如何在Qt C++中解析JSON数据并使之被QML应用
在先前的文章"如何在QML应用中设计一个C++ Model并使用它"中,我们介绍了如何利用Qt C++创建一个QAbstractListModel,并是我们的C++数据能够在我们的QML应用中呈现.在今天的文章中,我们将继续探讨这个话题.我们将利用另外一种方法来实现同样的目的.在今天的例程中,我们将展示如何从网路得到数据,并解析数据,进而在我们的QML应用中展示得到的数据.这个例程可以作为一个标准的例程供以后我们需要使用Qt C++来作为数据的来源的时候使用.
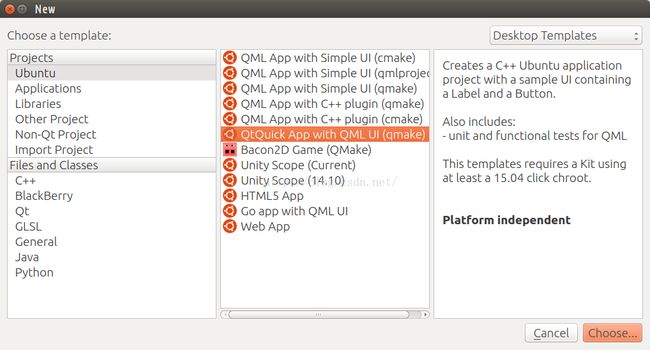
为了能够在我们的QML应用中很好地使用C++,我们采用了我们SDK提供的"QtQuick App with QML UI (qmake)".
我们创建一个叫做"baiduweather"的应用.我们想利用我们的百度提供的API接口:
http://api.map.baidu.com/telematics/v3/weather?location=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&output=json&ak=DdzwVcsGMoYpeg5xQlAFrXQt
来得到我们的数据.具体的数据结果如下:
{
"error": 0,
"status": "success",
"date": "2015-09-25",
"results": [
{
"currentCity": "北京",
"pm25": "25",
"index": [
{
"title": "穿衣",
"zs": "热",
"tipt": "穿衣指数",
"des": "天气热,建议着短裙、短裤、短薄外套、T恤等夏季服装。"
},
{
"title": "洗车",
"zs": "较适宜",
"tipt": "洗车指数",
"des": "较适宜洗车,未来一天无雨,风力较小,擦洗一新的汽车至少能保持一天。"
},
{
"title": "旅游",
"zs": "适宜",
"tipt": "旅游指数",
"des": "天气较好,风稍大,但温度适宜,是个好天气哦。适宜旅游,您可以尽情地享受大自然的无限风光。"
},
{
"title": "感冒",
"zs": "少发",
"tipt": "感冒指数",
"des": "各项气象条件适宜,无明显降温过程,发生感冒机率较低。"
},
{
"title": "运动",
"zs": "较适宜",
"tipt": "运动指数",
"des": "天气较好,但风力较大,推荐您进行室内运动,若在户外运动请注意避风保暖。"
},
{
"title": "紫外线强度",
"zs": "强",
"tipt": "紫外线强度指数",
"des": "紫外线辐射强,建议涂擦SPF20左右、PA++的防晒护肤品。避免在10点至14点暴露于日光下。"
}
],
"weather_data": [
{
"date": "周五 09月25日 (实时:25℃)",
"dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/qing.png",
"nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/qing.png",
"weather": "晴",
"wind": "北风3-4级",
"temperature": "27 ~ 13℃"
},
{
"date": "周六",
"dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/qing.png",
"nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/duoyun.png",
"weather": "晴转多云",
"wind": "微风",
"temperature": "26 ~ 15℃"
},
{
"date": "周日",
"dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/duoyun.png",
"nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/yin.png",
"weather": "多云转阴",
"wind": "微风",
"temperature": "26 ~ 16℃"
},
{
"date": "周一",
"dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/yin.png",
"nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/duoyun.png",
"weather": "阴转多云",
"wind": "微风",
"temperature": "22 ~ 15℃"
}
]
}
]
}
从上面的数据结构中,我们可以定义如下的相应的C++类:
#ifndef WEATHERDATA_H
#define WEATHERDATA_H
#include <QObject>
class WeatherData : public QObject {
Q_OBJECT
Q_PROPERTY(QString date
READ date WRITE setDate
NOTIFY dataChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString dayPictureUrl
READ dayPictureUrl WRITE setDayPictureUrl
NOTIFY dataChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString nightPictureUrl
READ nightPictureUrl WRITE setNightPictureUrl
NOTIFY dataChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString weather
READ weather WRITE setWeather
NOTIFY dataChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString wind
READ wind WRITE setWind
NOTIFY dataChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString temp
READ temp WRITE setTemp
NOTIFY dataChanged)
public:
explicit WeatherData(QObject *parent = 0);
WeatherData(const WeatherData &other);
QString date() const;
QString dayPictureUrl() const;
QString nightPictureUrl() const;
QString weather() const;
QString wind() const;
QString temp() const;
void setDate(const QString &value);
void setDayPictureUrl(const QString &value);
void setNightPictureUrl(const QString &value);
void setWeather(const QString &value);
void setWind(const QString &value);
void setTemp(const QString &value);
signals:
void dataChanged();
private:
QString m_date;
QString m_dayPictureUrl;
QString m_nightPictureUrl;
QString m_weather;
QString m_wind;
QString m_temp;
};
Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(WeatherData)
#endif // WEATHERDATA_H
这个数据结构相应于我们JSON数据中"weather_data"数据结果.我们把每个数据都设为property,这样可以在QML中进行直接的读写.
这里的每个property的写法,就像如下的:
QString WeatherData::date() const
{
return m_date;
}
void WeatherData::setDate(const QString &value)
{
if ( m_date == value )
return;
m_date = value;
emit dataChanged();
}
这也是最标准的property的写法.
下面我们来看看appmodel.h的写法.
appmodel.h
#ifndef APPMODEL_H
#define APPMODEL_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QGeoPositionInfo>
#include <QGeoPositionInfoSource>
#include <QQmlListProperty>
class AppModelPrivate;
class WeatherData;
class AppModel : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
Q_PROPERTY(bool ready
READ ready
NOTIFY readyChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QQmlListProperty<WeatherData> forecast
READ forecast
NOTIFY weatherChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString city
READ city WRITE setCity
NOTIFY cityChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString pm25
READ pm25 WRITE setCity
NOTIFY pm25Changed)
public:
explicit AppModel(QObject *parent = 0);
bool ready() const;
QQmlListProperty<WeatherData> forecast() const;
QString city() const;
void setCity(const QString &value);
QString pm25() const;
void setPm25(const QString &value);
private slots:
void handleWeatherNetworkData(QObject *replyObj);
void handleGeoNetworkData(QObject *replyObj);
void networkSessionOpened();
void positionUpdated(QGeoPositionInfo gpsPos);
void positionError(QGeoPositionInfoSource::Error e);
void queryCity();
public slots:
Q_INVOKABLE void refreshWeather();
signals:
void readyChanged();
void cityChanged();
void pm25Changed();
void weatherChanged();
private:
void hadError(bool tryAgain);
private:
AppModelPrivate *d;
};
#endif // APPMODEL_H
这里沿袭了上面WeatherData中对property的写法,但是有一点不同的是,我们这里有一个比较特殊的property:
Q_PROPERTY(QQmlListProperty<WeatherData> forecast
READ forecast
NOTIFY weatherChanged)
在上面的AppModel定义中,我们也看见了一个叫做AppModelPrivate的类的使用.它的定义如下:
class AppModelPrivate
{
public:
static const int baseMsBeforeNewRequest = 5 * 1000; // 5 s, increased after each missing answer up to 10x
QGeoPositionInfoSource *src;
QGeoCoordinate coord;
QString longitude, latitude;
QString city;
QNetworkAccessManager *nam;
QNetworkSession *ns;
WeatherData now;
QList<WeatherData*> forecast;
QQmlListProperty<WeatherData> *fcProp;
QSignalMapper *geoReplyMapper;
QSignalMapper *weatherReplyMapper;
bool ready;
bool useGps;
bool hasValidCity;
QElapsedTimer throttle;
int nErrors;
int minMsBeforeNewRequest;
QTimer delayedCityRequestTimer;
QString pm25;
AppModelPrivate() :
src(NULL),
nam(NULL),
ns(NULL),
fcProp(NULL),
ready(false),
useGps(true),
hasValidCity(false),
nErrors(0),
minMsBeforeNewRequest(baseMsBeforeNewRequest),
pm25("")
{
delayedCityRequestTimer.setSingleShot(true);
delayedCityRequestTimer.setInterval(1000); // 1 s
throttle.invalidate();
}
};
这在移植Qt时,是一个标准的写法.通常这个类不是继承于QObject的.在这个标准的写法,其实也是需要把AppModel这个类的q(继承于QObject)指针传人到我们的Private类中.这样做的目的是为了能够利用我们的q指针来发送我们的信号,从而使得我们的UI或其它的QObject类能够收到Private类中的数据.有关于这个话题的更进一步资料,可以详细参阅Qt porting之类的文章.这里不一一描述了.这个类可以使用已有的平台的API来获取我们所需要的服务中的数据.
在AppModel类的实现中,我们把我们从网路中得到的数据,进行组装.有些我们可以直接通过AppModel的property进行访问.对于我们关心的天气预报的数据(是一个数组)我们通过上面讲到的QQmlListProperty提供给QML来访问:
void AppModel::handleWeatherNetworkData(QObject *replyObj)
{
qDebug() << "handleWeatherNetworkData";
qDebug() << "got weather network data";
QNetworkReply *networkReply = qobject_cast<QNetworkReply*>(replyObj);
if (!networkReply)
return;
if (!networkReply->error()) {
// We need to clear the previously stored data
QJsonDocument document = QJsonDocument::fromJson(networkReply->readAll());
qDebug() << "document: " << document;
QVariantMap root = document.toVariant().toMap();
QString date = root["date"].toString();
qDebug() << "date: " << date;
QList<QVariant> list = root["results"].toList();
int count = list.count();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
QVariantMap item = list.at(i).toMap() ;
QString city = item["currentCity"].toString();
qDebug() << "city: " << city;
QString pm25 = item["pm25"].toString();
qDebug() << "PM25: " << pm25;
QList<QVariant> index = item["index"].toList();
int size = index.count();
qDebug() << "size: " << size;
for ( int j = 0; j < size; j ++ ) {
QVariantMap each = index.at(j).toMap() ;
QString title = each["title"].toString();
qDebug() << "title: " << title;
QString des = each["des"].toString();
qDebug() << "des: " << des;
}
d->forecast.clear();
foreach (const QVariant &k, item["weather_data"].toList()) {
QVariantMap each = k.toMap();
QString date = each["date"].toString();
qDebug() << "date: " << date << " length: " << date.length();
date = date.left(2);
qDebug() << "new date: " << date;
QString dayPictureUrl = each["dayPictureUrl"].toString();
qDebug() << "dayPictureUrl: " << dayPictureUrl;
QString nightPictureUrl = each["nightPictureUrl"].toString();
qDebug() << "nightPictureUrl: " << nightPictureUrl;
QString weather = each["weather"].toString();
qDebug() << "weather: " << weather;
QString wind = each["wind"].toString();
qDebug() << "wind: " << wind;
QString temperature = each["temperature"].toString();
qDebug() << "temperature: " << temperature;
// Now let's fill in the weather data
WeatherData *forecastEntry = new WeatherData();
forecastEntry->setDate(date);
forecastEntry->setDayPictureUrl(dayPictureUrl);
forecastEntry->setNightPictureUrl(nightPictureUrl);
forecastEntry->setWeather(weather);
forecastEntry->setWind(wind);
forecastEntry->setTemp(temperature);
d->forecast.append(forecastEntry);
}
}
if (!(d->ready)) {
d->ready = true;
emit readyChanged();
}
emit weatherChanged();
}
networkReply->deleteLater();
}
为了能够使得我们的AppModel能被我们的QML正确地使用,我们必须要对它进行注册:
main.cpp
#include <QGuiApplication>
#include <QQmlApplicationEngine>
#include <QQuickView>
#include "appmodel.h"
#include "weatherdata.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
qmlRegisterType<WeatherData>("WeatherInfo", 1, 0, "WeatherData");
qmlRegisterType<AppModel>("WeatherInfo", 1, 0, "AppModel");
QQuickView view;
view.setSource(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:///Main.qml")));
view.setResizeMode(QQuickView::SizeRootObjectToView);
view.show();
return app.exec();
}
相比较我们的AppModel来说,QML UI设计较为直接.我们直接来展示怎么实现的:
Main.qml
import QtQuick 2.0
import Ubuntu.Components 1.1
import WeatherInfo 1.0
/*!
\brief MainView with a Label and Button elements.
*/
MainView {
// objectName for functional testing purposes (autopilot-qt5)
objectName: "mainView"
// Note! applicationName needs to match the "name" field of the click manifest
applicationName: "baiduweather.liu-xiao-guo"
/*
This property enables the application to change orientation
when the device is rotated. The default is false.
*/
//automaticOrientation: true
// Removes the old toolbar and enables new features of the new header.
useDeprecatedToolbar: false
width: units.gu(60)
height: units.gu(85)
AppModel {
id: mymodel
onReadyChanged: {
console.log("ready is changed!");
console.log("city: " + city)
// console.log("forecast[0]: " + forecast[0].dayPictureUrl);
if (mymodel.ready) {
page.state = "ready"
input.text = mymodel.city
// listview.model = mymodel.forecast;
} else {
page.state = "loading"
}
}
}
Page {
id: page // We cannot name it window.
title: i18n.tr("Baidu Weather")
Column {
anchors.fill: parent
spacing: units.gu(1)
TextField {
id: input
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
onAccepted: {
mymodel.city = text;
}
onTextChanged: {
mymodel.city = text;
}
}
Image {
id: image
height: parent.height/3
width: height
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
source: {
if ( !mymodel.ready )
return ""
var date = new Date();
var n = date.getHours();
if ( n >= 7 && n < 18 ) {
return mymodel.forecast[0].dayPictureUrl;
}
else {
return mymodel.forecast[0].nightPictureUrl;
}
}
Label {
id: city
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
text: mymodel.city
fontSize: "large"
}
Label {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
anchors.top:city.bottom
anchors.bottomMargin: units.gu(1)
text: "PM25: " + mymodel.pm25;
fontSize: "large"
}
}
Row {
id: firstrow
spacing: units.gu(1)
width: parent.width
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
Repeater {
model: mymodel.forecast
width: page.width
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
Column {
spacing: units.gu(2)
Text {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
text: date
font.pixelSize: units.gu(3)
}
Image {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
width: (page.width - firstrow.spacing*3 ) /4
height: width
source: dayPictureUrl
}
Image {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
width: (page.width - firstrow.spacing*3) /4
height: width
source: nightPictureUrl
}
Text {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
text: mymodel.forecast[index].temp
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
在上面的设计中,我们使用了:
Repeater {
model: mymodel.forecast
....
}
来把我们的数据进行展示.当然,我们也可以选择ListView或其它的形式来完成.