拟队列
用两个栈,元素从一个栈stackA进入,从另一个栈stackB出来。进队列时直接添加到stackA,出队列时若stackA非空,则直接出,否则将stackB中元素全部初战装到stackA,然后从stackA出栈。
#ifndef MyQueue_H
#define MyQueue_H
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class MyQueue
{
private:
stack<int>stackA,stackB;
public:
void EnQueue(int);
int DeQueuep();
};
void MyQueue::EnQueue(int key)
{
stackA.push(key);
}
int MyQueue::DeQueuep()
{
if(stackB.empty())
{
while(!stackA.empty())
{
stackB.push(stackA.top());
stackA.pop();
}
if(stackB.empty())
throw new exception("队列已空!");
}
int ret=stackB.top();
stackB.pop();
return ret;
}
#endif MyQueue_H
2、队列模拟栈
用两个队列,进栈时进入其中一个空的队列,出栈时将其中一个队列中的元素进入另外一个空的队列,最后一个元素不进入直接出队列模拟出栈。
#ifndef MyStack_H
#define MyStack_H
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class MyStack
{
private:
queue<int>queueA,queueB;
bool tag;
public:
MyStack()
{
tag=false;
}
void push(int);
int pop();
};
void MyStack::push(int key)
{
if(!tag)queueA.push(key);
else queueB.push(key);
}
int MyStack::pop()
{
if(!tag)
{
if(queueA.empty())
throw new exception("栈为空");
while(queueA.size()>1)
{
queueB.push(queueA.front());
queueA.pop();
}
tag=true;
int ret=queueA.front();
queueA.pop();
return ret;
}
else
{
if(queueB.empty())
throw new exception("栈为空");
while(queueB.size()>1)
{
queueA.push(queueB.front());
queueB.pop();
}
tag=false;
int ret=queueB.front();
queueB.pop();
return ret;
}
}
#endif MyStack_H
3、栈的最小值与最大值操作
以最小值为例,直接开辟个辅助栈储存即可。上代码。
#ifndef StackWithMin_H
#define StackWithMin_H
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class StackWithMin
{
private:
stack<int>stackEle,stackMin;
public:
int min();
void push(int);
void pop();
int top();
bool empty();
};
int StackWithMin::min()
{
if(stackMin.empty())
throw new exception("栈为空!");
return stackMin.top();
}
void StackWithMin::push(int key)
{
stackEle.push(key);
if(stackMin.empty())
stackMin.push(key);
else
{
if(key>stackMin.top())
stackMin.push(stackMin.top());
else stackMin.push(key);
}
}
int StackWithMin::top()
{
if(stackEle.empty())
throw new exception("栈为空!");
return stackEle.top();
}
void StackWithMin::pop()
{
if(stackMin.empty())
throw new exception("栈为空!");
stackEle.pop();
stackMin.pop();
}
bool StackWithMin::empty()
{
return stackMin.empty();
}
#endif StackWithMin_H
4、队列的最小值与最大值操作
此处可以用优先级队列(堆+队列),此处栈模拟。与栈模拟队列类比,只不过这里的栈要用3中的栈,即包含最小(大)值的栈,其他比较简单,在此不多说了。
#ifndef QueueWithMin_H
#define QueueWithMin_H
#include"StackWithMin.h"
const int INF=1<<30;
class QueueWithMin
{
private:
StackWithMin staMinA,staMinB;
public:
void EnQueue(int);
int min();
int DeQueuep();
};
void QueueWithMin::EnQueue(int key)
{
staMinA.push(key);
}
int QueueWithMin::DeQueuep()
{
if(staMinB.empty())
{
while(!staMinA.empty())
{
staMinB.push(staMinA.top());
staMinA.pop();
}
if(staMinB.empty())
throw new exception("队列已空!");
}
int ret=staMinB.top();
staMinB.pop();
return ret;
}
int QueueWithMin::min()
{
int retAMIn=INF,retBMIn=INF;
if(!staMinA.empty())
retAMIn=staMinA.min();
if(!staMinB.empty())
retBMIn=staMinB.min();
return retAMIn<retBMIn?retAMIn:retBMIn;
}
#endif QueueWithMin_H
由于每个元素出入两个队列或栈的次数为常数,所以总的时间复杂度与直接用栈或队列相同,且最值求解的时间复杂度为O(1),是典型的牺牲空间换取时间。
由于时间有限,欠缺测试,如有错误或不足,欢迎斧正!