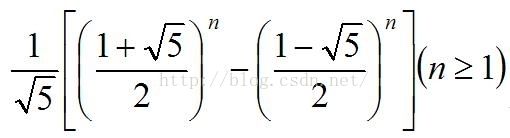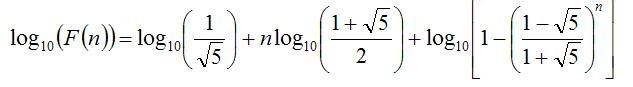ACM群赛(二)
链接:
http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/view.action?cid=104400#overview
Description
Problem A: Parity
| Source file: | parity.{c, cpp, java} |
| Input file: | parity.in |
A bit string has odd parity if the number of 1's is odd. A bit string has even parity if the number of 1's is even. Zero is considered to be an even number, so a bit string with no 1's has even parity. Note that the number of 0's does not affect the parity of a bit string.
Input: The input consists of one or more strings, each on a line by itself, followed by a line containing only "#" that signals the end of the input. Each string contains 1–31 bits followed by either a lowercase letter 'e' or a lowercase letter 'o'.
Output: Each line of output must look just like the corresponding line of input, except that the letter at the end is replaced by the correct bit so that the entire bit string has even parity (if the letter was 'e') or odd parity (if the letter was 'o').
| Example input: | Example output: |
| 101e 010010o 1e 000e 110100101o # |
1010 0100101 11 0000 1101001010 |
第一题就是简单的补零和补一。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
const int maxn = 52;
char str[maxn], ans[maxn];
int main ( )
{
int zero, one;
while ( ~ scanf ( "%s", str ) && strcmp ( str, "#" ) != 0 )
{
zero = one = 0;
strcpy ( ans, str );
int len = strlen ( str );
int pos = len-1;
for ( int i = 0; i < len-1; i ++ )
if ( str[i] == '0' )
zero ++;
else
one ++;
if ( str[len-1] == 'e' && one%2 == 1 || str[len-1] == 'o' && one%2 == 0 )
ans[pos ++] = '1';
else
ans[pos ++] = '0';
ans[pos] = '\0';
puts ( ans );
}
return 0;
}
Description
Input
Output
参看Sample Output.
Sample Input
2
13
10000
0
Sample Output
Second win
Second win
First win
这又是一道博弈的问题,但是可以自己用记忆化搜索推出规律。
可以发现当数字为斐波那契数列时第一个人必输,其他时候都是必赢。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LL long long
const int maxn = 1005, N = 55;
int win[maxn];
LL f[N];
int dfs ( int n, int cnt )
{
if ( win[n] != -1 )
return win[n];
if ( 2*cnt >= n )
return 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= 2*cnt; i ++ )
if ( dfs ( n-i, i ) == 0 )
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main ( )
{
int n;
memset ( win, -1, sizeof ( win ) );
win[0] = 0;
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 2;
for ( int i = 2; i < N; i ++ )
f[i] = f[i-1]+f[i-2];
while ( ~ scanf ( "%d", &n ) && n )
{
int w = 0;
/*
for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ )
if ( dfs ( n-i, i ) == 0 )
{
w = 1;
break ;
}
*/
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i ++ )
if ( n == f[i] )
{
w = 1;
break ;
}
printf ( w ? "Second win\n" : "First win\n" );
}
return 0;
}
Description
(f[0]=0,f[1]=1;f[i] = f[i-1]+f[i-2](i>=2))的值全部给背了下来。
接下来,CodeStar决定要考考他,于是每问他一个数字,他就要把答案说出来,不过有的数字太长了。所以规定超过4位的只要说出前4位就可以了,可是CodeStar自己又记不住。于是他决定编写一个程序来测验zouyu说的是否正确。
Input
Output
Sample Input
0
1
2
3
4
5
35
36
37
38
39
40
Sample Output
0
1
1
2
3
5
9227
1493
2415
3908
6324
1023
首先需要用到求斐波那契数列的公式
取对数得到
设((1-sqrt(5))/2)^n*x = ( ( 1+sqrt ( 5 ) )/2 )^n就可以划出后面那部分,
后面那部分小于1的。
lg5465 = lg5.465+3
而lg5.465 = 0.73759016..
则10^0.73759016..=5.465,然后乘1000就是前四位数了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
const int maxn = 25;
int f[maxn];
/*
log10 ( 32156456 ) = log10 ( 3.2156456 )+7
求出log10 ( 3.2156456 ) = x
那么10^x = 3.2156456
然后将10^x*1000就求出了前4位数
*/
int main ( )
{
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for ( int i = 2; i < maxn; i ++ )
f[i] = f[i-1]+f[i-2];
int n;
double a = ( 1+sqrt ( 5.0 ) )/2.0;
while ( ~ scanf ( "%d", &n ) )
{
if ( n <= 20 ) //前20位不超过4位数
{
printf ( "%d\n", f[n] );
continue ;
}
double t = -0.5*log10 ( 5.0 )+n*log10 ( a );
double p = t-( int )t;
double v = pow ( 10, p )*1000;
printf ( "%d\n", ( int )v );
}
return 0;
}
第四题为DP,表示本菜鸟不会。
Description
You are given a simple task. Given a sequence A[i] with N numbers. You have to perform Q operations on the given sequence.
Here are the operations:
- A v l, add the value v to element with index l.(1<=V<=1000)
- R a l r, replace all the elements of sequence with index i(l<=i<= r) with a(1<=a<=10^6) .
- Q l r, print the number of elements with index i(l<=i<=r) and A[i] is a prime number
Note that no number in sequence ever will exceed 10^7.
Input
The first line is a signer integer T which is the number of test cases.
For each test case, The first line contains two numbers N and Q (1 <= N, Q <= 100000) - the number of elements in sequence and the number of queries.
The second line contains N numbers - the elements of the sequence.
In next Q lines, each line contains an operation to be performed on the sequence.
Output
For each test case and each query,print the answer in one line.
Sample Input
1 5 10 1 2 3 4 5 A 3 1 Q 1 3 R 5 2 4 A 1 1 Q 1 1 Q 1 2 Q 1 4 A 3 5 Q 5 5 Q 1 5
Sample Output
2 1 2 4 0 4
动态修改查询,很明显是线段树(更新时需要注意细节),
首先打一个10^7的素数表,然后动态查询修改就行了,
需要用懒惰标记将R操作区间标记。
每次写线段树都要错好多次。
#include <stdio.h>
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m+1, r, rt << 1 | 1
const int maxn = 1e7+5, N = 100005;
int prime[maxn], val[maxn];
int a[N << 3], rev[N << 3], p_cnt[N << 3];
void PushUP ( int rt )
{
p_cnt[rt] = p_cnt[rt << 1]+p_cnt[rt << 1 | 1];
}
void PushDown ( int rt, int m )
{
if ( rev[rt] )
{
rev[rt << 1] = rev[rt << 1 | 1] = rev[rt];
if ( prime[ rev[rt] ] == 0 )
{
p_cnt[rt << 1] = m-( m >> 1 );
p_cnt[rt << 1 | 1] = m >> 1;
}
else
p_cnt[rt << 1] = p_cnt[rt << 1 | 1] = 0;
a[rt << 1] = a[rt << 1 | 1] = rev[rt];
//*值也需要更新(又错了一次)
rev[rt] = 0;
}
}
void Build ( int l, int r, int rt )
{
rev[rt] = p_cnt[rt] = 0;
if ( l == r )
{
scanf ( "%d", &a[rt] );
if ( prime[ a[rt] ] == 0 )
p_cnt[rt] = 1;
else
p_cnt[rt] = 0;
return ;
}
int m = ( l+r ) >> 1;
Build ( lson );
Build ( rson );
PushUP ( rt );
}
void update ( int q, int v, int l, int r, int rt )
{
if ( l == r )
{
a[rt] += v;
if ( prime[ a[rt] ] == 0 )
p_cnt[rt] = 1;
else
p_cnt[rt] = 0;
return ;
}
PushDown ( rt, r-l+1 );
int m = ( l+r ) >> 1;
if ( q <= m )
update ( q, v, lson );
else
update ( q, v, rson );
PushUP ( rt );
}
void rever ( int L, int R, int v, int l, int r, int rt )
{
if ( L <= l && r <= R )
{
rev[rt] = v;
if ( prime[v] == 0 )
p_cnt[rt] = r-l+1;
else
p_cnt[rt] = 0;
return ;
}
PushDown ( rt, r-l+1 );
int m = ( l+r ) >> 1;
if ( L <= m )
rever ( L, R, v, lson );
if ( R > m )
rever ( L, R, v, rson );
PushUP ( rt );
}
int query ( int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt )
{
if ( L <= l && r <= R )
return p_cnt[rt];
PushDown ( rt, r-l+1 );
int m = ( l+r ) >> 1, ret = 0;
if ( L <= m )
ret += query ( L, R, lson );
if ( R > m )
ret += query ( L, R, rson );
PushUP ( rt );
return ret;
}
int main ( )
{
int cnt = 0, T, n, m, l, r, x;
char op[2];
prime[1] = 1;
for ( int i = 2; i < maxn; i ++ )
{
if ( prime[i] == 0 )
val[cnt ++] = i;
for ( int j = 0; j < cnt && i*val[j] < maxn; j ++ )
{
prime[ i*val[j] ] = 1;
if ( i%val[j] == 0 )
break ;
}
}
scanf ( "%d", &T );
while ( T -- )
{
scanf ( "%d%d", &n, &m );
Build ( 1, n, 1 );
while ( m -- )
{
scanf ( "%s", op );
if ( op[0] == 'A' )
{
scanf ( "%d%d", &x, &l );
update ( l, x, 1, n, 1 );
}
else if ( op[0] == 'R' )
{
scanf ( "%d%d%d", &x, &l, &r );
rever ( l, r, x, 1, n, 1 );
}
else
{
scanf ( "%d%d", &l, &r );
printf ( "%d\n", query ( l, r, 1, n, 1 ) );
}
}
}
return 0;
}