day44 spring+jdbc(事务)==>spring+hibernate(事务)
一、spring+jdbc
1、jdbc编程的特点:
模板编程
固定代码+动态的参数
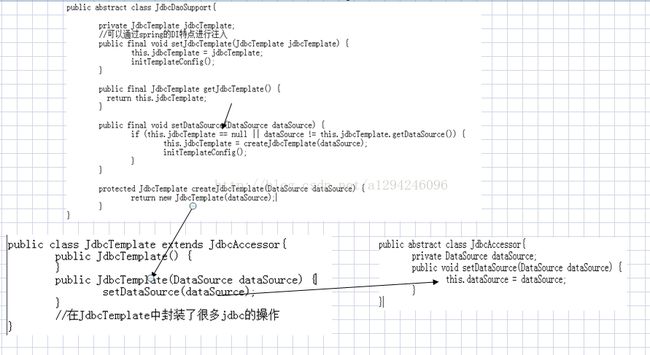
考虑到jdbc编程的模板性,这里介绍一种spring的JdbcDaoSupport
看类图模板
很明显,这个模板是需要datasource注入的
引入dataSource的方式:
1、在dataSource的设置中直接写值
2、引入properties文件
在dao的写法中有很多种,最终只需要把dataSource注入到jdbcTemplate中
二、模板的使用
1、让自己写的一个dao类继承JdbcDaoSupport
2、让自己写的一个dao类继承JdbcTemplate
3、让自己写的一个dao类里有一个属性为JdbcTemplate
看例子(开启事务编程)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.zjy.hibernate.PersonDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.zjy.hibernate.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDao">
<ref bean="personDao"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
<!--
通知 1、告诉spring容器,采用什么样的方法处理事务 2、告诉spring容器,目标方法应该采用什么样的事务处理策略
-->
<tx:advice id="tx" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--
name规定方法 isolation 默认值为DEFAULT propagation 传播机制 REQUIRED
-->
<tx:method name="savePerson" read-only="false"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<bean id="Exception" class="cn.zjy.hibernate.MyException"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut
expression="execution(* cn.zjy.hibernate.PersonServiceImpl.*(..))"
id="perform" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="tx" pointcut-ref="perform" />
<aop:aspect ref="Exception">
<aop:after-throwing method="myException" pointcut-ref="perform" throwing="ex"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>PersonDaoImpl.java
package cn.zjy.hibernate;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager;
import cn.zjy.hibernate.Person;
public class PersonDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements PersonDao{
public List<Person> getPerson() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from person", new RowMapper() {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Person person = new Person();
person.setPid(rs.getLong("pid"));
person.setPname(rs.getString("pname"));
person.setPsex(rs.getString("psex"));
return person;
}
});
}
public void savePerson() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.getJdbcTemplate().update("insert into person(pid,pname,psex) values(3,'a','a')");
}
}
客户端编程
package cn.zjy.hibernate;
import javax.activation.DataSource;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test()
{
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/zjy/hibernate/applicationContext.xml");
// PersonDaoImpl p1 = (PersonDaoImpl)context.getBean("personDao");
PersonService p1 = (PersonService)context.getBean("personService");//这里注意 代理类必须接口引用
p1.savePerson();
}
}
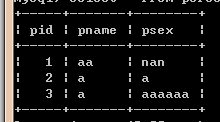
结果
三、spring+hibernate
刚才的代码中涉及事务,那么就好好聊一聊事务编程
spring声明式事务处理
spring
声明:针对的是程序员,程序员告诉spring容器,哪些方法需要事务,哪些方法不需要事务
事务处理 spring容器来做事务处理
目的:让spring管理事务,开发者不再关注事务
相对应的配置
搞懂了spring+jdbc的事务,那么hibernate的事务也就水到渠成了,hibernate也是利用了一个它自己实现的模板,由sessionFactory注入。spring容器的事务管理器也是sessionFactory注入的。不是datasource.
接着看个例子
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- sessionFactory 1、sessionFactoryImpl 2、利用spring的IOC和DI的特征 --> <!-- <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> <property name="mappingResources"> <list> <value>cn/itcast/spring/hiberante/transaction/domain/Person.hbm.xml</value> </list> </property> <property name="hibernateProperties"> <value> hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect </value> </property> </bean> --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation"> <value>classpath:cn/zjy/hibernate/up/hibernate.cfg.xml</value> </property> </bean> <bean id="PersonDao" class="cn.zjy.hibernate.up.PersonDaoImpl"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref bean="sessionFactory"/> </property> </bean> <bean id="PersonService" class="cn.zjy.hibernate.up.PersonServiceImpl"> <property name="personDao"> <ref bean="PersonDao"/> </property> </bean> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref bean="sessionFactory"/> </property> </bean> <tx:advice id="tx" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="savePerson" read-only="false"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.zjy.hibernate.up.PersonServiceImpl.*(..))" id="prfom"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="tx" pointcut-ref="prfom" /> </aop:config> </beans>PersonDaoImpl.java
package cn.zjy.hibernate.up; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport; import cn.zjy.hibernate.up.Person; import cn.zjy.hibernate.up.PersonDao; public class PersonDaoImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements PersonDao{ public void savePerson(Person person) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.getHibernateTemplate().save(person); } }测试
package cn.zjy.hibernate.up; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.zjy.hibernate.up.Person; import cn.zjy.hibernate.up.PersonService; public class PersonTest { @Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/zjy/hibernate/up/applicationContext.xml"); PersonService personService = (PersonService)context.getBean("PersonService"); Person person = new Person(); person.setPname("a"); person.setPsex("aaaaaa"); personService.savePerson(person); } }
异曲同工,不外如是。