android 开发之物理设备连接
前面文章介绍了搭建Android开发环境,接下来就应该是真机调试,真机调试还算比较简单,本文介绍Android开发机Nexus ONe调试过程(Google官方推荐机型之一),关于安装Android开发环境部分请参考前面文章。
本文环境:
Windows 7 + EClipse + SDK + 开发机Nexus One(下图,图片来源中关村)
一、下载GOOGLE USB驱动
如果是Unbuntu在配置完Eclipse环境后,一般均会自动识别Google的开发机,而Windows平台上则需通过Eclipse更新驱动包,方法如下:
- 启动Eclipse
- 点击Eclipse菜单Window -> Android SDK and AVD Manager
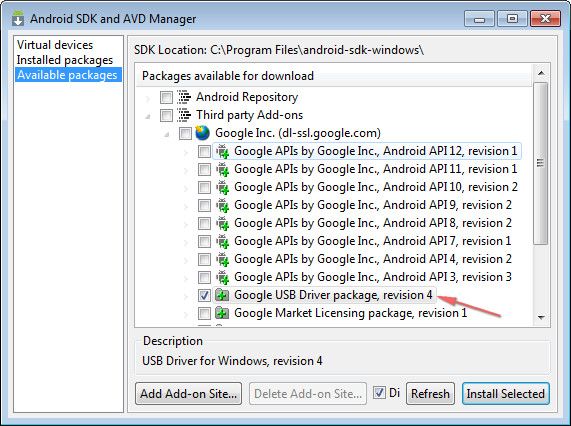
- 点选Available package里,如下图。
- 展开选择Third party Add-ons
- 点选安装“Google Inc.(dl-ssl.google.com)”下的Google USB Driver package,revision 4
- 接受许可协议并等待安装完成
下在完后,在您的android-sdk-windows(NDK目录下)安装目录下(C:\Program Files\android-sdk-windows\extras\google\usb_driver)会多出一个Extras文件夹,可以发现Google Usb Driver大侠,下文安装驱动时使用。
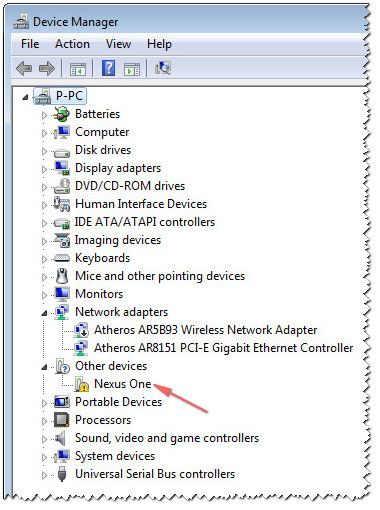
二、开机Nexus One并连接USB数据线到计算机
打开手机,插上USB线并连接到计算机,会发现Nexus One设备,如下图(设备管理器):
安装USB驱动方法很简单,只需在感叹号上点击鼠标右键,选择“更新软件驱动(Update software driver)”,然后再弹出窗口中点击浏览并定位到上文的Google驱动目录下,选中usb_driver目录点击确定开始安装。
安装完后,如下图:
三、测试检查设备是否在线
手机端设置:
把手机的“应用程序”->“开发”->“usb调试模式”打开,图略。
计算机端测试:
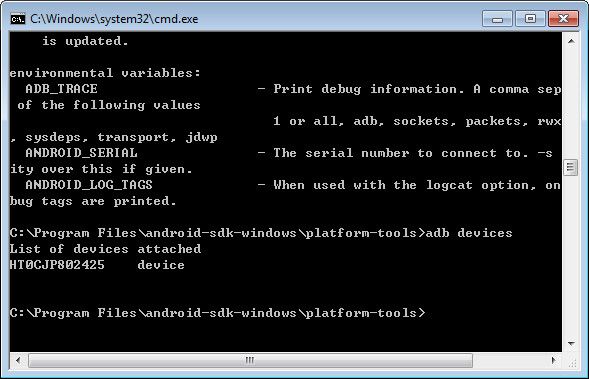
打开Windows自带的CMD终端,进入到C:\Program Files\android-sdk-windows\platform-tools或上级的TOOLS目录下(具体要看adb.exe安装到哪里)。输入:
adb devices
应该可以看到可用的开发机设备列表,如下图(HT0CJP802425就是开发机Nexus One):
后续很多针对开机机的命令行控制均可在此界面完成(比如提权、修改文件夹权限、安装、删除应用程序包等等),具体命令,请在上图中输入adb即可查看到:
C:\Program Files\android-sdk-windows\platform-tools>adb
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.26
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s <serial number> - directs command to the USB device or emulator with
the given serial number. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL environment variable.
-p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT environment variable is used, which must be an absolute path.
devices - list all connected devices
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this ocmmand with no additional arguments will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device
adb pull <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device
adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell <command> - run remote shell command
adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] <file> - push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
DATAOPTS:
(no option) - don't touch the data partition
-w - wipe the data partition
-d - flash the data partition
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port networking:
adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
<tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
- If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.
三、测试APK应用程序
接下来我们就可以验证自己的APK程序,步骤如下:
- 打开Eclipse演示工程(Windows环境下Android NDK环境搭建)。
- 点击RUN AS,选择Run Configurations,右侧Target里选择Manual,并点击Run按钮。
- 这时应该可以在新窗口中的Choose a running Android Device列表里看到手机终端。
- 双击该手机终端(或点击OK),APK将会自动安装并运行在开发机。
常见问题:
如果遇到开发机访问 no permissions拒绝访问时,可以尝试一下方法:
1、检查是否打开USB调试模式
2、在上文命令行下,执行:
adb kill-server
adb start-server
3、或尝试关机再次重新开机连接调试等。
更多文章:
Android源码在32位Linux系统上编译配置
Ubuntu环境Android平台源码下载及编
Windows下Android开发环境搭建和配置
Android开发入门之环境概念介绍