hdu 1401 bfs
Solitaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1871 Accepted Submission(s): 629
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
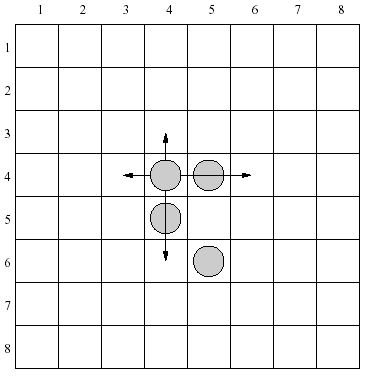
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).

There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5 2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
/*
尽管网上都是双广的解法,俺还是执着愚钝的单广...不小心还MLE了一次,于是vis改成了bool,且为88888888
*/
struct node
{
int x[4],y[4],step;
}p;
int move[][2]={0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0};
bool vis[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8];
bool mat[9][9];
void set(node s)
{
vis[s.x[0]][s.y[0]][s.x[1]][s.y[1]][s.x[2]][s.y[2]][s.x[3]][s.y[3]]=1;
}
bool test(node s)
{
return vis[s.x[0]][s.y[0]][s.x[1]][s.y[1]][s.x[2]][s.y[2]][s.x[3]][s.y[3]];
}
bool okend(node s)
{
int i;
for(i=0;mat[s.x[i]][s.y[i]]&&i<4;++i);
return (i==4);
}
bool inboard(int x,int y)
{
if(x>=8||x<0||y>=8||y<0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
bool isempty(node s,int k)
{
for(int i=0;i<4;++i)
if(i!=k&&s.x[i]==s.x[k]&&s.y[i]==s.y[k])
return 0;
return 1;
}
bool bfs()
{
p.step=0;
if(okend(p))
return 1;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
queue<node> que;
que.push(p);
int i,j,k;
node t;
while(!que.empty())
{
p=que.front();
/*好久以前一直没A的题,因为一些事就放下了.
之所以执着的些单广是因为结果是WA而不是TLE,终于找到原因
,这里之前竟然是>8,不淡定啊,然后就AC了。
*/
if(p.step>=8)
return 0;
que.pop();
for(k=0;k<4;++k)
for(i=0;i<4;++i)
{
t=p;
t.step++;
t.x[k]+=move[i][0];
t.y[k]+=move[i][1];
if(inboard(t.x[k],t.y[k]))
{
if(!test(t))
{
if(isempty(t,k))
{
if(okend(t))
return 1;
set(t);
que.push(t);
}
else
{
t.x[k]+=move[i][0];
t.y[k]+=move[i][1];
if(inboard(t.x[k],t.y[k])&&isempty(t,k)&&!test(t))
{
if(okend(t))
return 1;
set(t);
que.push(t);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i,x,y;
while(scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)==2)
{
--x;
--y;
p.x[0]=x;
p.y[0]=y;
for(i=1;i<4;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
--x;
--y;
p.x[i]=x;
p.y[i]=y;
}
memset(mat,0,sizeof(mat));
for(i=0;i<4;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
--x;
--y;
mat[x][y]=1;
}
printf(bfs()?"YES\n":"NO\n");
}
return 0;
}