关于OpenCV的那些事——Orb角点检测,BF匹配跟踪和LK光流跟踪
从这一节开始学习OpenCV并使用它实现PTAM 的另类版本:Feature Tracking and Synchronous Scene Generation with a Single Camera主要思想还是parallel,两个线程tracking和mapping并行运行。这里我将mapping简化为generation,细节以后会做具体介绍,今天开始记录我的研究历程。
上一节中我们选择Orb算法因为它速度快,性能佳,性价比极高。这一节第一部分我们首先使用Orb算法对两幅静态图像进行角点检测然后使用BF(Brute-Force)匹配并画出匹配点。第二部分我们从摄像头里得到的每一帧进行角点检测并作BF匹配。(我使用的OpenCV版本是2.4.10,关于OpenCV配置,感谢浅墨大神的入门教程)
第一部分:
Orb算法里简单的实现了检测和匹配。因为我们要进行的实时匹配,所以每两帧图相间的差别很小,镜头或物体在极短时间内属于小运动,位移差别不大,这正好为我们提供了过滤错误匹配的方法。如下面代码里我们说明若匹配点对中的点相隔距离大于30,我们即认为匹配错误。
#include <core/core.hpp>
#include <highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat img_1 = imread("C:\\Users\\柴\\Pictures\\Logitech Webcam\\Picture 9.jpg");
Mat img_2 = imread("C:\\Users\\柴\\Pictures\\Logitech Webcam\\Picture 10.jpg");
namedWindow("Matches");
DWORD t1,t2;
t1 = GetTickCount();
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,keypoints_2;
ORB orb;
orb.detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
orb.detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
orb.compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
orb.compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING);
vector<Mat> descriptors;
descriptors.push_back(descriptors_1);
matcher.add(descriptors);
vector<vector<DMatch>> matches,goodmatches;
DMatch bestMatch,betterMatch;
vector<DMatch> bestMatches;
matcher.knnMatch(descriptors_2,matches,2);
int n=0;
Point p1,p2;
for (int i=0; i<(int)matches.size(); i++)
{
bestMatch = matches[i][0];
betterMatch = matches[i][1];
p1 = keypoints_1[bestMatch.trainIdx].pt;
p2 = keypoints_2[bestMatch.queryIdx].pt;
double distance = sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
float distanceRatio = bestMatch.distance / betterMatch.distance;
if (distanceRatio< 0.8 && distance<30)
{
bestMatches.push_back(bestMatch);
line(img_2,p1,p2,Scalar(0,0,255),1,8,0);
}
}
imshow("Matches", img_2);
t2 = GetTickCount();
cout<<t2-t1<<"ms";
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}运行过程截图:
第二部分:
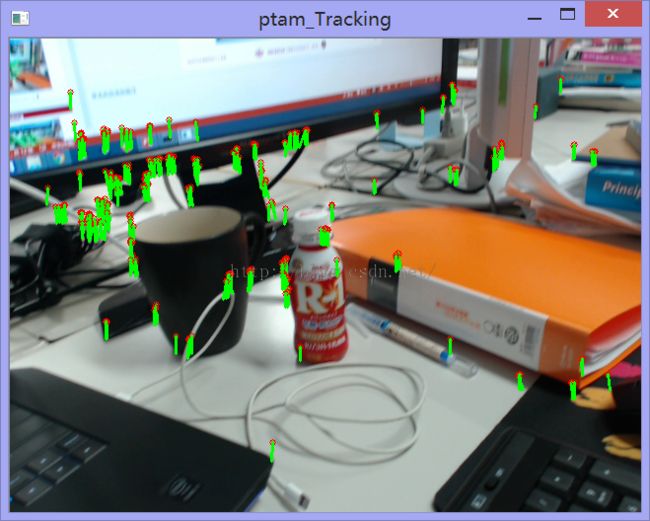
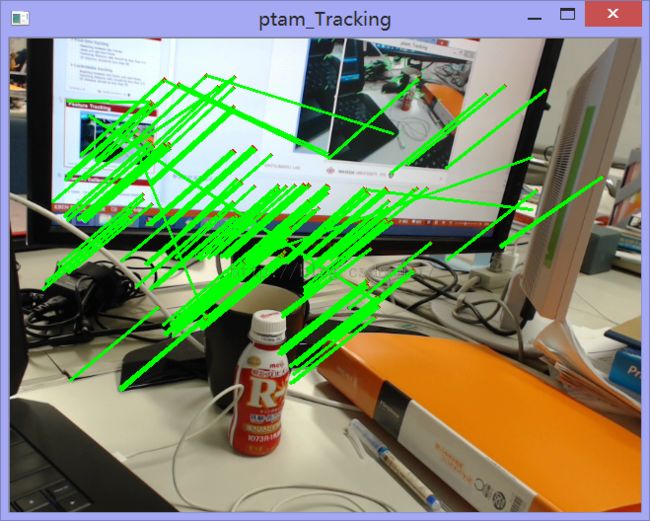
每两帧之间我们进行Orb角点检测,利用BF找出最佳匹配点并画出角点运动轨迹。当我们按下't'键时,保存当前帧为初始帧,之后每一帧以初始帧为训练图进行BF匹配找出最佳匹配点。
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
VideoCapture cap(1);
cap.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH,640);
cap.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT,480);
int framenum = 0;
float fps = 0;
DWORD t1,t2;
Mat frame,gray,nextgray,firstgray;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints,nextkeypoints,firstkeypoints;
Mat descriptors, nextdescriptors,firstdescriptors;
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING);
vector<Mat> vec_descriptors;
vector<vector<DMatch>> matches;
vector<DMatch> bestMatches;
DMatch bestMatch,betterMatch;
Point p1,p2;
double distance;
float distanceRatio;
bool firstornot = true;
bool trackmode = false;
bool firstframeornot = true;
namedWindow("ptam_Tracking");
int c = 1;
if(!cap.isOpened()){
cout<<"打开摄像头失败,退出";
exit(-1);
}
ORB orb;
t1 = GetTickCount();
while(c!=27)
{
if(c == 't' || c == 'T')
{
trackmode = !trackmode;
firstframeornot = true;
}
if(trackmode == false)
{
if(firstornot == true)
{
cap>>frame; //read the first frame
cvtColor(frame,gray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
orb.detect(gray, keypoints);
orb.compute(gray, keypoints, descriptors);
firstornot = false;
}
else{
gray.setTo(0);
gray = nextgray.clone();
nextgray.setTo(0);
keypoints.clear();
copy(nextkeypoints.begin(), nextkeypoints.end(), back_inserter(keypoints));
nextkeypoints.clear();
descriptors.setTo(0);
descriptors = nextdescriptors.clone();
nextdescriptors.setTo(0);
}
cap>>frame;
cvtColor(frame,nextgray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
orb.detect(nextgray, nextkeypoints);
orb.compute(nextgray,nextkeypoints, nextdescriptors);
vec_descriptors.clear();
vec_descriptors.push_back(descriptors);
matcher.clear();
matcher.add(vec_descriptors);
matches.clear();
matcher.knnMatch(nextdescriptors,matches,2);
bestMatches.clear();
for (int i=0; i<(int)matches.size(); i++)
{
bestMatch = matches[i][0];
betterMatch = matches[i][1];
p1 = keypoints[bestMatch.trainIdx].pt;
p2 = nextkeypoints[bestMatch.queryIdx].pt;
distance = sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
distanceRatio = bestMatch.distance / betterMatch.distance;
if (distanceRatio< 0.8 && distance<50)
{
bestMatches.push_back(bestMatch);
if(distance<5)
circle(frame,p2,1,Scalar(0,0,255));
else
{
circle(frame,p1,3,Scalar(0,0,255));
line(frame,p1,p2,Scalar(0,255,0),2);
}
}
}
}
else
{
cap>>frame; //read the first frame
if(firstframeornot)
{
firstgray.setTo(0);
cvtColor(frame,firstgray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
firstkeypoints.clear();
orb.detect(firstgray, firstkeypoints);
firstdescriptors.setTo(0);
orb.compute(firstgray, firstkeypoints, firstdescriptors);
firstframeornot = false;
}
else
{
nextgray.setTo(0);
cvtColor(frame,nextgray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
nextkeypoints.clear();
orb.detect(nextgray, nextkeypoints);
nextdescriptors.setTo(0);
orb.compute(nextgray,nextkeypoints, nextdescriptors);
vec_descriptors.clear();
vec_descriptors.push_back(firstdescriptors);
matcher.clear();
matcher.add(vec_descriptors);
matches.clear();
matcher.knnMatch(nextdescriptors,matches,2);
bestMatches.clear();
for (int i=0; i<(int)matches.size(); i++)
{
bestMatch = matches[i][0];
betterMatch = matches[i][1];
p1 = firstkeypoints[bestMatch.trainIdx].pt;
p2 = nextkeypoints[bestMatch.queryIdx].pt;
distance = sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
distanceRatio = bestMatch.distance / betterMatch.distance;
if (distanceRatio< 0.8 && distance<1000)
{
bestMatches.push_back(bestMatch);
circle(frame,p1,2,Scalar(0,0,255));
line(frame,p1,p2,Scalar(0,255,0),2);
}
}
}
}
imshow("ptam_Tracking",frame);
framenum++;
c = waitKey(1);
}
t2 = GetTickCount();
cout<<"fps:"<<framenum/((t2-t1)*1.0/1000)<<"\n";
cap.release();
return 0;
}运行过程截图:
普通模式
按't'模式
运行速度保持在15FPS左右,远没有达到实时的效果,下面将介绍LK光流法去实时跟踪这些Orb角点。
这里是我学习的两篇博文:光流Optical Flow介绍,Opencv学习笔记(九)光流法,供大家参考。
下面是稍作修改的OpenCV光流实现:
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
static void help()
{
DWORD t1,t2;
Point2f point;
bool addRemovePt = false;
int framenum = 0;
static void onMouse( int event, int x, int y, int /*flags*/, void* /*param*/ )
{
if( event == CV_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN )
{
point = Point2f((float)x, (float)y);
addRemovePt = true;
}
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
VideoCapture cap(0);
TermCriteria termcrit(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER|CV_TERMCRIT_EPS, 20, 0.03);
Size subPixWinSize(10,10), winSize(31,31);
const int MAX_COUNT = 500;
bool needToInit = false;
bool nightMode = false;
if( !cap.isOpened() )
{
cout << "Could not initialize capturing...\n";
return 0;
}
namedWindow( "LK Demo", 1 );
setMouseCallback( "LK Demo", onMouse, 0 );
Mat gray, prevGray, image;
vector<Point2f> points[2];
t1 = GetTickCount();
for(;;)
{
Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
if( frame.empty() )
break;
frame.copyTo(image);
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
if( nightMode )
image = Scalar::all(0);
if( needToInit )
{
// automatic initialization
goodFeaturesToTrack(gray, points[1], MAX_COUNT, 0.01, 10, Mat(), 3, 0, 0.04);
cornerSubPix(gray, points[1], subPixWinSize, Size(-1,-1), termcrit);
addRemovePt = false;
}
else if( !points[0].empty() )
{
vector<uchar> status;
vector<float> err;
if(prevGray.empty())
gray.copyTo(prevGray);
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(prevGray, gray, points[0], points[1], status, err, winSize,
3, termcrit, 0, 0.001);
size_t i, k;
for( i = k = 0; i < points[1].size(); i++ )
{
if( addRemovePt )
{
if( norm(point - points[1][i]) <= 5 )
{
addRemovePt = false;
continue;
}
}
if( !status[i] )
continue;
points[1][k++] = points[1][i];
circle( image, points[1][i], 3, Scalar(0,255,0), -1, 8);
}
points[1].resize(k);
}
if( addRemovePt && points[1].size() < (size_t)MAX_COUNT )
{
vector<Point2f> tmp;
tmp.push_back(point);
cornerSubPix( gray, tmp, winSize, cvSize(-1,-1), termcrit);
points[1].push_back(tmp[0]);
addRemovePt = false;
}
needToInit = false;
imshow("LK Demo", image);
char c = (char)waitKey(5);
if( c == 27 )
break;
switch( c )
{
case 'r':
needToInit = true;
break;
case 'c':
points[0].clear();
points[1].clear();
break;
case 'n':
nightMode = !nightMode;
break;
}
std::swap(points[1], points[0]);
cv::swap(prevGray, gray);
framenum++;
}
t2 = GetTickCount();
cout<<"fps:"<<framenum/((t2-t1)*1.0/1000)<<"\n";
return 0;
}
运行平均速度在30FPS,追踪良好。
下一节我们将介绍相机标定获得内参。之后结合LK光流跟踪的角点和对应的3D空间点利用solvePnP获得相机外参(旋转与平移)。