算法面试题
近期面试,下面这些是经常被问到的数据结构算法的内容,虽然一般工作中用的不多,但随着系统开发扩展下去,服务器并发量上来了或者服务器中数据扭转过多,性能瓶颈也越来越明显,设计适当的数据结构的优势就显现出来了。下面几道是非常基础的题目,想了解算法,祥看《算法导论(第三版)》
1.冒泡
void BubbleSort(int arr[],int count)
{
int temp=0;
bool swapped=false;
for(int i=1;i<count;i++)
{
swapped=false;
for(int j=count-1;j>=i;j--)
{
if(arr[j-1]>arr[j])
{
temp=arr[j-1];
arr[j-1]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
swapped=true;
}
if(!swapped)//本趟排序未发生交换,提前终止算法
return;
}
}
2.二分查找
int BinSearch(int *arr, int n , int key)
{
int low = 0;
int high = n-1;
int mid;
if(arr[low] == key)
{
return 0;
}
while(low <= high)
{
mid = low + ((high - low)/2);
if(arr[mid] == key)
{
return mid;
}
if(arr[mid] > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
3.堆排序
4.快排
#include <stdio.h>
int a[100] = { 1, 2, 8, 7, 9, 5, 6, 4, 3, 66, 77, 33, 22, 11 };
/* 输出数组前n各元素*/
void prt(int n) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d\t", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/* 数据交换*/
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int tmp;
tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp;
}
void quick_sort(int a[], int left, int right)
{
int i = left + 1, j = right;
int key = a[left];
if (left >= right) return;
/* 从i++和j--两个方向搜索不满足条件的值并交换 *
* 条件为:i++方向小于key,j--方向大于key */
while (1) {
while (a[j] > key) j--;
while (a[i] < key&&i<j) i++;
if(i >= j) break;
swap(&a[i],&a[j]);
if(a[i]==key)j--;
else i++;
}
/* 关键数据放到‘中间’*/
swap(&a[left],&a[j]);
if(left < i - 1) quick_sort(a, left, i - 1);
if(j + 1 < right) quick_sort(a, j + 1 , right);
}
int main(void) {
/* 排序与输出*/
quick_sort(a, 0, 13);
prt(14);
return 0;
}
5.编程判断两个链表是否相交
深信服面试的时候被问到这题,出自编程之美。
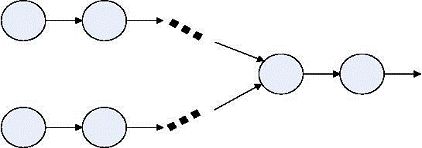
给出两个单向链表的头指针(如图所示),比如 h1、h2,判断这两个链表是否相交。这里为了简化问题,我们假设两个链表均不带环。
图链表相交示意图
问题分析:
1.如果相交,两个链表从第一个相交节点至尾节点都会相同;
2.如果相交,两个链表的尾节点相同
【解法】
先遍历第一个链表,记住最后一个节点。然后遍历第二个链表,到最后一个节点时和第一个链表的最后一个节点做比较,如果相同,则相交,否则,不相交。这样我们就得到了一个时间复杂度,它为 O((Length(h1) + Length(h2)),而且只用了一个额外的指针来存储最后一个节点。
7.扩展一点,上题只需要判断是否相交,那如何找出第一个相交节点呢?
答:
延续上题的思路,两个链表h1和h2相交,两个链表的长度分别为Length1和Length2,第一个相交节点离h1的距离为firstnode1,该节点离h2的距离为firstnode2,那么Length1 - firstnode1 == Length2 - firstnode2。假设Length1> Length2,那么遍历寻找节点时,长链表h1应该比短链表h2早出发Length1- Length2。
代码如下:
// 判断两个链表是否相交,并返回第一个相交节点
const ListNode* FirstCommonNode(const ListNode* listhead1, const ListNode* listhead2)
{
if(listhead1 == NULL || listhead2 == NULL)
return NULL;
int Length1 = 1,Length2 = 1;
const ListNode* curhead1 = listhead1, *curB = listhead2;
while(curhead1->next)
{
++Length1;
curhead1 = curhead1->next;
}
while(curB->next)
{
++Length2;
curB = curB->next;
}
if(curhead1 != curB)
return NULL;
curhead1 = listhead1;
curB = listhead2;
if(Length1 > Length2)
{
for(int i = 0; i < Length1 - Length2; ++i)
curhead1 = curhead1->next;
}
else
{
for(int i = 0; i< Length2 - Length1; ++i)
curB = curB->next;
}
while(curhead1 && curhead1 != curB)
{
curhead1 = curhead1->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return curhead1;
}
8.判断单链表是否有环?
答:
设置两个指针(fast, slow),初始值都指向头,slow每次前进一步,fast每次前进二步,如果链表存在环,则fast必定先进入环,而slow后进入环,两个指针必定相遇。(当然,fast先行头到尾部为NULL,则为无环链表)程序如下:
bool IsExitsLoop(slist *head)
{
slist *slow = head, *fast = head;
while ( fast && fast->next )
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if ( slow == fast ) break;
}
return !(fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL);
}
当fast若与slow相遇时,slow肯定没有走遍历完链表,而fast已经在环内循环了n圈(1<=n)。假设slow走了s步,则fast走了2s步(fast步数还等于s 加上在环上多转的n圈),设环长为r,则:
2s = s + nr
s= nr
9.单链表反转
struct ListNode { int nKey; ListNode* pNext; }; void ReverseLink(ListNode *&pHead) { if (NULL == pHead) { return; } ListNode *pNode = pHead; ListNode *Prev = NULL; ListNode *pNext = NULL; while (NULL != pNode) { pNext = pNode->pNext; if (NULL == pNext) { pHead = pNode;s } pNode->pNext = Prev; Prev = pNode; pNode = pNext; } }
10.前序遍历二叉树,不递归和递归的实现
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
前序遍历的递归代码:
void preorder(bintree t)
{
if(t)
{
printf("%c ",t->data);
preorder(t->lchild);
preorder(t->rchild);
}
}
前序遍历的非递归代码:
#define SIZE 100
typedef struct seqstack{
bintree data[SIZE];
int tag[SIZE]; //为后续遍历准备的
int top; //top为数组的下标
}seqstack;
void push(seqstack *s,bintree t){
if(s->top == SIZE){
printf("the stack is full\n");
}else{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=t;
}
}
bintree pop(seqstack *s){
if(s->top == -1){
return NULL;
}else{
s->top--;
return s->data[s->top+1];
}
}
void preorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty\n");
}else{
while(t || s.top != -1){
while(t){
printf("%c ",t->data);
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
11.一个类,实现栈的功能,具有push和pop操作?
答:
内核中定义了程序栈的空间大小,当然编译器也可以设置栈空间,也就是说栈是有大小限制的,那么我们在类中声明一个数组8K来实现这个栈, 然后成员变量数组进行操作push和pop,代码量也不大,这在腾讯视频的面试中出现过。
12.vector/list/map等的实现
答:
(1)vector是一个线性顺序结构。相当于数组,但其大小可以不预先指定,并且自动扩展。它可以像数组一样被操作,由于它的特性我们完全可以将vector看作动态数组。初始的空间大小可以预先指定也可以由vector 默认指定,这个大小即 capacity ()函数的返回值。当存储的数据超过分配的空间时vector 会重新分配 一块内存块,但这样的分配是很耗时的,在重新分配空间时它会做这样的动作。
优缺点:vector随机访问非常方便,想数组一样通过下标访问;当数据量大时候,插入和删除时性能低劣。
(2)list采用链表实现,链表的结构再熟悉不过,插入和删除非常方便。
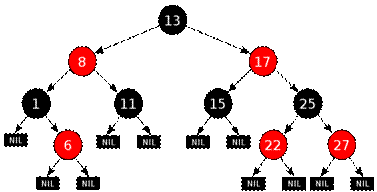
(3)map采用红黑树实现,红黑树是一种自平衡二叉查找树,时间复杂度是O(logn)。
红黑树本身是二叉搜索树,同时它应该始终满足五个性质:
1.红黑树每个节点颜色非红即黑;
2.根节点颜色必须为黑色;
3.每个叶节点(指的NULL指针节点)颜色均为黑;
4.不可以出现相邻的两个红色节点;
5.对于每个节点,其左右子树中的黑色节点个数必须相等;
一棵正常的红黑树如下图(引自wiki):
13.解决哈希冲突的方法
开放定址法
溢出区法
拉链法
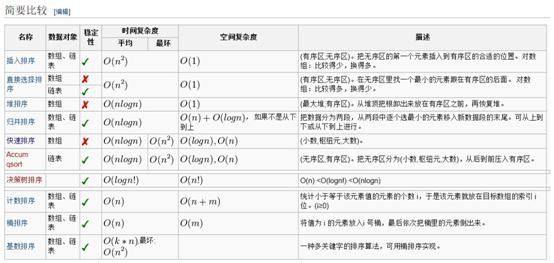
http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/排序算法