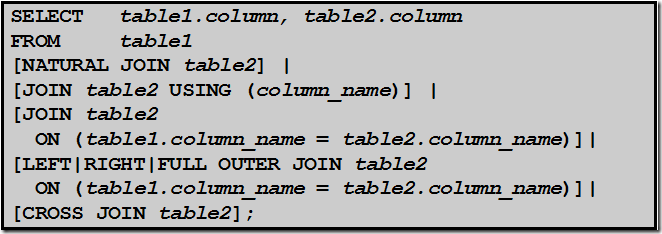
SQL之多表连接
这章主要讲通过使用左连接,右连接,内连接,外连接及自然连接等方式进行多表查询。例如要查询人员的编号、姓名、部门编号及部门名字,只是通过人员表,是查不到部门名字的,只能查到部门编号,这就需要通过人员表的部门编号(外键)和部门表的部门编号(主键)进行关联查询。
表连接方式:
- 交叉连接(笛卡尔积)cross joins
- 自然连接 natural joins
- 内连接 inner joins
- 左外连接、右外连接及全外连接
在SQL:1999标准中连接表的语法:
1、创建自然连接
- 两个表有相同列名才能创建自然连接,且不用添加连接条件
- 把相同列名值相等的记录连接起来,有多列相同的话,都会被连接起来
- 列名相同,但是类型不同,连接时会报错
例子:查询部门编号、部门名称、部门所在位置及城市
SQL> select department_id,department_name,location_id,city from departments natural join locations;
DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_NAME LOCATION_ID CITY
------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
60 IT 1400 Southlake
2、使用using子句创建内连接
- 当2个表有多列可以进行连接匹配的时候,可以使用using子句指定某一列进行匹配,可以用于列名相同但类型不同的列
- 在using子句中指定的公共列,在整个语句中都不能使用表名或者表别名前缀进行限定,但是可以使用列别名
- 没有在using子句中指定,但是两个表都有这个列,就必须要加上表名限定,同时最好使用列别名以便对结果进行区分
- 如果列只出现在一个表中,表名限定可加可不加,但是如果加上,可以减少解析,提高性能
- 使用using子句创建的连接为内连接,不是自然连接,不能和自然连接同时使用
例子:查询人员的编号、姓名、位置编号及部门编号,仅使用部门编号进行连接(不使用manager_id进行连接)
SQL> select employees.employee_id,employees.last_name,departments.location_id,department_id from employees join departments using (department_id);
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME LOCATION_ID DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- ------------------------- ----------- -------------
200 Whalen 1700 10
106 rows selected.
因为人员表里面有一条记录的部门编号为null,所有这里只有106条结果
例子:使用表别名简化书写,减少解析,减少网络传输量,提高你的性能
SQL> select e.employee_id,e.last_name,d.location_id,department_id from employees e join departments d using(department_id);
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME LOCATION_ID DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- ------------------------- ----------- -------------
200 Whalen 1700 10
3、使用on子句创建连接
- 用于进行不同列名的连接,即使类型不同,也可以使用
- 平时用得更多,也更容易理解
- on子句中的列,在整个语句中必须使用表名或者表别名前缀进行限定
- 后面可以使用and或者where进行条件限定
例子:使用on子句修改上面的例子
SQL> select e.employee_id,e.last_name,d.location_id,e.department_id,d.department_id from employees e join departments d on(e.department_id=d.department_id);
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME LOCATION_ID DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- ------------------------- ----------- ------------- -------------
200 Whalen 1700 10 10
4、使用on子句创建自连接
自连接就是将一张表当成多张表进行连接,以人员表为例,每一条记录里面有员工编号及对应的经理编号,如果想要查询员工名字及对应的经理名字,那么就要使用自连接,先将人员表作为工作人员表,取出员工的名字及其经理的编号(外键),再将人员表作为经理人员表,与其员工编号(主键)进行关联,就可以找到经理名字了。
例子:查询员工名字及其经理的名字
SQL> select e.last_name emp,e.manager_id,m.employee_id,m.last_name mgr
2 from employees e join employees m
3 on(e.manager_id=m.employee_id);
EMP MANAGER_ID EMPLOYEE_ID MGR
------------------------- ---------- ----------- -------------------------
Smith 148 148 Cambrault
5、给连接增加额外的条件限定
(1)使用and进行条件限定
例子:查询部门编号为50的人员信息和部门信息
SQL> select e.employee_id,e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_id
2 from employees e join departments d
3 on (e.department_id=d.department_id)
4 and d.department_id=50;
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- ------------------------- ------------- -------------
198 OConnell 50 50
(2)使用where进行条件限定
例子:使用where改写上面语句
SQL> select e.employee_id,e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_id
2 from employees e join departments d
3 on (e.department_id=d.department_id)
4 where d.department_id=50;
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- ------------------------- ------------- -------------
198 OConnell 50 50
6、使用on子句创建多表连接
运行顺序是从下往上
例子:查询人员编号,所在城市及部门名称
SQL> select employee_id,city,department_name
2 from employees e
3 join departments d
4 on e.department_id=d.department_id
5 join locations l
6 on d.location_id=l.location_id;
EMPLOYEE_ID CITY DEPARTMENT_NAME
----------- ------------------------------ ------------------------------
100 Seattle Executive
7、不等连接
连接条件不是字段的值相等,而是不相等
例子:查询人员的薪水等级
需要先创建薪水等级表并插入数据
创建表:
create table job_grades(
grade_level char(1),
lowest_sal number(10),
highest_sal number(10));
插入数据:
insert into job_grades values('A',1000,2999);
insert into job_grades values('B',3000,5999);
insert into job_grades values('C',6000,9999);
insert into job_grades values('D',10000,14999);
insert into job_grades values('E',15000,24999);
insert into job_grades values('F',25000,40000);
提交:
commit;
查询结果:
select * from job_grades;
G LOWEST_SAL HIGHEST_SAL
- ---------- -----------
A 1000 2999
B 3000 5999
C 6000 9999
D 10000 14999
E 15000 24999
F 25000 40000
6 rows selected.
创建连接查询
SQL> select e.last_name,e.salary,j.grade_level
2 from employees e join job_grades j
3 on e.salary between j.lowest_sal and j.highest_sal;
LAST_NAME SALARY G
------------------------- ---------- -
Olson 2100 A
结果自动进行了排序
8、外连接
- 在sql99标准里面,两张表进行连接,只返回两个字段相匹配的记录,叫inner join
- 两张表进行连接,除了inner join的结果,不匹配的也要取出来,根据方向,如果以左边为主,叫左连接,如果以右边为主,叫右连接,如果左边右边都要取出来,我们叫全外连接
(1)左连接
例子:查询所有人员的部门编号及部门名称,即使该人员不属于任何部门
SQL> select e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_name
2 from employees e left join departments d
3 on e.department_id=d.department_id;
LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_NAME
------------------------- ------------- ------------------------------
Whalen 10 Administration
Grant
107 rows selected.
即使“Grant”这个人不属于任何部门,也取出来了,但是部门编号和部门名称为null
(2)右连接
例子:查询所有部门的部门编号、部门名称及对应的人员,即使该部门没有任何人员
SQL> 2
2* from employees e left join departments d
SQL> c/left/right
2* from employees e right join departments d
SQL> l
1 select e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_name
2 from employees e right join departments d
3* on e.department_id=d.department_id
SQL> r
1 select e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_name
2 from employees e right join departments d
3* on e.department_id=d.department_id
LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_NAME
------------------------- ------------- ------------------------------
Whalen 10 Administration
Payroll
122 rows selected.
总共122行,因为部门表中有27个部门,人员表中有11个部门,故会多出16行,现在人员表有107行,除去没有部门的一行,还有106行,106行加上16行就是122行。
SQL> select count(distinct department_id) from employees;
COUNT(DISTINCTDEPARTMENT_ID)
----------------------------
11
SQL> select count(distinct department_id) from departments;
COUNT(DISTINCTDEPARTMENT_ID)
----------------------------
27
(3)全外连接
例子:查询所有人员对应的部门以及所有部门对应的人员
SQL> select e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_name
2 from employees e full join departments d
3 on e.department_id=d.department_id;
LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID DEPARTMENT_NAME
------------------------- ------------- ------------------------------
OConnell 50 Shipping
Grant
NOC
123 rows selected.
总共123行,将刚才没有部门的那一行也加上了
这个是sql99语法,那么使用oracle自己的写法
左连接:
SQL> select employee_id,last_name,e.department_id,d.department_id,department_name
2 from employees e,departments d
3 where e.department_id=d.department_id(+);
右连接:
SQL> select employee_id,last_name,e.department_id,d.department_id,department_name
2 from employees e,departments d
3 where e.department_id(+)=d.department_id;
那么全外连接呢,
SQL> select employee_id,last_name,e.department_id,d.department_id,department_name
2 from employees e,departments d
3 where e.department_id(+)=d.department_id(+);
where e.department_id(+)=d.department_id(+)
*
ERROR at line 3:
ORA-01468: a predicate may reference only one outer-joined table
报错,oracle自己语法中没有全外连接的写法,只能使用集合加起来。
用+来实现, 这个+可以这样来理解:+表示补充,即哪个表有加号,这个表就是匹配表。所以加号写在左表,右表就是全部显示,故是右连接。
9、交叉连接(笛卡尔积)
- 实际当中很少使用,主要用于测试时快速创建一张大表
- 结果是2张表行数的乘积
例子:交叉连接
SQL> select last_name,department_name from employees cross join departments;
Zlotkey Payroll
2889 rows selected.
看看这条语句的执行计划:
SQL> explain plan
2 for
3 select employee_id,last_name,department_name
4 from employees cross join departments
5 ;
Explained.
SQL> select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1162840532
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 2889 | 69336 | 41 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | MERGE JOIN CARTESIAN| | 2889 | 69336 | 41 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | DEPARTMENTS | 27 | 324 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 3 | BUFFER SORT | | 107 | 1284 | 38 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 4 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | EMPLOYEES | 107 | 1284 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11 rows selected.
这里两张表进行全表扫描,然后进行笛卡尔积,执行计划里面,如果有笛卡尔积,去看一下,到底是什么原因导致的,可以进行优化。
Oracle自己的语法处理笛卡尔积
SQL> select employee_id,last_name,department_name from employees,departments;
这里两张表直接加逗号,不加where条件,就是笛卡尔积,所以不要忘了加where条件。
10、总结
本章主要讲了内连接,外连接以及笛卡尔积,内连接包含我们的自然连接,using子句,on子句,还有自连接,落在某个范围。外连接包含我们的左连接,右连接,全外连接。
11、相关习题
(1)View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the ORDERS and ORDER_ITEMS tables. Evaluate the following SQL statement: SELECT oi.order_id, product_id, order_date FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o USING(order_id);Which statement is true regarding the execution of this SQL statement?
A.The statement would not execute because table aliases are not allowed in the JOIN clause.
B.The statement would not execute because the table alias prefix is not used in the USING clause.
C.The statement would not execute because all the columns in the SELECT clause are not prefixed with table aliases.
D.The statement would not execute because the column part of the USING clause cannot have a qualifier in the SELECT list.
答案:D
(2)View the Exhibit and examine the description of the ORDER_ITEMS and PRODUCT_INFORMATION tables. The ORDER_ITEM table has records pertaining to details for each product in an order. The PRODUCT_INFORMATION table has records for all the products available for ordering. Evaluate the following SQL statement: SELECT oi.order_id, pi.product_id FROM order_items oi RIGHT OUTER JOIN product_information pi ON (oi.product_id=pi.product_id);Which statement is true regarding the output of this SQL statement?
A.The query would return the ORDER_ID and PRODUCT_ID for only those products that are ordered.
B.The query would return the ORDER_ID and PRODUCT_ID for the products that are ordered as well as for the products that have never been ordered.
C.The query would return the ORDER_ID and PRODUCT_ID for the products that are ordered but not listed in the PRODUCT_INFORMATION table.
D.The query would return the ORDER_ID and PRODUCT_ID for those products that are ordered as well as for the products that have never been ordered, and for the products that are not listed in the PRODUCT_INFORMATION table.
答案:B
(3)View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the ORDER_ITEMS and ORDERS tables. You are asked to retrieve the ORDER_ID, PRODUCT_ID, and total price (UNIT_PRICE multiplied by QUANTITY), where the total price is greater than 50,000. You executed the following SQL statement: SELECT order_id, product_id, unit_price*quantity "Total Price" FROM orde_items WHERE unit_price*quantity > 50000 NATURAL JOIN orders;Which statement is true regarding the execution of the statement?
A.The statement would execute and provide the desired result.
B.The statement would not execute because the ON keyword is missing in the NATURAL JOIN clause.
C.The statement would not execute because the WHERE clause is before the NATURAL JOIN clause.
D.The statement would not execute because the USING keyword is missing in the NATURAL JOIN clause.
答案:C
(4)View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table. You want to display all employees and their managers having 100 as the MANAGER_ID. You want the output in two columns: the first column would have the LAST_NAME of the managers and the second column would have LAST_NAME of the employees. Which SQL statement would you execute?
A.SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee" FROM employees m JOIN employees e ON m.employee_id = e.manager_id WHERE m.manager_id=100;
B.SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee" FROM employees m JOIN employees e ON m.employee_id = e.manager_id WHERE e.manager_id=100;
C.SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee" FROM employees m JOIN employees e ON e.employee_id = m.manager_id WHERE m.manager_id=100;
D.SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee" FROM employees m JOIN employees e WHERE m.employee_id = e.manager_id AND e.manager_id=100;
答案:B
(5)View the Exhibit and examine the description of the DEPARTMENTS and EMPLOYEES tables. To retrieve data for all the employees for their EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, and DEPARTMENT NAME, the following SQL statement was written: SELECT employee_id, first_name, department_name FROM employees NATURAL JOIN departments? The desired output is not obtained after executing the above SQL statement. What could be the reason for this?
A.The NATURAL JOIN clause is missing the USING clause.
B.The table prefix is missing for the column names in the SELECT clause.
C.The DEPARTMENTS table is not used before the EMPLOYEES table in the FROM clause.
D.The EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables have more than one column with the same column name and data type.
答案:D
(6)View the Exhibit and examine the description of the EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables. You want to display the LAST_NAME for the employees, LAST_NAME for the manager of the employees, and the DEPARTMENT_NAME for the employees having 100 as MANAGER_ID. The following SQL statement was written: SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee", department_name "Department" FROM employees m JOIN employees e ON (m.employee_id = e.manager_id) WHERE e.manager_id=100 JOIN departments d ON (e.department_id =d.department_id)? Which statement is true regarding the output of this SQL statement?
A.The statement would provide the desired results.
B.The statement would not execute because the ON clause is written twice.
C.The statement would not execute because the WHERE clause is wrongly placed.
D.The statement would not execute because the self join uses the ON clause instead of the USING clause.
答案:C
(7)View the Exhibit and examine the structure for the ORDERS and ORDER_ITEMS tables. You want to display ORDER_ID, PRODUCT_ID, and TOTAL (UNIT_PRICE multiplied by QUANTITY) for all the orders placed in the last seven days. Which query would you execute ?
A.SELECT order_id, product_id, unit_price*quantity "TOTAL" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o ON (o.order_id=oi.order_id) WHERE o.order_date>=SYSDATE-7 ;
B.SELECT o.order_id,oi.product_id, oi.unit_price*oi.quantity "TOTAL" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o USING (order_id) WHERE o.order_date>=SYSDATE-7 ;
C.SELECT o.order_id, oi.product_id, oi.unit_price*oi.quantity "TOTAL" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o WHERE o.order_date>=SYSDATE-7 ON (o.order_id=oi.order_id);
D.SELECT o.order_id, oi.product_id, oi.unit_price*oi.quantity "TOTAL" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o ON (o.order_id=oi.order_id) WHERE o.order_date>=SYSDATE-7 ;
答案:D
(8)View the Exhibit and examine the table structure of DEPARTMENTS and LOCATIONS tables. You want to display all the cities that have no departments and the departments that have not been allocated cities. Which type of join between DEPARTMENTS and LOCATIONS tables would produce this information as part of its output?
A.NATURAL JOIN
B.FULL OUTER JOIN
C.LEFT OUTER JOIN
D.RIGHT OUTER JOIN
答案:B
(9)View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PRODUCT_INFORMATION and INVENTORIES tables. You have a requirement from the supplies department to give a list containing PRODUCT_ID, SUPPLIER_ID, and QUANTITY_ON_HAND for all the products wherein QUANTITY_ON_HAND is less than five. Which two SQL statements can accomplish the task?(Choose two.)
A.SELECT product_id, quantity_on_hand , supplier_id FROM product_information NATURAL JOIN inventories AND quantity_on_hand < 5;
B.SELECT i.product_id, i.quantity_on_hand , pi.supplier_id FROM product_information pi JOIN inventories i USING (product_id) AND quantity_on_hand < 5 ;
C.SELECT i.product_id, i.quantity_on_hand , pi.supplier_id FROM product_information pi JOIN inventories i ON (pi.product_id=i.product_id) WHERE quantity_on_hand < 5 ;
D.SELECT i.product_id, i.quantity_on_hand , pi.supplier_id FROM product_information pi JOIN inventories i ON (pi.product_id=i.product_id) AND quantity_on_hand < 5 ;
答案:CD
(10)View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PRODUCT_INFORMATION and INVENTORIES tables. You want to display the quantity on hand for all the products available in the PRODUCT_INFORMATION table that have the PRODUCT_STATUS as 'orderable'. QUANTITY_ON_HAND is a column in the INVENTORIES table. The following SQL statement was written to accomplish the task: SELECT pi.product_id, pi.product_status, sum(i.quantity_on_hand) FROM product_information pi LEFT OUTER JOIN inventories i ON (pi.product_id = i.product_id) WHERE (pi.product_status = 'orderable') GROUP BY pi.product_id, pi.product_status;Which statement is true regarding the execution of this SQL statement?
A.The statement would execute and produce the desired output.
B.The statement would not execute because the WHERE clause is used before the GROUP BY clause.
C.The statement would not execute because prefixing table alias to column names is not allowed with the ON clause.
D.The statement would not execute because the WHERE clause is not allowed with LEFT OUTER JOIN.
答案:A
(11)Which two statements are true regarding the types of table joins available in Oracle Database 10g?(Choose two.)
A.You can use the JOIN clause to join only two tables.
B.You can explicitly provide the join condition with a NATURAL JOIN.
C.You can use the USING clause to join tables on more than one column.
D.You can use the ON clause to specify multiple conditions while joining tables.
答案:CD