WGS84坐标和UTM坐标的转换
如题。做了一个Demo,主要是把最后面的参考资料1里面的脚本改成了C语言版本的.
代码:
1 #ifndef __COORCONV_H__ 2 #define __COORCONV_H__ 3 4 #include <cmath> 5 6 double pi = 3.14159265358979; 7 8 /* Ellipsoid model constants (actual values here are for WGS84) */ 9 double sm_a = 6378137.0; 10 double sm_b = 6356752.314; 11 double sm_EccSquared = 6.69437999013e-03; 12 double UTMScaleFactor = 0.9996; 13 14 typedef struct tagUTMCorr 15 { 16 double x; 17 double y; 18 }UTMCoor; 19 20 typedef struct tagWGS84Corr 21 { 22 double lat; 23 double log; 24 }WGS84Corr; 25 /* 26 * DegToRad 27 * 28 * Converts degrees to radians. 29 * 30 */ 31 inline double DegToRad (double deg) 32 { 33 return (deg / 180.0 * pi); 34 } 35 36 /* 37 * RadToDeg 38 * 39 * Converts radians to degrees. 40 * 41 */ 42 inline double RadToDeg (double rad) 43 { 44 return (rad / pi * 180.0); 45 } 46 47 /* 48 * ArcLengthOfMeridian 49 * 50 * Computes the ellipsoidal distance from the equator to a point at a 51 * given latitude. 52 * 53 * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., 54 * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. 55 * 56 * Inputs: 57 * phi - Latitude of the point, in radians. 58 * 59 * Globals: 60 * sm_a - Ellipsoid model major axis. 61 * sm_b - Ellipsoid model minor axis. 62 * 63 * Returns: 64 * The ellipsoidal distance of the point from the equator, in meters. 65 * 66 */ 67 double ArcLengthOfMeridian (double phi) 68 { 69 double alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, n; 70 double result; 71 72 /* Precalculate n */ 73 n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); 74 75 /* Precalculate alpha */ 76 alpha = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * (1.0 + (pow(n, 2.0) / 4.0) + (pow(n, 4.0) / 64.0)); 77 78 /* Precalculate beta */ 79 beta = (-3.0 * n / 2.0) + (9.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 16.0) + (-3.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 32.0); 80 81 /* Precalculate gamma */ 82 gamma = (15.0 * pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-15.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); 83 84 /* Precalculate delta */ 85 delta = (-35.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 48.0) + (105.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 256.0); 86 87 /* Precalculate epsilon */ 88 epsilon = (315.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); 89 90 /* Now calculate the sum of the series and return */ 91 result = alpha * (phi + (beta * sin(2.0 * phi)) + (gamma * sin(4.0 * phi)) + (delta * sin(6.0 * phi)) + (epsilon * sin(8.0 * phi))); 92 93 return result; 94 } 95 96 /* 97 * UTMCentralMeridian 98 * 99 * Determines the central meridian for the given UTM zone. 100 * 101 * Inputs: 102 * zone - An integer value designating the UTM zone, range [1,60]. 103 * 104 * Returns: 105 * The central meridian for the given UTM zone, in radians, or zero 106 * if the UTM zone parameter is outside the range [1,60]. 107 * Range of the central meridian is the radian equivalent of [-177,+177]. 108 * 109 */ 110 inline double UTMCentralMeridian (int zone) 111 { 112 return DegToRad(-183.0 + (zone * 6.0)); 113 } 114 115 116 /* 117 * FootpointLatitude 118 * 119 * Computes the footpoint latitude for use in converting transverse 120 * Mercator coordinates to ellipsoidal coordinates. 121 * 122 * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., 123 * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. 124 * 125 * Inputs: 126 * y - The UTM northing coordinate, in meters. 127 * 128 * Returns: 129 * The footpoint latitude, in radians. 130 * 131 */ 132 double FootpointLatitude (double y) 133 { 134 double y_, alpha_, beta_, gamma_, delta_, epsilon_, n; 135 double result; 136 137 /* Precalculate n (Eq. 10.18) */ 138 n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); 139 140 /* Precalculate alpha_ (Eq. 10.22) */ 141 /* (Same as alpha in Eq. 10.17) */ 142 alpha_ = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * (1 + (pow(n, 2.0) / 4) + (pow(n, 4.0) / 64)); 143 144 /* Precalculate y_ (Eq. 10.23) */ 145 y_ = y / alpha_; 146 147 /* Precalculate beta_ (Eq. 10.22) */ 148 beta_ = (3.0 * n / 2.0) + (-27.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 32.0) + (269.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 512.0); 149 150 /* Precalculate gamma_ (Eq. 10.22) */ 151 gamma_ = (21.0 * pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-55.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); 152 153 /* Precalculate delta_ (Eq. 10.22) */ 154 delta_ = (151.0 * pow (n, 3.0) / 96.0) + (-417.0 * pow (n, 5.0) / 128.0); 155 156 /* Precalculate epsilon_ (Eq. 10.22) */ 157 epsilon_ = (1097.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); 158 159 /* Now calculate the sum of the series (Eq. 10.21) */ 160 result = y_ + (beta_ * sin(2.0 * y_)) + (gamma_ * sin(4.0 * y_)) + (delta_ * sin(6.0 * y_)) + (epsilon_ * sin(8.0 * y_)); 161 162 return result; 163 } 164 165 /* 166 * MapLatLonToXY 167 * 168 * Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the 169 * Transverse Mercator projection. Note that Transverse Mercator is not 170 * the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them. 171 * 172 * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., 173 * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. 174 * 175 * Inputs: 176 * phi - Latitude of the point, in radians. 177 * lambda - Longitude of the point, in radians. 178 * lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians. 179 * 180 * Outputs: 181 * xy - A 2-element array containing the x and y coordinates 182 * of the computed point. 183 * 184 * Returns: 185 * The function does not return a value. 186 * 187 */ 188 void MapLatLonToXY (double phi, double lambda, double lambda0, UTMCoor &xy) 189 { 190 double N, nu2, ep2, t, t2, l; 191 double l3coef, l4coef, l5coef, l6coef, l7coef, l8coef; 192 double tmp; 193 194 /* Precalculate ep2 */ 195 ep2 = (pow(sm_a, 2.0) - pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / pow(sm_b, 2.0); 196 197 /* Precalculate nu2 */ 198 nu2 = ep2 * pow(cos(phi), 2.0); 199 200 /* Precalculate N */ 201 N = pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * sqrt(1 + nu2)); 202 203 /* Precalculate t */ 204 t = tan (phi); 205 t2 = t * t; 206 tmp = (t2 * t2 * t2) - pow (t, 6.0); 207 208 /* Precalculate l */ 209 l = lambda - lambda0; 210 211 /* Precalculate coefficients for l**n in the equations below 212 so a normal human being can read the expressions for easting 213 and northing 214 -- l**1 and l**2 have coefficients of 1.0 */ 215 l3coef = 1.0 - t2 + nu2; 216 217 l4coef = 5.0 - t2 + 9 * nu2 + 4.0 * (nu2 * nu2); 218 219 l5coef = 5.0 - 18.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 14.0 * nu2 - 58.0 * t2 * nu2; 220 221 l6coef = 61.0 - 58.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 270.0 * nu2 - 330.0 * t2 * nu2; 222 223 l7coef = 61.0 - 479.0 * t2 + 179.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); 224 225 l8coef = 1385.0 - 3111.0 * t2 + 543.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); 226 227 /* Calculate easting (x) */ 228 xy.x = N * cos (phi) * l + (N / 6.0 * pow(cos(phi), 3.0) * l3coef * pow(l, 3.0)) 229 + (N / 120.0 * pow(cos(phi), 5.0) * l5coef * pow(l, 5.0)) 230 + (N / 5040.0 * pow(cos (phi), 7.0) * l7coef * pow(l, 7.0)); 231 232 /* Calculate northing (y) */ 233 xy.y = ArcLengthOfMeridian (phi) 234 + (t / 2.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 2.0) * pow(l, 2.0)) 235 + (t / 24.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 4.0) * l4coef * pow(l, 4.0)) 236 + (t / 720.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 6.0) * l6coef * pow(l, 6.0)) 237 + (t / 40320.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 8.0) * l8coef * pow(l, 8.0)); 238 } 239 240 241 242 /* 243 * MapXYToLatLon 244 * 245 * Converts x and y coordinates in the Transverse Mercator projection to 246 * a latitude/longitude pair. Note that Transverse Mercator is not 247 * the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them. 248 * 249 * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., 250 * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. 251 * 252 * Inputs: 253 * x - The easting of the point, in meters. 254 * y - The northing of the point, in meters. 255 * lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians. 256 * 257 * Outputs: 258 * philambda - A 2-element containing the latitude and longitude 259 * in radians. 260 * 261 * Returns: 262 * The function does not return a value. 263 * 264 * Remarks: 265 * The local variables Nf, nuf2, tf, and tf2 serve the same purpose as 266 * N, nu2, t, and t2 in MapLatLonToXY, but they are computed with respect 267 * to the footpoint latitude phif. 268 * 269 * x1frac, x2frac, x2poly, x3poly, etc. are to enhance readability and 270 * to optimize computations. 271 * 272 */ 273 void MapXYToLatLon (double x, double y, double lambda0, WGS84Corr &philambda) 274 { 275 double phif, Nf, Nfpow, nuf2, ep2, tf, tf2, tf4, cf; 276 double x1frac, x2frac, x3frac, x4frac, x5frac, x6frac, x7frac, x8frac; 277 double x2poly, x3poly, x4poly, x5poly, x6poly, x7poly, x8poly; 278 279 /* Get the value of phif, the footpoint latitude. */ 280 phif = FootpointLatitude (y); 281 282 /* Precalculate ep2 */ 283 ep2 = (pow(sm_a, 2.0) - pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / pow(sm_b, 2.0); 284 285 /* Precalculate cos (phif) */ 286 cf = cos (phif); 287 288 /* Precalculate nuf2 */ 289 nuf2 = ep2 * pow (cf, 2.0); 290 291 /* Precalculate Nf and initialize Nfpow */ 292 Nf = pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * sqrt(1 + nuf2)); 293 Nfpow = Nf; 294 295 /* Precalculate tf */ 296 tf = tan (phif); 297 tf2 = tf * tf; 298 tf4 = tf2 * tf2; 299 300 /* Precalculate fractional coefficients for x**n in the equations 301 below to simplify the expressions for latitude and longitude. */ 302 x1frac = 1.0 / (Nfpow * cf); 303 304 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**2) */ 305 x2frac = tf / (2.0 * Nfpow); 306 307 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**3) */ 308 x3frac = 1.0 / (6.0 * Nfpow * cf); 309 310 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**4) */ 311 x4frac = tf / (24.0 * Nfpow); 312 313 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**5) */ 314 x5frac = 1.0 / (120.0 * Nfpow * cf); 315 316 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**6) */ 317 x6frac = tf / (720.0 * Nfpow); 318 319 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**7) */ 320 x7frac = 1.0 / (5040.0 * Nfpow * cf); 321 322 Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**8) */ 323 x8frac = tf / (40320.0 * Nfpow); 324 325 /* Precalculate polynomial coefficients for x**n. 326 -- x**1 does not have a polynomial coefficient. */ 327 x2poly = -1.0 - nuf2; 328 329 x3poly = -1.0 - 2 * tf2 - nuf2; 330 331 x4poly = 5.0 + 3.0 * tf2 + 6.0 * nuf2 - 6.0 * tf2 * nuf2 - 3.0 * (nuf2 *nuf2) - 9.0 * tf2 * (nuf2 * nuf2); 332 333 x5poly = 5.0 + 28.0 * tf2 + 24.0 * tf4 + 6.0 * nuf2 + 8.0 * tf2 * nuf2; 334 335 x6poly = -61.0 - 90.0 * tf2 - 45.0 * tf4 - 107.0 * nuf2 + 162.0 * tf2 * nuf2; 336 337 x7poly = -61.0 - 662.0 * tf2 - 1320.0 * tf4 - 720.0 * (tf4 * tf2); 338 339 x8poly = 1385.0 + 3633.0 * tf2 + 4095.0 * tf4 + 1575 * (tf4 * tf2); 340 341 /* Calculate latitude */ 342 philambda.lat = phif + x2frac * x2poly * (x * x) + x4frac * x4poly * pow(x, 4.0) + x6frac * x6poly * pow(x, 6.0) + x8frac * x8poly * pow(x, 8.0); 343 344 /* Calculate longitude */ 345 philambda.log = lambda0 + x1frac * x + x3frac * x3poly * pow(x, 3.0) + x5frac * x5poly * pow(x, 5.0) + x7frac * x7poly * pow(x, 7.0); 346 } 347 348 349 /* 350 * LatLonToUTMXY 351 * 352 * Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the 353 * Universal Transverse Mercator projection. 354 * 355 * Inputs: 356 * lat - Latitude of the point, in radians. 357 * lon - Longitude of the point, in radians. 358 * zone - UTM zone to be used for calculating values for x and y. 359 * If zone is less than 1 or greater than 60, the routine 360 * will determine the appropriate zone from the value of lon. 361 * 362 * Outputs: 363 * xy - A 2-element array where the UTM x and y values will be stored. 364 * 365 * Returns: 366 * void 367 * 368 */ 369 void LatLonToUTMXY (double lat, double lon, int zone, UTMCoor &xy) 370 { 371 MapLatLonToXY (lat, lon, UTMCentralMeridian(zone), xy); 372 373 /* Adjust easting and northing for UTM system. */ 374 xy.x = xy.x * UTMScaleFactor + 500000.0; 375 xy.y = xy.y * UTMScaleFactor; 376 if (xy.y < 0.0) 377 xy.y += 10000000.0; 378 } 379 380 381 382 /* 383 * UTMXYToLatLon 384 * 385 * Converts x and y coordinates in the Universal Transverse Mercator 386 * projection to a latitude/longitude pair. 387 * 388 * Inputs: 389 * x - The easting of the point, in meters. 390 * y - The northing of the point, in meters. 391 * zone - The UTM zone in which the point lies. 392 * southhemi - True if the point is in the southern hemisphere; 393 * false otherwise. 394 * 395 * Outputs: 396 * latlon - A 2-element array containing the latitude and 397 * longitude of the point, in radians. 398 * 399 * Returns: 400 * The function does not return a value. 401 * 402 */ 403 void UTMXYToLatLon (double x, double y, int zone, bool southhemi, WGS84Corr &latlon) 404 { 405 double cmeridian; 406 407 x -= 500000.0; 408 x /= UTMScaleFactor; 409 410 /* If in southern hemisphere, adjust y accordingly. */ 411 if (southhemi) 412 y -= 10000000.0; 413 414 y /= UTMScaleFactor; 415 416 cmeridian = UTMCentralMeridian (zone); 417 MapXYToLatLon (x, y, cmeridian, latlon); 418 } 419 420 #endif //__COORCONV_H__
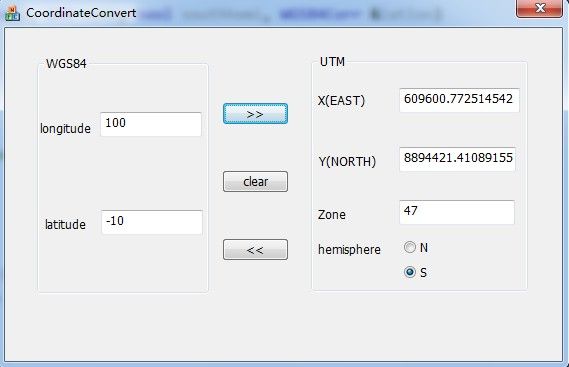
然后用MFC写了一个类似的对话框程序:
全部的源代码:
http://files.cnblogs.com/wb-DarkHorse/CoordinateConvert.rar
RERERENCE:
1 http://home.hiwaay.net/~taylorc/toolbox/geography/geoutm.html 网页版demo
2 http://www.mogoo.org/fang/?p=65 一位博客里面的,用Java写的
3 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Transverse_Mercator_coordinate_system wiki的介绍,公式都写的很清楚,不多说
4 http://my.oschina.net/lidayong/blog/59869 一位博客里的,用c#写的
5 http://www.zhdzch.com/xxyd/chzs/200904/522.html 比较清楚的介绍,用VB写的
下面是国外的几篇资料:
http://www.movable-type.co.uk/scripts/latlong-vincenty-direct.html 根据经纬度求距离
http://www.ngs.noaa.gov/PUBS_LIB/inverse.pdf 对应上面链接的文章
http://trac.osgeo.org/proj/ 一个开源的地图投影库