Combination Sum(leetcode)
</pre><pre code_snippet_id="516969" snippet_file_name="blog_20141112_1_5676001" name="code" class="cpp">
Given a set of candidate numbers (C) and a target number (T), find all unique combinations in C where the candidate numbers sums to T.
The same repeated number may be chosen from C unlimited number of times.
Note:
- All numbers (including target) will be positive integers.
- Elements in a combination (a1, a2, … ,ak) must be in non-descending order. (ie, a1 ≤ a2 ≤ … ≤ ak).
- The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
For example, given candidate set 2,3,6,7 and target 7,
A solution set is:
[7]
[2, 2, 3]
问题描述如上,简单说就是找出数组中a1,a2....an中能够组合成目标和的个数,每一个数可以取多次。
采用深度优先搜索实现,先将数组排序,从最小的元素开始
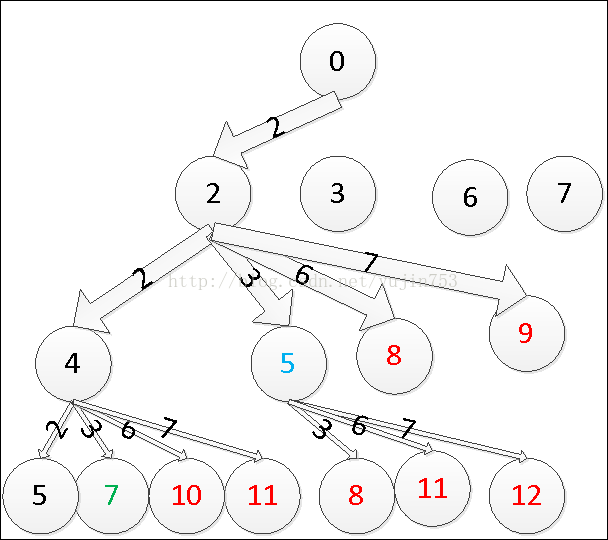
如图所示:
图中红色为剪枝的节点,不会保留下来。
有人可能会问,纹身模蓝色节点5处,为什么是从3开始,因为上一次选择的是3,所以不会出现下次的选择小于上次的,这样就不会出现 2,3,2之类的
也就是说选择出来的结果也是有序的
代码如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > combinationSum(vector<int> &candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> temp;
int i;
dfs(candidates,target,0,temp,result);
return result;
}
void dfs(vector<int> &candidates,int target,int start,vector<int> &temp,vector<vector<int>> &result)
{
if(target==0)
{
result.push_back(temp);
return;
}
for(int i=start;i<candidates.size();i++)
{
if(target<candidates[i])
return;
temp.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates,target-candidates[i],i,temp,result);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
};
</span>
如果,数组的元素只能够选择一次呢,即相同的元素只能够选择一次
那么我们需要将当前选择的元素保存下来,下次选择时先判断是否当前元素等于保留的元素,如果是,则跳过,否则继续
代码如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > combinationSum2(vector<int> &num, int target) {
sort(num.begin(),num.end());
vector<int> temp;
vector<vector<int>> result;
dfs(num,target,0,temp,result);
return result;
}
void dfs(vector<int>&num,int target,int start,vector<int> &temp,vector<vector<int>> &result)
{
if(target==0)
{
result.push_back(temp);
return;
}
int remark=0;
for(int i=start;i<num.size();i++)
{
if(target<num[i])
return;
if(remark==num[i])
continue;
remark=num[i];
temp.push_back(num[i]);
dfs(num,target-num[i],i+1,temp,result);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
};</span>