Linux进程管理
一、进程概述
进程(任务):是处于执行期的程序以及它所包含的资源的总称。
线程:是一种特殊的进程。
虚拟处理器:让进程觉得自己在独享处理器
虚拟内存:在获取和使用内存时,觉得自己拥有整个系统的所有内存资源。
线程之间,共享虚拟内存,拥有各自的虚拟处理器。
fork/exit/wait
二、进程描述符及其任务结构
内核把进程放在叫做任务队列的双向循环链表中。
链表中的每一项都是task_struct,成为进程描述符(process descriptor)。
2.1 进程描述符分配
Linux通过slab分配器分配task_struct。
进程的栈底或栈顶存放着struct thread_info,thread_info中存有task_struct,可以通过thread_info快速找到当前进程。
当前进程current,通过thread_info来获取。(include/asm-generic/current.h)
#ifndef __ASM_GENERIC_CURRENT_H #define __ASM_GENERIC_CURRENT_H #include <linux/thread_info.h> #define get_current() (current_thread_info()->task) #define current get_current() #endif /* __ASM_GENERIC_CURRENT_H */
2.2 进程描述符存放
进程标识符PID,用pid_t表示,实际是一个int类型。
最大值为32768。
可以通过/proc/sys/kernel/pid_max修改系统最大进程数。
2.3 进程状态与设置
TASK_RUNNING(运行)
进程是可执行的;它正在执行,或者在运行队列中等待执行。
TASK_INITERRUPTIBLE(可中断)
进程正在睡眠(阻塞),等待某些条件的达成。
TASK_UNINITERRUPTIBLE(不可中断)
除了不会因为接收到信号而被唤醒,投入运行外,这个状态与可中断状态相同。
TASK_ZOMBIE(僵死)
进程已经结束了,但是其父进程还没有调用wait4()系统调用。
TASK_STOPPED(停止)
进程停止运行。
设置进程状态
#define set_task_state(tsk, state_value) \ set_mb((tsk)->state, (state_value)) #define set_current_state(state_value) \ set_mb(current->state, (state_value))
2.4 进程上下文
2.5 进程家族树
所有的进程都是PID为1的init进程的后代。
系统中每个进程都有一个父进程。
每个进程可以有零个或多个子进程。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/udp.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
unsigned int hook_mark1(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *iph;
struct udphdr *udph;
u16 dst_port,src_port;
u32 src_ip,dst_ip;
struct task_struct *task;
struct list_head *list;
iph = ip_hdr(skb);
if (iph->protocol == 17)
{
udph = (struct udphdr*)((u_int8_t*)iph + (iph->ihl << 2));
dst_port = ntohs(udph->dest);
src_port = ntohs(udph->source);
src_ip = ntohl(iph->saddr);
dst_ip = ntohl(iph->daddr);
if (dst_port == 53)
{
printk("----process parameter:\n");
printk("state:%d\n", current->state);
printk("prio:%d\n", current->prio);
printk("static_prio:%d\n", current->static_prio);
printk("normal_prio:%d\n", current->normal_prio);
printk("rt_priority:%d\n", current->rt_priority);
printk("policy:%d\n", current->policy);
printk("task pid:%d\n", current->pid);
printk("task tgid:%d\n", current->tgid);
printk("\n----child process:\n");
list_for_each(list, ¤t->children)
{
task = list_entry(list, struct task_struct, tasks);
if (task)
{
printk("task pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
}
printk("----parent process:\n");
for (task = current; task != &init_task; task = task->parent)
{
printk("pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
printk("----prev process:\n");
task = list_entry(task->tasks.prev, struct task_struct, tasks);
if (task)
{
printk("pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
printk("----next process:\n");
task = list_entry(task->tasks.next, struct task_struct, tasks);
if (task)
{
printk("pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
task = next_task(task);
if (task)
{
printk("pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
printk("----all process:");
for_each_process(task)
{
printk("pid:%d\n", task->pid);
}
}
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
static struct nf_hook_ops nfho_marker1;
u8 nfho_marker1_flag = 0;
static int __init init_marker(void)
{
printk("init marker.\n");
nfho_marker1.hook=hook_mark1;
nfho_marker1.hooknum=NF_INET_POST_ROUTING;
nfho_marker1.pf=PF_INET;
nfho_marker1.priority=NF_IP_PRI_LAST;
nf_register_hook(&nfho_marker1);
nfho_marker1_flag = 1;
return 0;
}
static void __exit exit_marker(void)
{
if(nfho_marker1_flag == 1)
{
nf_unregister_hook(&nfho_marker1);
}
printk("exit marker.\n");
}
module_init(init_marker);
module_exit(exit_marker);
MODULE_VERSION("1.0.0_0");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("gwy");
MODULE_ALIAS("the alias of module name");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("the description about the use of the module");
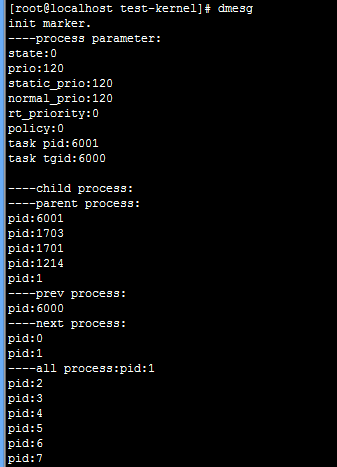
输出结果:
三、进程创建
fork通过拷贝当前进程创建一个子进程,子进程与父进程的区别在于pid,ppid,以及资源计数。
exec读取可执行文件,载入地址空间开始运行。
3.1 写时拷贝
是一种推迟甚至免除拷贝的技术。
3.2 fork()
clone()
do_fork()
copy_process()
3.3 vfork()
不拷贝父进程页表项;
子进程作为父进程的一个线程运行,父进程阻塞,直到子进程退出或执行exec;
子进程不能向地址空间写入。
四、线程
线程是与其他进程共享资源的进程。
内核线程没有独立的地址空间(与进程的区别)只在内核运行。
五、进程销毁
exit()/do_exit()释放资源并处于TASK_ZOMBIE状态。
wait()释放内核栈、thread_info、task_struct。
孤儿进程,在当前进程组找一个线程作为父进程,不行的话,让init作为其父进程。