Codeforce 338 C. Divisor Tree(爆搜,3级)
A divisor tree is a rooted tree that meets the following conditions:
- Each vertex of the tree contains a positive integer number.
- The numbers written in the leaves of the tree are prime numbers.
- For any inner vertex, the number within it is equal to the product of the numbers written in its children.
Manao has n distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an. He tries to build a divisor tree which contains each of these numbers. That is, for each ai, there should be at least one vertex in the tree which contains ai. Manao loves compact style, but his trees are too large. Help Manao determine the minimum possible number of vertices in the divisor tree sought.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 8). The second line contains n distinct space-separated integers ai (2 ≤ ai ≤ 1012).
Print a single integer — the minimum number of vertices in the divisor tree that contains each of the numbers ai.
2 6 10
7
4 6 72 8 4
12
1 7
1
Sample 1. The smallest divisor tree looks this way: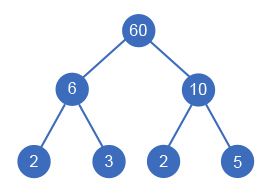
Sample 2. In this case you can build the following divisor tree: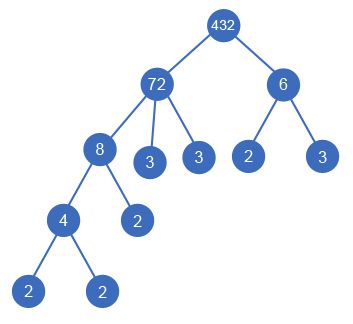
Sample 3. Note that the tree can consist of a single vertex.
思路:直接爆搜吧。
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;++i)
#define clr(f,z) memset(f,z,sizeof(f))
#define LL long long
#define ll(x) (1<<x)
using namespace std;
LL f[12];
int b[12],fa[12],id[12];
int n,ans;
int get(LL x)
{ if(x==1)return 0;
int num=0;
for(LL i=2;i*i<=x;++i)
{
while(x%i==0)
{
++num;x/=i;
}
}
if(x>1)++num;
return num;
}
void DP(int x)///算非叶子节点数
{
if(x==0)
{
int num=0,ddd=0;
FOR(i,1,n)
if(fa[i]==n+1)
{
++num;ddd+=b[i];
}
if(num!=1)ddd++;///多一个根节点
FOR(i,1,n)if(id[i]==0&&b[i]==1)///叶子
--ddd;
ans=min(ans,ddd+n);
return ;
}
FOR(i,x+1,n+1)///0 除任何数都是0
if(f[i]%f[x]==0)
{
id[i]++;///add a edge
f[i]/=f[x];
fa[x]=i;
DP(x-1);
f[i]*=f[x];
id[i]--;
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
FOR(i,1,n)
{scanf("%lld",&f[i]);
}
sort(f+1,f+n+1);
clr(b,0);clr(fa,-1);
FOR(i,1,n)
{b[i]=get(f[i]);
// cout<<b[i]<<endl;
}
ans=9999999;clr(id,0);
DP(n);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
、、、、DP
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int dp[1100],dp1[1100];
__int64 a[11];
int arr[11];
int main(void)
{
int n,i,j,k;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
sort(a,a+n);
dp[1]=1;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
memset(dp1,0,sizeof(dp1));
for(j=0;j<(1<<i);j++)if(dp[j])
for(k=j;;k=((k-1)&j))
{
__int64 num=a[i];
int is=0;
for(int t=0;t<i;t++)if(k&(1<<t))
{
if(num%a[t])
{
is=1;
break;
}
num/=a[t];
}
if(!is)
dp1[j-k+(1<<i)]=1;
if(k==0) break;
}
memcpy(dp,dp1,sizeof(dp));
}
__int64 ans=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
__int64 num=a[i];
j=0;
for(__int64 t=2;t*t<=num;t++)if(num%t==0)
while(num%t==0)
{
j++;
num/=t;
}
if(num>1) j++;
if(j==1) arr[i]=1,ans++;
else arr[i]=j,ans+=j+1;
}
int mm=2100000000;
for(i=0;i<(1<<n);i++)if(dp[i])
{
k=ans;
int cc=0;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(!(i&(1<<j)))
k-=arr[j];
else
cc++;
if(cc!=1)
k++;
mm=min(mm,k);
}
ans=mm;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}