Ural 1557 1557. Network Attack
题目链接:http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1557
题目大意:给一个N个点M条边的无向连通图,求所有删除两条边使得图不连通的方案数。
数据范围:1<= N <= 2000 , 0 <= M <= 100000
两种情况:
第一: 有一条边是桥,其他任意删一条边,就可使得图不连通
第二: 两条边都不是桥,删除这两条边使得图不连通。
使用DFS搜索出所有的桥便可算出第一类;
第二类,同样是使用DFS,生成DFS树,由于DFS树没有横向边,所以我们只需要考虑子节点和父节点的关系。
首先,对于节点u,假如 u 和 u 的所有子数里面的点只有两条边可以访问到u的祖先节点,那么u边可以贡献一个答案。
还有,若 u 和其父亲只有一条连边,则扫描u的子数中所有节点,不包括u的节点j,假如j满足以下条件:
(1): j 与其父亲只有一条连边
(2):j 以及j的子树 可以访问到的j的祖先的边 和 u及u的子树可以访问到的u的祖先的边 相等
(3):j 可以用回边访问到的最近的祖先(即除了其直接父亲过来的边以外,能访问到的最近的祖先节点) 要 在u上面 (即深度小于u的深度)
满足这三个条件,对答案贡献 1 。
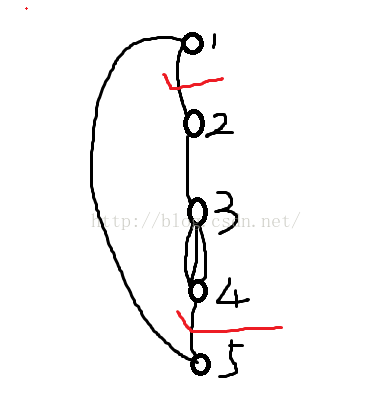
当满足这三个条件是,就是下图中画上红色的这种情况:
在u的子树种,找到所有满足这种情况的即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2005;
struct Edge
{
int from,to;
};
vector<Edge>E;
vector<int>G[maxn];
int bridge,nobridge;
int dep[maxn];
int low_set[maxn][maxn];
int s[maxn],t[maxn];
bool check(int x,int fa)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<G[fa].size();i++)
if( E[ G[fa][i] ].to == x ) res++;
return res == 1;
}
bool vis[maxn];
void dfs2(int x,int tx,int sx)
{
for(int i=0;i<G[x].size();i++)
{
int to = E[ G[x][i] ].to;
if(dep[to] != dep[ x ]+1) continue;
if(vis[to]) continue; // 防止重边进入子树多次
vis[to] = 1;
if( check(to,x) && t[to] < tx && s[to] == sx )
nobridge++;
dfs2(to,tx,sx);
}
}
void dfs(int x, int fa, int deep,int NE)
{
dep[x] = deep;
if(fa == -1) s[x] = 0;
else s[x] = 1;
t[x] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<G[x].size();i++)
if( (G[x][i] ^ 1) != NE )
{
int to = E[ G[x][i] ].to;
if( !dep[to] ){
dfs(to,x,deep+1,G[x][i]);
for(int j=1; j<=deep; j++)
{
if( low_set[ to ][ j ] )
{
low_set[x][j] += low_set[ to ][j];
}
}
}
else if( dep[to] < dep[x] )
{
low_set[ x ][ dep[ to ] ] ++ ;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<deep;i++)
{
if(low_set[x][i]){
s[x] += low_set[x][i];
t[x] = i;
}
}
if(s[x] == 1) bridge++;
else if(s[x] == 2) nobridge++;
if( s[x] != 1 && check(x,fa) )
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
dfs2(x,dep[x],s[x]);
}
}
void Add_Edge(int from,int to)
{
E.push_back( (Edge){from,to} );
E.push_back( (Edge){to,from} );
int m = E.size();
G[from].push_back(m-2);
G[to].push_back(m-1);
}
int n,m,u,v;
void init()
{
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
memset(low_set,0,sizeof(low_set));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) G[i].clear();
E.clear();
bridge = nobridge = 0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
init();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
Add_Edge(u,v);
}
dfs(1,-1,1,-1);
int ans = bridge*(m-bridge) + bridge*(bridge-1)/2;
cout<<ans+nobridge<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
5 7
4 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 4
3 4
1 5
6
*/