仿射变换:
拉伸、收缩、扭曲、旋转是图像的几何变换,在三维视觉技术中大量应用到这些变换,又分为仿射变换和透视变换。仿射变换通常用单应性建模,利用cvWarpAffine解决密集映射,用cvTransform解决稀疏映射。仿射变换可以将矩形转换成平行四边形,它可以将矩形的边压扁但必须保持边是平行的,也可以将矩形旋转或者按比例变化。透视变换提供了更大的灵活性,一个透视变换可以将矩阵转变成梯形。当然,平行四边形也是梯形,所以仿射变换是透视变换的子集。
1)CloneImage:制作图像的完整拷贝
IplImage* cvCloneImage( const IplImage* image );
image :原图像.
函数 cvCloneImage 制作图像的完整拷贝包括头、ROI和数据
2)GetAffineTransform:由三对点计算仿射变换
CvMat* cvGetAffineTransform( const CvPoint2D32f* src,const CvPoint2D32f* dst, CvMat* map_matrix );
src:输入图像的三角形顶点坐标。
dst:输出图像的相应的三角形顶点坐标。
map_matrix:指向2×3输出矩阵的指针。
函数cvGetAffineTransform计算满足以下关系的仿射变换矩阵: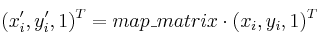
这里,dst(i)= (x'i,y'i),src(i)= (xi,yi),i = 0..2.
3)WarpAffine
对图像做仿射变换
void cvWarpAffine( const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, constCvMat* map_matrix,
int flags=CV_INTER_LINEAR+CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS,
CvScalar fillval=cvScalarAll(0) );
src:输入图像.
dst:输出图像.
map_matrix:2×3 变换矩阵
flags:插值方法和以下开关选项的组合:
· CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充所有输出图像的象素。如果部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
· CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP - 指定 map_matrix是输出图像到输入图像的反变换,因此可以直接用来做象素插值。否则, 函数从 map_matrix 得到反变换。
fillval:用来填充边界外面的值
函数 cvWarpAffine 利用下面指定的矩阵变换输入图像: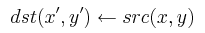
- 如果没有指定 CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP ,
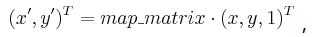
- 否则,
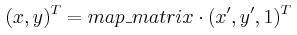
函数与 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 类似,但是不完全相同。cvWarpAffine 要求输入和输出图像具有同样的数据类型,有更大的资源开销(因此对小图像不太合适)而且输出图像的部分可以保留不变。而 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 可以精确地从8位图像中提取四边形到浮点数缓存区中,具有比较小的系统开销,而且总是全部改变输出图像的内容。要变换稀疏矩阵,使用 cxcore 中的函数 cvTransform 。
| 4)2DRotationMatrix |
| 2DRotationMatrix:计算二维旋转的仿射变换矩阵
CvMat* cv2DRotationMatrix( CvPoint2D32f center, double angle, double scale, CvMat* map_matrix );
center :输入图像的旋转中心坐标
angle :旋转角度(度)。正值表示逆时针旋转(坐标原点假设在左上角).
scale :各项同性的尺度因子
map_matrix :输出 2×3 矩阵的指针
函数 cv2DRotationMatrix 计算矩阵:
[ α β | (1-α)*center.x - β*center.y ]
[ -β α | β*center.x + (1-α)*center.y ]
where α=scale*cos(angle), β=scale*sin(angle)
该变换并不改变原始旋转中心点的坐标,如果这不是操作目的,则可以通过调整平移量改变其坐标(译者注:通过简单的推导可知,仿射变换的实现是首先将旋转中心置为坐标原点,再进行旋转和尺度变换,最后重新将坐标原点设定为输入图像的左上角,这里的平移量是center.x, center.y).
5)cvResize:重新调整图像src(或它的ROI),使它精确匹配目标dst(或其ROI)。 函数形式:void cvResize( const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, int interpolation=CV_INTER_LINEAR ); 参数列表: src: 源图像 dst :目标图像 interpolation 修改、插补的方法,取值如下: ·CV_INTER_NN - 最近-邻居插补 ·CV_INTER_LINEAR - 双线性插值(默认方法) ·CV_INTER_AREA - 像素面积相关重采样。当缩小图像时,该方法可以避免波纹的出现。当放大图像时,类似于方法CV_INTER_NN。(It is the preferred method for image decimation that gives moire-free results. In case of zooming it is similar to CV_INTER_NN method. ) ·CV_INTER_CUBIC - 双三次插值。
6)cvGetQuadrangleSubPix:提取象素四边形,使用子象素精度 函数说明: 提取象素四边形,使用子象素精度 void cvGetQuadrangleSubPix( const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, const CvMat* map_matrix, int fill_outliers=0, CvScalar fill_value=cvScalarAll(0) );
-
src:输入图像.
-
dst:提取的四边形.
-
map_matrix:3 × 2 变换矩阵 [A|b] (见讨论).
-
fill_outliers:该标志位指定是否对原始图像边界外面的象素点使用复制模式(fill_outliers=0)进行差值或者将其设置为指定值(fill_outliers=1)。
-
fill_value:对原始图像边界外面的象素设定固定值,当 fill_outliers=1.
函数 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 从图像 src 中提取四边形,使用子象素精度,并且将结果存储于 dst ,计算公式是: dst(x+width(dst)/2, y+height(dst)/2)= src( A11x+A12y+b1, A21x+A22y+b2), where A and b are taken frommap_matrix | A11 A12 b1 | map_matrix = | | | A21 A22 b2 |
其中在非整数坐标 A•(x,y)T+b 的象素点值通过双线性变换得到。多通道图像的每一个通道都单独计算.
代码如下:
#include <cv.h>
#include <highgui.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
IplImage *src_image=cvLoadImage("f.jpg",1);
assert(src_image!=NULL);
IplImage *dst_image=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(src_image),src_image->depth,src_image->nChannels);
assert(dst_image!=NULL);
dst_image->origin=src_image->origin;//左上角顶点位置对齐
dst_image=cvCloneImage(src_image);
CvPoint2D32f srcTri[3];
CvPoint2D32f dstTri[3];
CvMat *warp_mat=cvCreateMat(2,3,CV_32FC1);
srcTri[0].x=0.0f;
srcTri[0].y=0.0f;
srcTri[1].x=(float)src_image->width-1;//缩小一个像素
srcTri[1].y=0.0f;
srcTri[2].x=0.0f;
srcTri[2].y=(float)src_image->height-1;
cvNamedWindow("show_src",1);
cvNamedWindow("show_dst",1);
cvShowImage("show_src",src_image);
cvShowImage("show_dst",dst_image);
while(1)
{
char c=cvWaitKey(0);
switch(c)
{
case '1':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.90;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.10;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.10;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->height*0.90;
}
break;
case '2':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.80;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.20;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.20;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.80;
}
break;
case '3':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.70;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.30;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.30;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.70;
}
break;
case '4':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.60;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.40;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.40;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.60;
}
break;
case '5':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.55;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.45;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.45;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.55;
}
break;
case '6':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.40;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.60;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.60;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.40;
}
break;
case '7':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.30;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.70;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.70;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.30;
}
break;
case '8':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.20;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.80;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.80;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.20;
}
break;
case '9':
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.10;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.90;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.90;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*0.10;
}
break;
default:
{
dstTri[0].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[0].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[1].x=src_image->width*0.10;
dstTri[1].y=src_image->height*0.0;
dstTri[2].x=src_image->width*0.0;
dstTri[2].y=src_image->height*1.0;
}
}
//得到仿射矩阵。由三对不共线的点得到,这样具有唯一性
cvGetAffineTransform(srcTri,dstTri,warp_mat);
//实现仿射变换,第三个参数为上一个函数得到的仿射矩阵
cvWarpAffine(src_image,dst_image,warp_mat);
cvShowImage("show_dst",dst_image);
if(cvWaitKey(0)==27)
break;
IplImage* dst_1=0; //放大目标图像
IplImage* dst_2; //缩小目标图像
float scaler1 = 1.5; //图像放大为原来的5倍
float scaler2 = 0.618; //图像缩小为原来的0.5倍
CvSize Size; //放大目标图像大小
CvSize Size1; //缩小目标图像大小
//设置放大的图像的尺寸
Size.width= src_image->width*scaler1;
Size.height= src_image->height*scaler1;
dst_1 = cvCreateImage(Size,src_image->depth,src_image->nChannels);
cvResize(src_image,dst_1,CV_INTER_LINEAR);//重新调整图像src_image,使它精确匹配目标dst_1
Size1.width=src_image->width*scaler2;
Size1.height=src_image->height*scaler2;
dst_2 = cvCreateImage(Size1,src_image->depth,src_image->nChannels);
cvResize(src_image,dst_2,CV_INTER_LINEAR);
cvNamedWindow("dst_max");
cvNamedWindow("dst_min");
cvShowImage("dst_max",dst_1);
cvShowImage("dst_min",dst_2);
cvWaitKey();
/*********************************** c ***************************/
int delta = 1; //用于控制旋转的角度
int angle = 0; //旋转的角度
int opt = 0; // 1: 旋转加缩放
// 0: 仅仅旋转
double factor; //控制旋转
IplImage* dst; //目标图像存放
dst = cvCloneImage (src_image);
for(;;)
{
float m[6];
CvMat M = cvMat (2, 3, CV_32F, m);
int w = src_image->width;
int h = src_image->height;
if (1) // 一直旋转加缩放
factor = (cos (angle * CV_PI / 180.0) + 1.0) * 2;
else
factor = 1;
m[0] = (float) (factor * cos (-angle * 2 * CV_PI / 180.));
m[1] = (float) (factor * sin (-angle * 2 * CV_PI / 180.));
m[3] = -m[1];
m[4] = m[0];
// 将旋转中心移至图像中间
m[2] = w * 0.5f;
m[5] = h * 0.5f;
// dst(x,y) = A * src(x,y) + b
cvZero (dst);
//从图像 src 中提取四边形,使用子象素精度,并且将结果存储于 dst
cvGetQuadrangleSubPix (src_image, dst, &M);
cvNamedWindow ("dst", 1);
cvShowImage ("dst", dst);
if (cvWaitKey (1) == 27)
break;
angle = (int) (angle + delta) % 360;
}
return 0;
}
}
|
![]()
![]()