微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用
微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用(上)
概述
Repository Factory是微软模式与实践小组发布的一个开发指南包,它把之前的Web Service Software Factory(WSSF)集成的Data Access Guidance Package分离出来,形成了一个单独的开发指南包。引用Johnny Halife的话说:“它不是一个对象-关系映射(Object-Relational Mapping,ORM)工具,它的目的是作为一个轻量级的代码生成器,以自动化完成绝大部分生成领域模型对象,并将之持久化到数据库的任务代码。”本文为微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用上篇。
Johnny指出了Repository Factory的改进之处:
1.开发包被移植到GAT/GAX上。
2.对WSSF的依赖全部移除,因此Repository Factory现在是一个完全独立的指南开发包。
3.之前由开发包生成并且包含多个基类的通用代码,现在被打包成为一个独立的DLL,并由Repository Factory项目引用。
4.生成了一个通用基本接口,来支持IOC模式。
5.除通用基本接口外,还生成了一个Factory类,并可以在项目配置文件中进行配置。因此,Repository Factory的实现方式可以通过修改配置文件切换。
6.为自定义存储操作的方便,加入了从实体字段到存储过程参数的自动映射。
7.数据库名称和配置从生成的Repository移植到了Repository<T>基类,连接字符串定义在配置文件中。
8.Repository方案的设置(操作和映射)现在可以保存起来以供重用。
下载安装
可以到RepositoryFactory官方主页上下载最新版本:http://www.codeplex.com/RepositoryFactory
注意安装之前请确保安装:
1.Guidance Automation Extensions
2.Guidance Automation Toolkit
启用RepositoryFactory
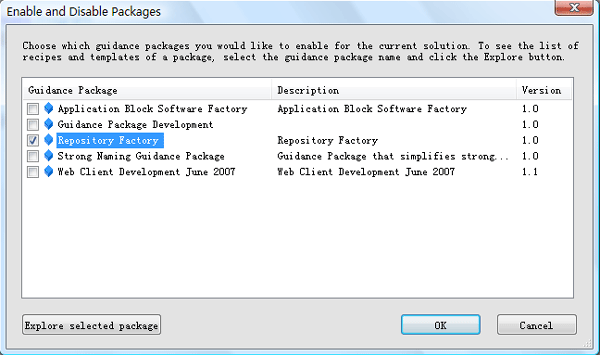
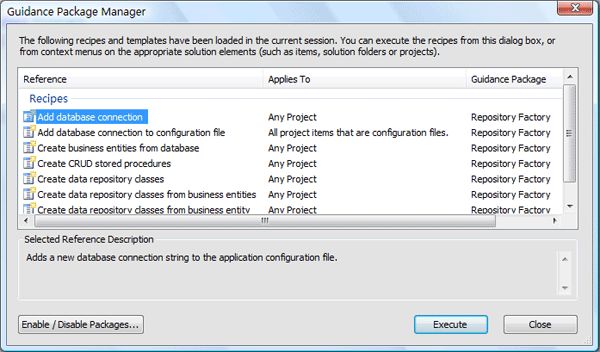
Step1:在Visual Studio 2005工具菜单中,选择Guidance Package Manager,可以打开指导包管理器:
Step2:选择Repository Factory
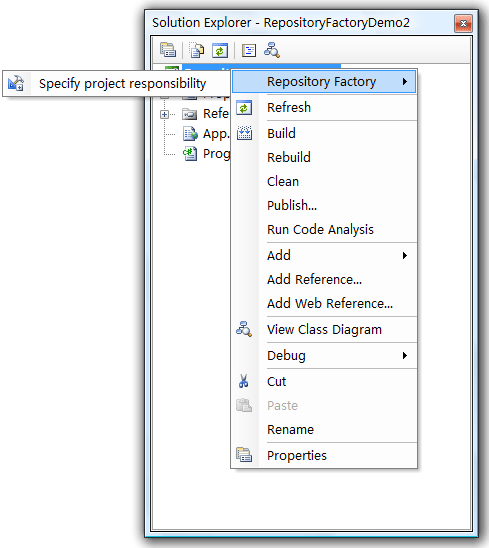
Step3:同时还需要在项目上右键菜单中,选择Specify project responsibility
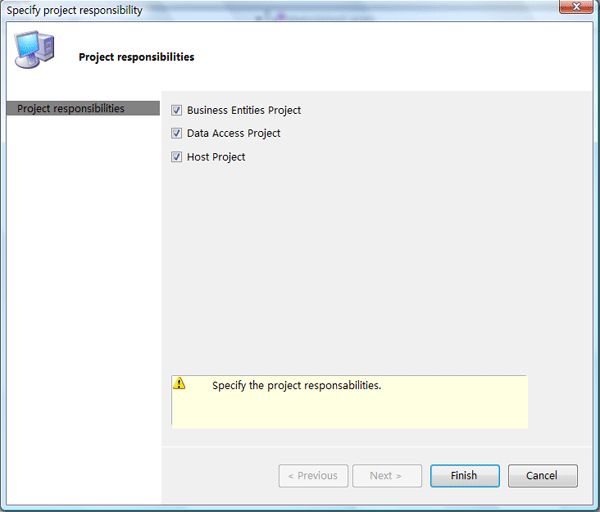
Step4:分别选择Business Entities Project、Data Access Project、Host Project。
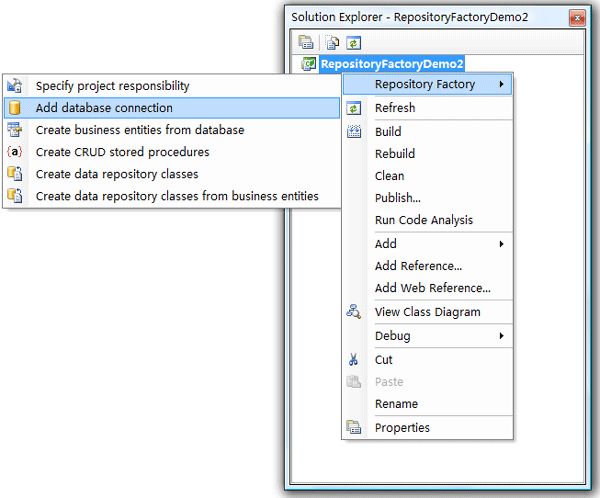
添加数据库连接
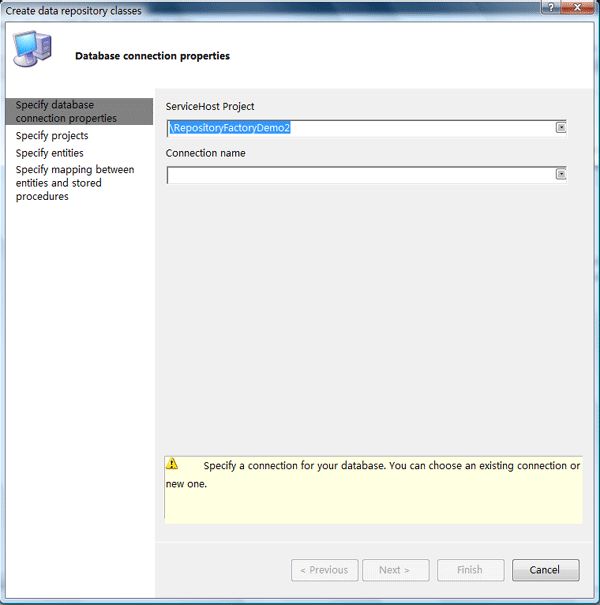
Step1:接下来需要添加数据库连接
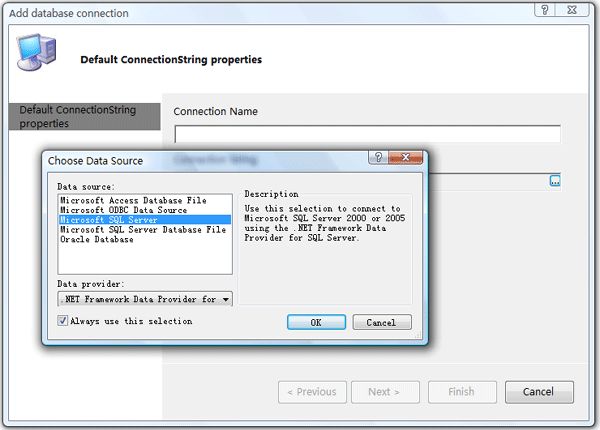
Step2:输入数据库连接串的名称:
创建连接完成后,将会在配置文件添加代码:
<connectionStrings> <add name="RFConnectionString" connectionString="Data Source=Esint-lhj/Sql2005;Initial
Catalog=AdventureWorksDW;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings>
创建实体类
用Repository Factory可以很方便的通过数据库架构,生成业务实体的代码。
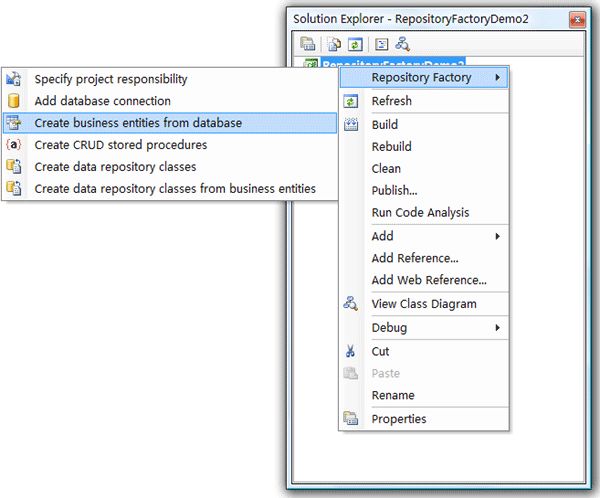
Step1:创建业务实体
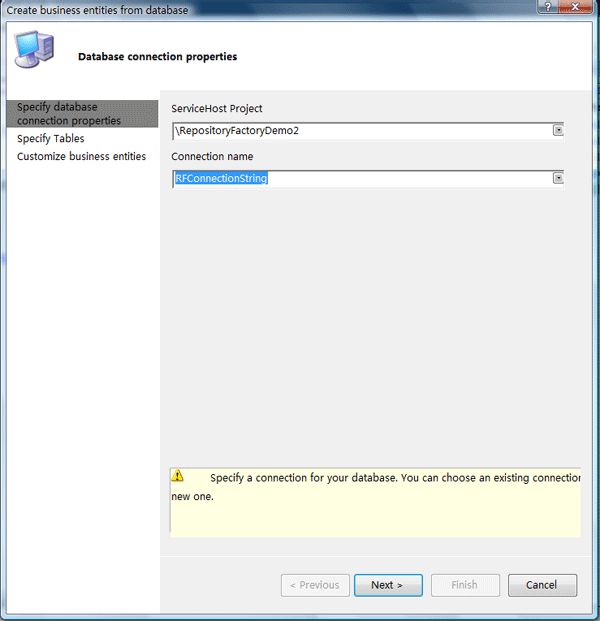
Step2:选择数据库连接字符串
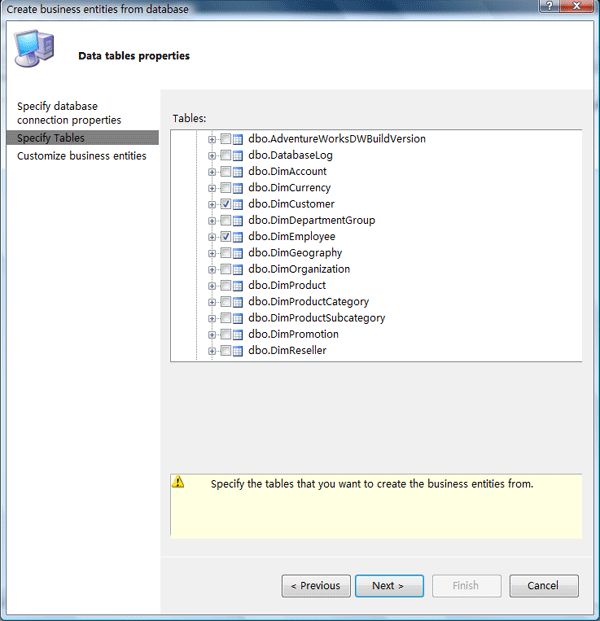
Step3:选择数据表、视图和字段
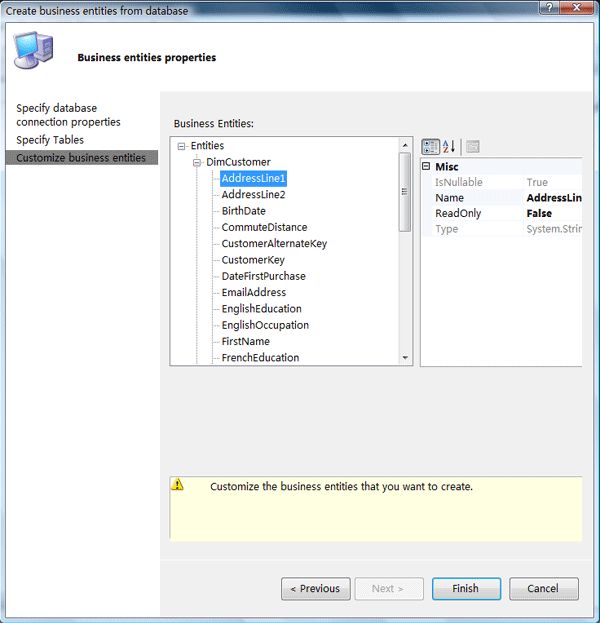
Step4:设置实体的属性了,可以设置业务实体的名称,默认的是表名;设置业务实体的属性名和该属性是否为只读属性
点击完成后,会生成业务实体的代码,并且为局部类型,这样便于用户在该业务实体上添加自己的一些操作,示例代码如下:
public partial class DimGeography { public DimGeography() { } public DimGeography(System.String city, System.String countryRegionCode, System.String englishCountryRegionName,
System.String frenchCountryRegionName, System.Int32 geographyKey, System.String postalCode,
Nullable<System.Int32> salesTerritoryKey, System.String spanishCountryRegionName, System.String stateProvinceCode,
System.String stateProvinceName) { this.cityField = city; this.countryRegionCodeField = countryRegionCode; this.englishCountryRegionNameField = englishCountryRegionName; this.frenchCountryRegionNameField = frenchCountryRegionName; this.geographyKeyField = geographyKey; this.postalCodeField = postalCode; this.salesTerritoryKeyField = salesTerritoryKey; this.spanishCountryRegionNameField = spanishCountryRegionName; this.stateProvinceCodeField = stateProvinceCode; this.stateProvinceNameField = stateProvinceName; } private System.String cityField; public System.String City { get { return this.cityField; } set { this.cityField = value; } } private System.String countryRegionCodeField; public System.String CountryRegionCode { get { return this.countryRegionCodeField; } set { this.countryRegionCodeField = value; } } private System.String englishCountryRegionNameField; public System.String EnglishCountryRegionName { get { return this.englishCountryRegionNameField; } set { this.englishCountryRegionNameField = value; } } private System.String frenchCountryRegionNameField; public System.String FrenchCountryRegionName { get { return this.frenchCountryRegionNameField; } set { this.frenchCountryRegionNameField = value; } } private System.Int32 geographyKeyField; public System.Int32 GeographyKey { get { return this.geographyKeyField; } set { this.geographyKeyField = value; } } private System.String postalCodeField; public System.String PostalCode { get { return this.postalCodeField; } set { this.postalCodeField = value; } } private Nullable<System.Int32> salesTerritoryKeyField; public Nullable<System.Int32> SalesTerritoryKey { get { return this.salesTerritoryKeyField; } set { this.salesTerritoryKeyField = value; } } private System.String spanishCountryRegionNameField; public System.String SpanishCountryRegionName { get { return this.spanishCountryRegionNameField; } set { this.spanishCountryRegionNameField = value; } } private System.String stateProvinceCodeField; public System.String StateProvinceCode { get { return this.stateProvinceCodeField; } set { this.stateProvinceCodeField = value; } } private System.String stateProvinceNameField; public System.String StateProvinceName { get { return this.stateProvinceNameField; } set { this.stateProvinceNameField = value; } } }
创建CRUD的存储过程
利用Repository Factory可以很方便的生成针对数据表的CRUD存储过程,可以生成Insert、Update、Delete、GetAll、GetOne、GetMany六种类型的存储过程。
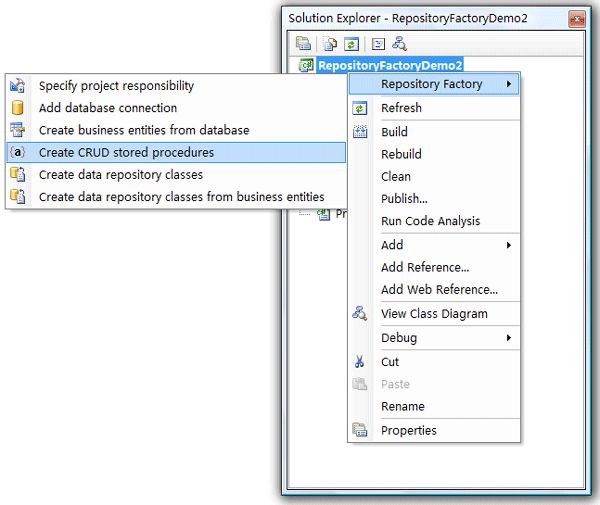
Step1:选择Create CRUD Stored Procedures菜单
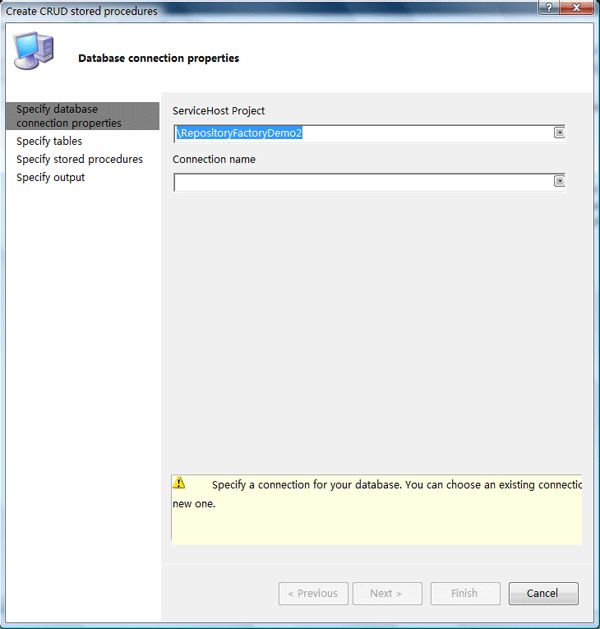
Step2:仍然是选择连接
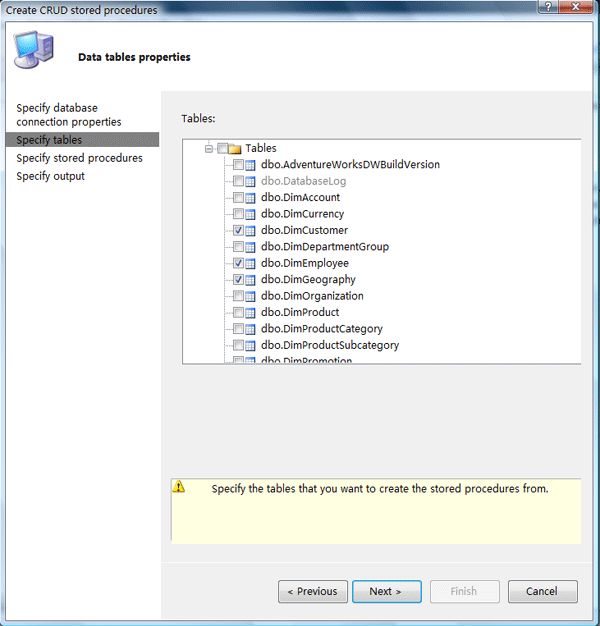
Step3:选择要生成存储过程的数据表
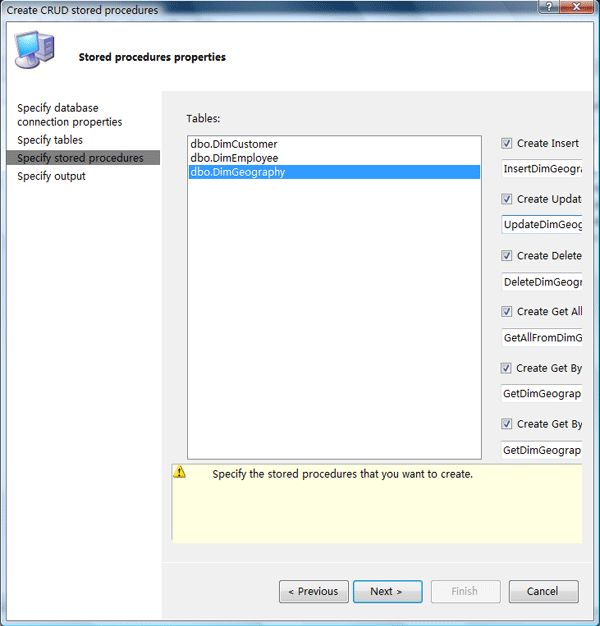
Step4:设置是否生成上面所说的六种存储过程以及存储过程的名称
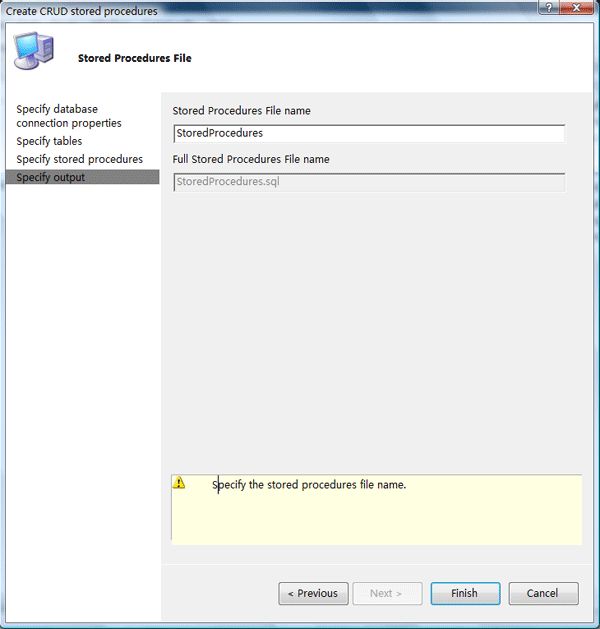
Step5:设置存储过程的输出文件
生成的存储过程部分代码:
---------------------------------------------------------------- -- [dbo].[DimGeography] Table -- IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT NAME FROM sys.objects WHERE TYPE = 'P' AND NAME = 'InsertDimGeography') BEGIN EXEC('CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[InsertDimGeography] AS RETURN') END GO ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[InsertDimGeography] @city nvarchar(30) = NULL, @countryRegionCode nvarchar(3) = NULL, @englishCountryRegionName nvarchar(50) = NULL, @frenchCountryRegionName nvarchar(50) = NULL, @geographyKey int OUT, @postalCode nvarchar(15) = NULL, @salesTerritoryKey int, @spanishCountryRegionName nvarchar(50) = NULL, @stateProvinceCode nvarchar(3) = NULL, @stateProvinceName nvarchar(50) = NULL AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON BEGIN TRY INSERT INTO [dbo].[DimGeography] ([City], [CountryRegionCode], [EnglishCountryRegionName], [FrenchCountryRegionName], [PostalCode], [SalesTerritoryKey], [SpanishCountryRegionName], [StateProvinceCode], [StateProvinceName]) VALUES (@city, @countryRegionCode, @englishCountryRegionName, @frenchCountryRegionName, @postalCode, @salesTerritoryKey, @spanishCountryRegionName, @stateProvinceCode, @stateProvinceName) SET @geographyKey = SCOPE_IDENTITY() END TRY BEGIN CATCH EXEC RethrowError; END CATCH SET NOCOUNT OFF END GO
结束语
使用Repository Factory生成业务实体和存储过程,就介绍到这里,限于篇幅,
分成了上下两篇,其他内容放在微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用(下)。
微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用(下)
概述
Repository Factory是微软模式与实践小组发布的一个开发指南包,
它把之前的Web Service Software Factory(WSSF)
集成的Data Access Guidance Package分离出来,形成了一个单独的开发指南包。
引用Johnny Halife的话说:“它不是一个对象-关系映射(Object-Relational Mapping,ORM)工具,
它的目的是作为一个轻量级的代码生成器,以自动化完成绝大部分生成领域模型对象,
并将之持久化到数据库的任务代码。”本文为微软轻量级“代码生成器”—Repository Factory使用下篇。生成Data Repository 类
接上篇,生成存储过程脚本之后,我们执行脚本,在数据库中生成相应的存储过程。接下来就可以生成Data Repository类了。
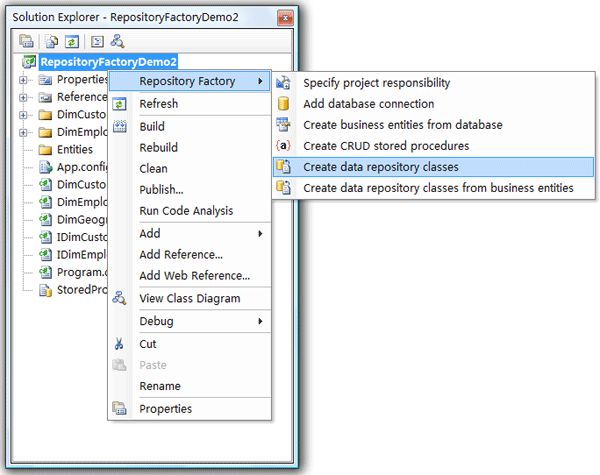
Step1:选择Create Data Repository Classes
Step2:仍然是指定数据库连接
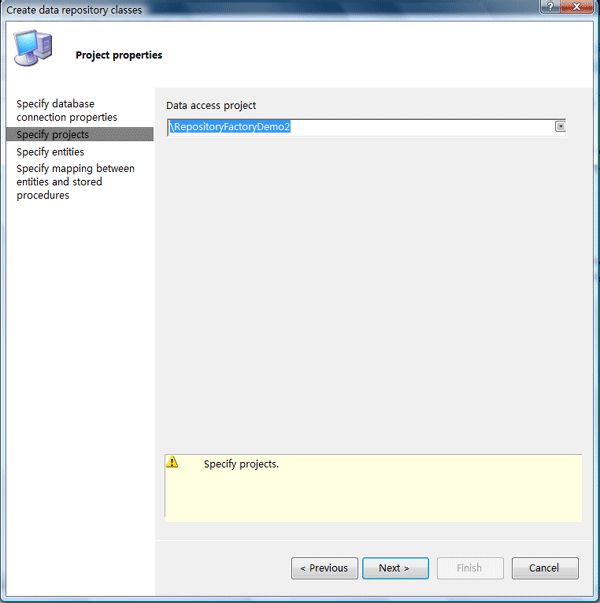
Step3:指定作为数据访问层的项目
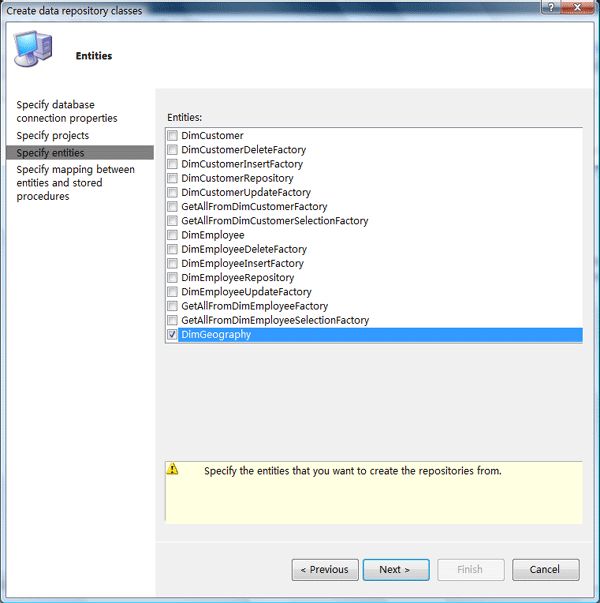
Step4:指定要生成代码的实体
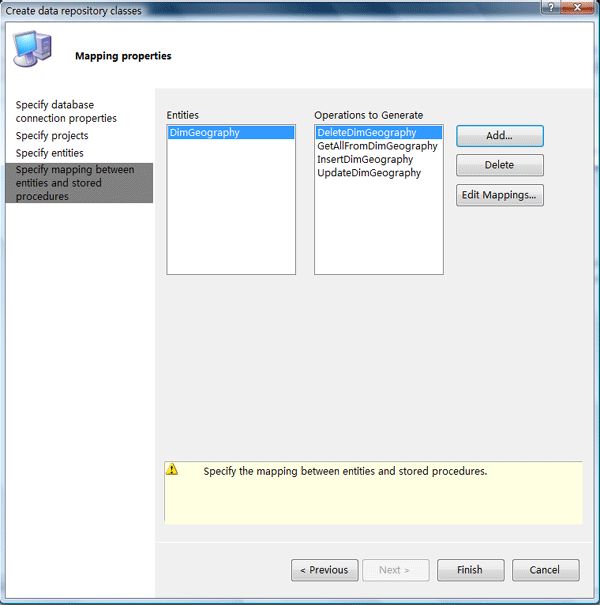
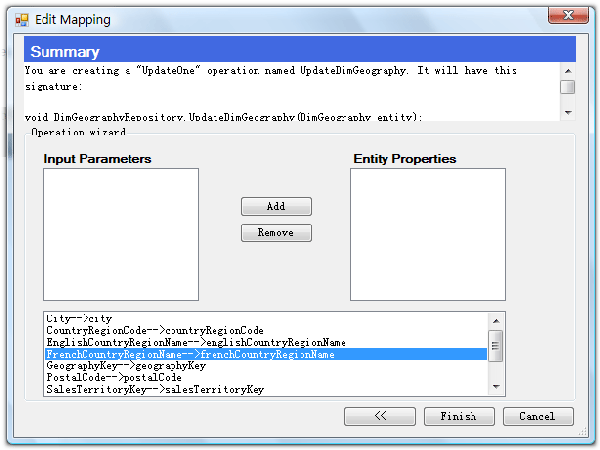
Step5:指定实体和存储过程之间的映射
在这一步还可以指定存储过程参数和业务实体属性之间的映射关系
Step6:生成代码:
生成Data Repository代码,生成的代码包括Repository接口和实现,分别针对每种操作生成一个工厂类。
生成的IDimCustomerRepository类:
public interface IDimCustomerRepository { List<DimCustomer> GetAllFromDimCustomer(); void Add(DimCustomer dimCustomer); void Remove(System.Int32 customerKey); void Save(DimCustomer dimCustomer); }生成的DimCustomerRepository类:
public class DimCustomerRepository : Repository<DimCustomer>, IDimCustomerRepository { public DimCustomerRepository(string databaseName) : base(databaseName) { } public DimCustomerRepository() : base() { } public List<DimCustomer> GetAllFromDimCustomer() { ISelectionFactory<NullableIdentity> selectionFactory = new GetAllFromDimCustomerSelectionFactory(); try { NullableIdentity nullableIdentity = new NullableIdentity(); return base.Find(selectionFactory, new GetAllFromDimCustomerFactory(), nullableIdentity); } catch (SqlException ex) { HandleSqlException(ex, selectionFactory); } return new List<DimCustomer>(); } public void Add(DimCustomer dimCustomer) { DimCustomerInsertFactory insertFactory = new DimCustomerInsertFactory(); try { base.Add(insertFactory, dimCustomer); } catch (SqlException ex) { HandleSqlException(ex, insertFactory); } } public void Remove(System.Int32 customerKey) { IDeleteFactory<System.Int32> deleteFactory = new DimCustomerDeleteFactory(); try { base.Remove(deleteFactory, customerKey); } catch (SqlException ex) { HandleSqlException(ex, deleteFactory); } } public void Save(DimCustomer dimCustomer) { DimCustomerUpdateFactory updateFactory = new DimCustomerUpdateFactory(); try { base.Save(updateFactory, dimCustomer); } catch (SqlException ex) { HandleSqlException(ex, updateFactory); } } private void HandleSqlException(SqlException ex, IDbToBusinessEntityNameMapper mapper) { if (ex.Number == ErrorCodes.SqlUserRaisedError) { switch (ex.State) { case ErrorCodes.ValidationError: string[] messageParts = ex.Errors[0].Message.Split(':'); throw new RepositoryValidationException( mapper.MapDbParameterToBusinessEntityProperty(messageParts[0]), messageParts[1], ex); case ErrorCodes.ConcurrencyViolationError: throw new ConcurrencyViolationException(ex.Message, ex); } } throw new RepositoryFailureException(ex); } }DimCustomerInsertFactory类:
internal class DimCustomerInsertFactory : IDbToBusinessEntityNameMapper, IInsertFactory<DimCustomer> { /// <summary> /// Creates the DimCustomerInsertFactory to build an insert statement for /// the given DimCustomer object. /// </summary> /// <param name="DimCustomer">New DimCustomer to insert into the database.</param> public DimCustomerInsertFactory() { } #region IInsertFactory<DimCustomer> Members public DbCommand ConstructInsertCommand(Database db, DimCustomer dimCustomer) { DbCommand command = db.GetStoredProcCommand("dbo.InsertDimCustomer"); if (dimCustomer.AddressLine1 != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "addressLine1", DbType.String, dimCustomer.AddressLine1); } if (dimCustomer.AddressLine2 != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "addressLine2", DbType.String, dimCustomer.AddressLine2); } if (dimCustomer.BirthDate != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "birthDate", DbType.DateTime, dimCustomer.BirthDate); } if (dimCustomer.CommuteDistance != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "commuteDistance", DbType.String, dimCustomer.CommuteDistance); } if (dimCustomer.CustomerAlternateKey != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "customerAlternateKey", DbType.String, dimCustomer.CustomerAlternateKey); } db.AddOutParameter(command, "customerKey", DbType.Int32, 4); if (dimCustomer.DateFirstPurchase != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "dateFirstPurchase", DbType.DateTime, dimCustomer.DateFirstPurchase); } if (dimCustomer.EmailAddress != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "emailAddress", DbType.String, dimCustomer.EmailAddress); } if (dimCustomer.EnglishEducation != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "englishEducation", DbType.String, dimCustomer.EnglishEducation); } if (dimCustomer.EnglishOccupation != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "englishOccupation", DbType.String, dimCustomer.EnglishOccupation); } if (dimCustomer.FirstName != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "firstName", DbType.String, dimCustomer.FirstName); } if (dimCustomer.FrenchEducation != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "frenchEducation", DbType.String, dimCustomer.FrenchEducation); } if (dimCustomer.FrenchOccupation != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "frenchOccupation", DbType.String, dimCustomer.FrenchOccupation); } if (dimCustomer.Gender != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "gender", DbType.String, dimCustomer.Gender); } if (dimCustomer.GeographyKey != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "geographyKey", DbType.Int32, dimCustomer.GeographyKey); } if (dimCustomer.HouseOwnerFlag != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "houseOwnerFlag", DbType.String, dimCustomer.HouseOwnerFlag); } if (dimCustomer.LastName != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "lastName", DbType.String, dimCustomer.LastName); } if (dimCustomer.MaritalStatus != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "maritalStatus", DbType.String, dimCustomer.MaritalStatus); } if (dimCustomer.MiddleName != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "middleName", DbType.String, dimCustomer.MiddleName); } if (dimCustomer.NameStyle != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "nameStyle", DbType.Boolean, dimCustomer.NameStyle); } if (dimCustomer.NumberCarsOwned != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "numberCarsOwned", DbType.Byte, dimCustomer.NumberCarsOwned); } if (dimCustomer.NumberChildrenAtHome != null) { db.AddInParameter(command, "numberChildrenAtHome", DbType.Byte, dimCustomer.NumberChildrenAtHome); }//......return command; } public void SetNewID(Database db, DbCommand command, DimCustomer dimCustomer) { System.Int32 id1 = (System.Int32)(db.GetParameterValue(command, "customerKey")); dimCustomer.CustomerKey = id1; } #endregion #region IDbToBusinessEntityNameMapper Members public string MapDbParameterToBusinessEntityProperty(string dbParameter) { switch (dbParameter) { case "addressLine1": return "AddressLine1"; case "addressLine2": return "AddressLine2"; case "birthDate": return "BirthDate"; case "commuteDistance": return "CommuteDistance"; case "customerAlternateKey": return "CustomerAlternateKey"; case "dateFirstPurchase": return "DateFirstPurchase"; case "emailAddress": return "EmailAddress"; //......default: throw new RepositoryInvalidParameterException(dbParameter); } } #endregion }并且会在配置文件中,自动配置Repository接口和实现之间的关系:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <configSections> <section name="repositoryFactory" type="Microsoft.Practices.Repository.Configuration.RepositoryFactorySection,
Microsoft.Practices.Repository, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" /> </configSections> <connectionStrings> <add name="RFConnectionString" connectionString="Data Source=Esint-lhj/Sql2005;Initial
Catalog=AdventureWorksDW;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=sql2005" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings> <repositoryFactory> <repositories> <add interfaceType="RepositoryFactoryDemo2.IDimEmployeeRepository, RepositoryFactoryDemo2" repositoryType="RepositoryFactoryDemo2.DimEmployeeRepositoryArtifacts.DimEmployeeRepository, RepositoryFactoryDemo2" /> <add interfaceType="RepositoryFactoryDemo2.IDimCustomerRepository, RepositoryFactoryDemo2" repositoryType="RepositoryFactoryDemo2.DimCustomerRepositoryArtifacts.DimCustomerRepository, RepositoryFactoryDemo2" /> </repositories> </repositoryFactory> </configuration>使用生成的代码
如下示例代码所示:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IDimEmployeeRepository repository = RepositoryFactory.Create<IDimEmployeeRepository>(); List<DimEmployee> employees = repository.GetAllFromDimEmployee(); } }自定义生成代码的风格
如果上面生成的代码风格,并不适合您现在所在团队的编码规范,
譬如说您习惯于以“_”开头来命名业务实体中的私有字段。
在Repository Factory中可以自定义生成代码的风格,
因为Repository Factory中的代码生成也是基于模板引擎的,
您可以通过修改模板来完成自定义生成代码的风格。
打开<安装目录>/Microsoft Patterns & Practices/Data Access Guidance Package Setup/Templates,
就可以看到生成代码所使用的模板了。模板编写说明:
1.以<#@ Template Language="C#" #>开头来指定一个模板
2.通过Assembly来添加对程序集的引用
<#@ Assembly Name="System.dll" #>
3.通过Import来导入命名空间
<#@ Import Namespace="System.Data" #>
4.通过Property来指定输入的参数
<#@ Property Processor="PropertyProcessor" Name="Entities"#>
5.通过include来引入外部的文件
<#@ include file="Templates/T4/Common/NamingHelper.t4" #>
6.完全使用C#语言来编写代码,是不是也可以通过<#@ Template Language="C#" #>来指定使用VB.NET编写,我没做过尝试:)
<# foreach(Property property in entity.Properties)
{
#>
private <#= (property.IsNullable && property.Type.IsValueType) ? "Nullable<" + property.Type.ToString() + ">" :property.Type.ToString() #> <#= GetFieldName(property.Name) #>;
public <#= (property.IsNullable && property.Type.IsValueType) ? "Nullable<" + property.Type.ToString() + ">" :
property.Type.ToString() #> <#= property.Name #>
{
get { return this.<#= GetFieldName(property.Name) #>; }
<#
if(!property.ReadOnly)
{
#>
set { this.<#= GetFieldName(property.Name) #> = value; }
<#
}
#>
}譬如,想在生成的业务实体私有字段前都加上下划线“_”,可以打开NamingHelper.t4文件,修改其中的GetFieldName方法如下:
private string GetFieldName(string type)
{
return "_" + NamingHelper.GetFieldName(type);
}这时再使用Repository Factory时可以看到生成的代码如下,私有字段命名前都加上“_”:
private System.String _classField; public System.String Class { get { return this._classField; } set { this._classField = value; } } private System.String _colorField; public System.String Color { get { return this._colorField; } set { this._colorField = value; } }结束语
通过Repository Factory我们可以很方便的生成自己的数据访问层,减少重复的体力劳动,并且支持灵活的自定义功能。
祝大家编程愉快:)
http://www.cnblogs.com/Terrylee/archive/2007/11/29/repository-factory-step-by-step-part1.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/Terrylee/archive/2007/11/29/repository-factory-step-by-step-part2.html