Strategic Game(二分匹配)
Link:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1054
Strategic Game
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5142 Accepted Submission(s): 2364
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
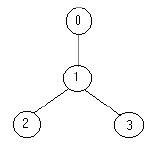
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
4 0:(1) 1 1:(2) 2 3 2:(0) 3:(0) 5 3:(3) 1 4 2 1:(1) 0 2:(0) 0:(0) 4:(0)
1 2
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1505;
vector<int>map[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int match[maxn],ans,un;
bool dfs(int u)
{
for(int i=0;i<map[u].size();i++)
{
if(!vis[map[u][i]])
{
vis[map[u][i]]=true;
if(match[map[u][i]]==-1||dfs(match[map[u][i]]))
{
match[map[u][i]]=u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void hangry()
{
ans=0;
memset(match,-1,sizeof(match));
for(int i=0;i<un;i++)
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
if(dfs(i))
ans++;
}
ans/=2;
}
int main()
{
int i,u,v,n;
while(scanf("%d",&un)==1)
{
for(i=0;i<maxn;i++)
map[i].clear();
for(i=0;i<un;i++)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)",&u,&n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
map[u].push_back(v);
map[v].push_back(u);
}
}
hangry();
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}