C++基础学习教程(三)
承接上一讲。
2.7文件I/O
关于读写文件,C++中有一个专门的头文件<fstream>。
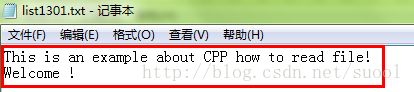
首先是读文件示例,如下:
</pre><pre>
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1301_file.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月22日 星期四 22时15分11秒
************************************************************************/
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in ("list1301.txt");
if (not in )
{
perror("list1301.txt");
}
else
{
string x;
while(in >> x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
in.close();
}
return 0;
}
文件内容:
读操作结果:

然后是写文件,示例如下:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1302_write.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月24日 星期六 12时24分23秒
> Aim at:Copying Integers from a Named File to a Named File
************************************************************************/
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Read data from file in
ifstream in("data.txt");
if (not in)
perror("data.txt"); // 文件不存在
else
{
ofstream out("out.txt"); // Write the data to out
if (not out)
perror("out.txt"); // 文件不存在
else
{
int x(0);
while (in >> x)
out << x << '\n';
out.close();
in.close(); // 关闭文件流
}
}
return 0;
}
文件内容如下:
运行结果:

不过上面的读写文件存在一定的问题,就是程序没有检查输出操作是否成功执行,下面的程序的改造就是带有最小错误检查的示例:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1302_write_check.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月24日 星期六 12时58分50秒
************************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// read data from in
ifstream in("data.txt");
if(not in)
perror("data.txt");
else
{
ofstream out("out.txt");
if(not out)
perror("out.txt");
else
{
int x(0);
while(in >> x)
out << x<< endl;
out.close();
if(not out)
{
perror("ou.txt");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
就是这一部分:
2.8数据结构——映射
前面我们已经介绍并学习了C++的一个特有的数据结构——向量,现在我要介绍另外一个C++的特有数据结构——映射,其他的高级语言成称之为字典等,其实都一样就是键值对的映射罢了。其中键是唯一的,值不限。
下面是一个示例:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1401_data.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月24日 星期六 13时17分39秒
************************************************************************/
// 读取单词并统计出现的次数
#include<cstdio>
#include<iomanip>
#include<ios>
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, int> counts;
string word;
fstream in("data.txt");
if(not in)
{
perror("data.txt");
}
// Read words from the standard input and count the number of times
// each word occurs.
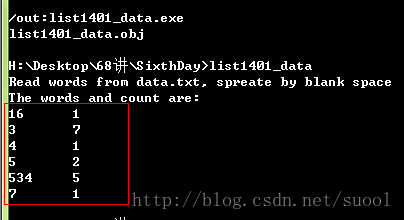
cout << "Read words from data.txt, spreate by blank space" << endl;
// For each word/count pair...
ofstream out("out.txt");
if(not out)
{
perror("out.txt");
}
while(in >> word)
{
++counts[word];
out << word << endl;
}
// out.close();
in.close();
cout << "The words and count are:" << endl;
out << "The words and count are:" << endl;
for (map<string,int>::iterator iter(counts.begin()); iter != counts.end(); ++iter)
{
// Print the word, tab, the count, newline.
cout << iter->first << '\t' << iter->second << '\n';
out << iter->first << '\t' << iter->second << '\n';
}
out.close();
if(not out)
{
perror("out.txt");
}
return 0;
}
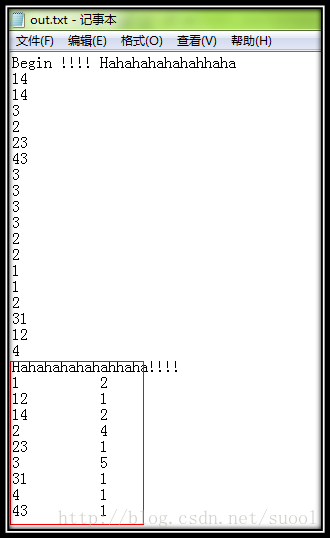
数据文件依然上面那个,结果如下:
下面一个示例是利用迭代器循环格式化输出映射内容:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1401_data_compat.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月24日 星期六 14时58分34秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iomanip>
#include <ios>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include<fstream>
#include <string>
// Aligning Words and Counts Neatly
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, int> counts;
string word;
// read data from data.txt
fstream in("data.txt");
if(not in)
{
perror("data.txt");
}
cout << "Read words from data.txt, spreate by blank space" << endl;
ofstream out("out.txt");
if(not out)
{
perror("out.txt");
}
// write data to out.txt
out << "Begin !!!! Hahahahahahahhaha" << endl;
while(in >> word)
{
++counts[word];
out << word << endl;
}
// Determine the longest word.
string::size_type longest(0);
for (map<string,int>::iterator iter(counts.begin()); iter != counts.end(); ++iter)
if (iter->first.size() > longest)
longest = iter->first.size();
// For each word/count pair...
const int count_size(10); // Number of places for printing the count
out << "Hahahahahahahhaha!!!!" << endl;
for (map<string,int>::iterator iter(counts.begin()); iter != counts.end(); ++iter)
{
// Print the word, count, newline. Keep the columns neatly aligned.
cout << setw(longest) << left << iter->first <<
setw(count_size) << right << iter->second << '\n';
out << setw(longest) << left << iter->first <<
setw(count_size) << right << iter->second << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
文件内容:
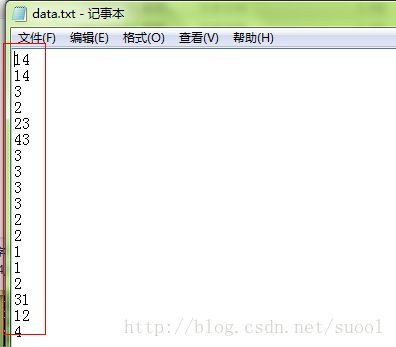
运行结果:
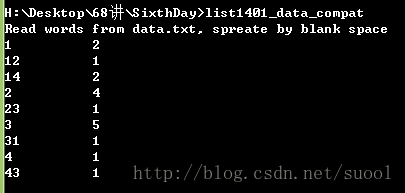
下面一个例子是搜索映射中的指定键:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: list1401_data_serach.cpp
> Author: suool
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年05月24日 星期六 15时17分30秒
************************************************************************/
#include<cstdio>
#include<fstream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, int> counts;
string word;
// read data from data.txt
ifstream in ("word.txt");
if(not in)
{
perror("word.txt");
}
// write data to out.txt
ofstream out ("out.txt");
if(not out)
{
perror("out.txt");
}
out << "Begin !!!! Hahahhahahah!!! \n";
while(in >> word)
{
++counts[word];
out << word << '\n';
}
out.close();
map<string, int>::iterator the(counts.find("the"));
if(the == counts.end())
cout << "\"the\" is not found!!!!" << endl;
else if(the->second == 1)
cout << "\"the\" occurs " << the->second << " time\n";
else
cout << "\"the\" occurs " << the->second << " times\n";
return 0;
}
文件内容:

运行结果:
未完待续。。。。。。。。。