XML基础编程解析(DOM SAX Dom4J)
XML编程:利用java程序去增删改查(CRUD)xml中的数据
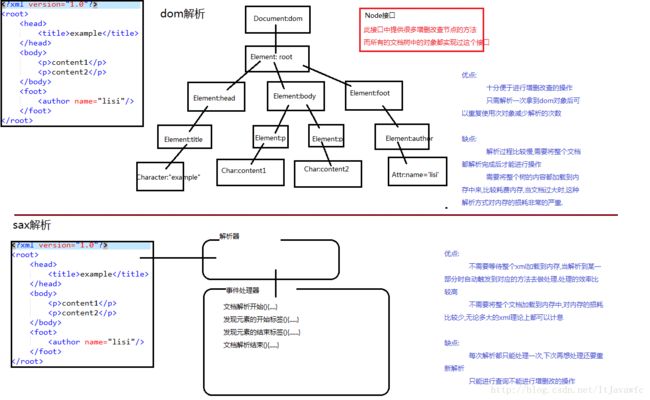
解析思想:
dom解析
sax解析
基于这两种解析思想市面上就有了很多的解析api
sun jaxp既有dom方式也有sax方式,并且这套解析api已经加入到j2se的规范中,意味这不需要导入任何第三方开发包就可以直接使用这种解析方式.但是这种解析方式效率低下,没什么人用.
dom4j 可以使用dom方式高效的解析xml.
pull
!!dom4j
导入开发包,通常只需要导入核心包就可以了,如果在使用的过程中提示少什么包到lib目录下在导入缺少的包即可
先看看两种解析思想的比较:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<书架>
<书>
<书名>Java就业培训教程</书名>
<作者>张孝祥</作者>
<售价>39.00元</售价>
</书>
<书>
<书名>JavaScript网页开发</书名>
<作者>张孝祥</作者>
<售价>28.00元</售价>
</书>
</书架>
package com.itheima.sax;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.ContentHandler;
import org.xml.sax.Locator;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.XMLReader;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
public class SaxDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.获取解析器工厂
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
//2.通过工厂获取sax解析器
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
//3.获取读取器
XMLReader reader = parser.getXMLReader();
//4.注册事件处理器
reader.setContentHandler(new MyContentHandler2() );
//5.解析xml
reader.parse("book.xml");
}
}
//适配器设计模式
class MyContentHandler2 extends DefaultHandler{
private String eleName = null;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String name,
Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
this.eleName = name;
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
if("书名".equals(eleName) && ++count==2){
System.out.println(new String(ch,start,length));
}
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String name)
throws SAXException {
eleName = null;
}
}
class MyContentHandler implements ContentHandler{
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
System.out.println("文档解析开始了.......");
}
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String name,
Attributes atts) throws SAXException {
System.out.println("发现了开始标签,"+name);
}
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
System.out.println(new String(ch,start,length));
}
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String name)
throws SAXException {
System.out.println("发现结束标签,"+name);
}
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
System.out.println("文档解析结束了.......");
}
public void endPrefixMapping(String prefix) throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void ignorableWhitespace(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void processingInstruction(String target, String data)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void setDocumentLocator(Locator locator) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void skippedEntity(String name) throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void startPrefixMapping(String prefix, String uri)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
这里要了解适配器模式,Sax解析的两大步骤:解析器 事件处理器
//1.获取解析器工厂
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
//2.通过工厂获取sax解析器
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
//3.获取读取器
XMLReader reader = parser.getXMLReader();
//4.注册事件处理器
reader.setContentHandler(new MyContentHandler2() );
//5.解析xml
reader.parse("book.xml");
package com.itheima.dom4j;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Dom4jDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.获取解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2.解析xml获取代表整个文档的dom对象
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
//3.获取根节点
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
//4.获取书名进行打印
String bookName = root.element("书").element("书名").getText();
System.out.println(bookName);
}
}
这个例子要了解Sax即系的基本步骤:分为那几步
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
package com.itheima.dom4j;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Demo4jDemo2 {
@Test
public void attr() throws Exception{
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
Element bookEle = root.element("书");
//bookEle.addAttribute("出版社", "传智出版社");
//String str = bookEle.attributeValue("出版社");
//System.out.println(str);
Attribute attr = bookEle.attribute("出版社");
attr.getParent().remove(attr);
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("book.xml"),OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());
writer.write(dom);
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void del() throws Exception{
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
Element price2Ele = root.element("书").element("特价");
price2Ele.getParent().remove(price2Ele);
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("book.xml"),OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());
writer.write(dom);
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void update()throws Exception{
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
root.element("书").element("特价").setText("4.0元");
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("book.xml"),OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());
writer.write(dom);
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void add()throws Exception{
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
//凭空创建<特价>节点,设置标签体
Element price2Ele = DocumentHelper.createElement("特价");
price2Ele.setText("40.0元");
//获取父标签<书>将特价节点挂载上去
Element bookEle = root.element("书");
bookEle.add(price2Ele);
//将内存中的dom树会写到xml文件中,从而使xml中的数据进行更新
// FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("book.xml");
// dom.write(writer);
// writer.flush();
// writer.close();
//加了一个OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint()格式转化器,作用是让让新增节点对齐
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("book.xml"),OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint());
writer.write(dom);
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void find() throws Exception{
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document dom = reader.read("book.xml");
Element root = dom.getRootElement();
List<Element> list = root.elements();
Element book2Ele = list.get(1);
System.out.println(book2Ele.element("书名").getText());
}
}
你所应该知道的Dom4J
创建解析器:
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
利用解析器读入xml文档:
Document document = reader.read(new File("input.xml"));
获取文档的根节点:
Element root = document.getRootElement();
接口继承结构:
Node ---
Branch
--Document
--Element
----
Attribute
Node接口
| String |
asXML() 将一个节点转换为字符串 |
| String |
getName() 获取节点的名称,如果是元素则获取到元素名,如果是属性获取到属性名 |
| short |
getNodeType() 获取节点类型,在Node接口上定义了一些静态short类型的常量用来表示各种类型 |
| Element |
getParent() 获取父节点,如果是根元素调用则返回null,如果是其他元素调用则返回父元素,如果是属性调用则返回属性所依附的元素。 |
| String |
getText() 返回节点文本,如果是元素则返回标签体,如果是属性则返回属性值 |
| List |
selectNodes(String xpathExpression) 利用xpath表达式,选择节点 |
| void |
setName(String name) 设置节点的名称,元素可以更改名称,属性则不可以,会抛出UnsupportedOperationException 异常 |
| void |
setText(String text) 设置节点内容,如果是元素则设置标签体,如果是属性则设置属性的值 |
| void |
write(Writer writer) 将节点写出到一个输出流中,元素、属性均支持 |
Branch接口(实现了Node接口)
| void |
add(Element element) 增加一个子节点 |
| Element |
addElement(QName qname) 增加一个给定名字的子节点,并且返回这个新创建的节点的引用 |
| int |
indexOf(Node node) 获取给定节点在所有直接点中的位置号,如果该节点不是此分支的子节点,则返回-1 |
| boolean |
remove(Element element) 删除给定子元素,返回布尔值表明是否删除成功。 |
Element接口(实现了Branch, Node接口)
| void |
add(Attribute attribute) 增加一个属性 |
| Element |
addAttribute(QName qName, String value) 为元素增加属性,用给定的属性名和属性值,并返回该元素 |
| Element |
addAttribute(String name, String value) 为元素增加属性 |
| Attribute |
attribute(int index) 获取指定位置的属性 |
| Attribute |
attribute(QName qName) 获取指定名称的属性 |
| Iterator |
attributeIterator() 获取属性迭代器 |
| List |
attributes() 获取该元素的所有属性,以一个list返回 |
| String |
attributeValue(QName qName) 获取指定名称属性的值,如果不存在该属性返回null,如果存在该属性但是属性值为空,则返回空字符串 |
| Element |
element(QName qName) 获取指定名称的子元素,如果有多个该名称的子元素,则返回第一个 |
| Element |
element(String name) 获取指定名称的子元素,如果有多个该名称的子元素,则返回第一个 |
| Iterator |
elementIterator() 获取子元素迭代器 |
| Iterator |
elementIterator(QName qName) 获取指定名称的子元素的迭代器 |
| List |
elements() 获取所有子元素,并用一个list返回 |
| List |
elements(QName qName) 获取所有指定名称的子元素,并用一个list返回 |
| String |
getText() 获取元素标签体 |
| boolean |
remove(Attribute attribute) 移除元素上的属性 |
| void |
setAttributes(List attributes) 将list中的所有属性设置到该元素上 |
Attribute接口(实现了Node接口)
| QName |
getQName() 获取属性名称 |
| String |
getValue() 获取属性的值 |
| void |
setValue(String value) 设置属性的值 |
DocumentHelper 类
| static Attribute |
createAttribute(Element owner, QName qname, String value) 创建一个Attribute |
|
| static Document |
createDocument() 创建一个Document |
|
| static Document |
createDocument(Element rootElement) 以给定元素作为根元素创建Document |
|
|
|
static Element |
createElement(QName qname) 以给定名称创建一个Element |
| static Document |
parseText(String text) 将一段字符串转化为Document |
将节点写出到XML文件中去
方法1:
调用Node提供的write(Writer writer) 方法,使用默认方式将节点输出到流中:
node.write(new FileWriter("book.xml"));
乱码问题:
Dom4j在将文档载入内存时使用的是文档声明中encoding属性声明的编码集进行编码, 如果在此时使用writer输出时writer使用的内部编码集与encoding不同则会有乱码问题。
FileWriter默认使用操作系统本地码表即gb2312编码,并且无法更改。
此时可以使用OutputStreamWriter(FileOutputStream("filePath"),"utf-8");的方式自己封装 一个指定码表的Writer使用,从而解决乱码问题。
方式2:
利用XMLWriter写出Node:
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileWriter("output.xml"));
writer.write(node);
writer.close();
乱码问题:
(1)使用这种方式输出时,XMLWriter首先会将内存中的docuemnt翻译成UTF-8 格式的document,在进行输出,这时有可能出现乱码问题。
可以使用OutputFormat 指定XMLWriter转换的编码为其他编码。
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
format.setEncoding("GBK");
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileWriter("output.xml"),format);
(2)Writer使用的编码集与文档载入内存时使用的编码集不同导致乱码,使用字节流 或自己封装指定编码的字符流即可(参照方法1)。