【DFS】 hdu3260 Facer is learning to swim
Facer is learning to swim
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3260
Problem Description
Facer is addicted to a game called “Tidy is learning to swim”. But he finds it too easy. So he develops a new game called “Facer is learning to swim” which is more difficult and more interesting.
In the new game, a robot named “Facer” is swimming in a pool. The pool can be considered as a vertical N×M grid. The coordinates of the top-left cell is (1,1), and the coordinates of the bottom-right cell is (N,M). Cells in the top rows are called “surface cells”, and all other cells are called “under water cells”.
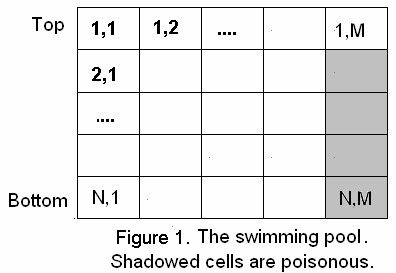
Facer starts swimming from the top-left cell (1,1) and must arrive at the top-right cell (1,M). He has a constant horizontal speed of 1 per second, and a vertical speed of v per second. v is always integer and can be changed. If v is positive, it means Facer is moving down; and if v is negative, it means Facer is moving up. So if Facer is at cell (x,y) now , he will arrive at cell (x+v,y+1) after a second. Be careful that if x+v>N, Facer will get to cell (N,y+1) because he cannot move down anymore and of course if x+v<1, Facer will get to cell (1,y+1) because he cannot fly. Please remember that all the “under water cells” in the right-most column are poisonous. If Facer goes into those cells, he will die.
The capacity of Facer’s oxygen bottle is limited, and when Facer gets into a surface cell, the oxygen bottle is refilled automatically. Facer has to refill his oxygen bottle every K seconds, which means that during the time between two refillings, Facer can only pass at most K-1 under water cells in the horizontal direction.
In every cell, there is either a “speed changing machine” or a “money box” (can’t be both). Every speed changing machine has a value T and every money box has a value P.
You have got enough number of devices called “speedo”. Every speedo has a value Q which is 1 or -1. You can put your speedos in any cells, but you can put at most one speedo in a cell.
When Facer reaches a cell, the speed changing machine of value T in that cell (if there is one) will change his vertical speed by T, and the speedo of value Q in that cell (if there is one) will change his vertical speed by Q. For example, if Facer’s vertical speed is v when he arrives at a cell with a speed changing machine of value T and a speedo of value Q, his vertical speed will be changed to v + T + Q immediately. There are three more things you need to know about speed changing:
1. All speed changing machines in the surface cells can’t work.
2. When reaching a surface cell without a speedo, Facer’s vertical speed becomes zero immediately; and when reaching a surface cell with a speedo of value Q, Facer’s vertical speed becomes Q immediately.
3. When reaching a bottom cell, though Facer can’t go down any more, his vertical speed will NOT be changed unless there is a speedo or a speed changing machine in that cell. It’s maybe sound a little bit weird but Facer really is such a weird guy.
When arriving at a cell with a money box of value P, Facer gets P dollars (In fact, if P is negative, Facer loses |P| dollars). Facer’s total amount of money can be negative --- that means Facer owes some money to the pool’s owner.
You task is deploying your speedos in a smart way before Facer starts swimming, so Facer can get money as much as possible when he arrives at cell (1,M). Facer’s initial vertical speed is zero and if you put a speedo in the cell (1,1), it will change Facer’s initial vertical speed.
In the new game, a robot named “Facer” is swimming in a pool. The pool can be considered as a vertical N×M grid. The coordinates of the top-left cell is (1,1), and the coordinates of the bottom-right cell is (N,M). Cells in the top rows are called “surface cells”, and all other cells are called “under water cells”.

Facer starts swimming from the top-left cell (1,1) and must arrive at the top-right cell (1,M). He has a constant horizontal speed of 1 per second, and a vertical speed of v per second. v is always integer and can be changed. If v is positive, it means Facer is moving down; and if v is negative, it means Facer is moving up. So if Facer is at cell (x,y) now , he will arrive at cell (x+v,y+1) after a second. Be careful that if x+v>N, Facer will get to cell (N,y+1) because he cannot move down anymore and of course if x+v<1, Facer will get to cell (1,y+1) because he cannot fly. Please remember that all the “under water cells” in the right-most column are poisonous. If Facer goes into those cells, he will die.
The capacity of Facer’s oxygen bottle is limited, and when Facer gets into a surface cell, the oxygen bottle is refilled automatically. Facer has to refill his oxygen bottle every K seconds, which means that during the time between two refillings, Facer can only pass at most K-1 under water cells in the horizontal direction.
In every cell, there is either a “speed changing machine” or a “money box” (can’t be both). Every speed changing machine has a value T and every money box has a value P.
You have got enough number of devices called “speedo”. Every speedo has a value Q which is 1 or -1. You can put your speedos in any cells, but you can put at most one speedo in a cell.
When Facer reaches a cell, the speed changing machine of value T in that cell (if there is one) will change his vertical speed by T, and the speedo of value Q in that cell (if there is one) will change his vertical speed by Q. For example, if Facer’s vertical speed is v when he arrives at a cell with a speed changing machine of value T and a speedo of value Q, his vertical speed will be changed to v + T + Q immediately. There are three more things you need to know about speed changing:
1. All speed changing machines in the surface cells can’t work.
2. When reaching a surface cell without a speedo, Facer’s vertical speed becomes zero immediately; and when reaching a surface cell with a speedo of value Q, Facer’s vertical speed becomes Q immediately.
3. When reaching a bottom cell, though Facer can’t go down any more, his vertical speed will NOT be changed unless there is a speedo or a speed changing machine in that cell. It’s maybe sound a little bit weird but Facer really is such a weird guy.
When arriving at a cell with a money box of value P, Facer gets P dollars (In fact, if P is negative, Facer loses |P| dollars). Facer’s total amount of money can be negative --- that means Facer owes some money to the pool’s owner.
You task is deploying your speedos in a smart way before Facer starts swimming, so Facer can get money as much as possible when he arrives at cell (1,M). Facer’s initial vertical speed is zero and if you put a speedo in the cell (1,1), it will change Facer’s initial vertical speed.
Input
Multiple test cases, ended by a line of “0 0 0”. For each test case:
The first line contains three integers N,M and K (1<=N<=100, 1<=M<=1000, 1<=K<=10), tells the size of the pool and Facer must refill the oxygen bottle every K seconds.
Following are N lines describing the cells by top to bottom order. Each line contains M elements, separated by blanks, telling the information about the cells of a row, by left to right order. There are only two kinds of elements:
1. a char “v” followed by an integer T, meaning that there is a “speed changing machine” of value T (-20<=T<=20) in the correspondent cell.
2. a char “$” followed by an integer P, meaning that there is a “money box” of value P (-1000000<=P<=1000000) in the correspondent cell.
The first line contains three integers N,M and K (1<=N<=100, 1<=M<=1000, 1<=K<=10), tells the size of the pool and Facer must refill the oxygen bottle every K seconds.
Following are N lines describing the cells by top to bottom order. Each line contains M elements, separated by blanks, telling the information about the cells of a row, by left to right order. There are only two kinds of elements:
1. a char “v” followed by an integer T, meaning that there is a “speed changing machine” of value T (-20<=T<=20) in the correspondent cell.
2. a char “$” followed by an integer P, meaning that there is a “money box” of value P (-1000000<=P<=1000000) in the correspondent cell.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing an integer representing the maximum amount of money Facer can get when he reaches cell (1,M).
Sample Input
5 10 3 $81 $47 $3 $0 $82 $31 $89 v0 $97 v-1 $14 $94 v1 v-1 v1 $106 v1 v0 v-1 v0 $93 $105 v-1 $219 v0 v0 v-1 v1 $225 v1 v0 $160 v1 v1 $348 $120 $240 $392 $280 $172 $305 $455 $140 v-1 $455 v0 v-1 v0 v1 $410 0 0 0
Sample Output
430
题意:用一个游泳池,深n,宽m.有一个机器人从(1,1)点出发,在游泳池的每个点中会有一个钱袋(-1000000<=p<=1000000)或者变速器(-20<=T<=20),同时你也可以在每个点放一个(只能一个)改变速度的东西(Q=-1或1),问到(1,,m)的最大收益是多少。
有以下几种要求:
1:水平速度恒为1(只能向右)
2:深度最小为1,小于1的都视为1,在深度1时纵向速度为0,任何变速器都没有作用(即T没有作用,Q还有有用的)。
3:深度最大为n,大于n的都视为n,在深度n时纵向速度不会改变,直到被变速器或者改变速度的东西改变。
For example, if Facer’s vertical speed is v when he arrives at a cell with a speed changing machine of value T and a speedo of value Q, his vertical speed will be changed to v + T + Q immediately.
题解:这个题目应该也可以用动态规划去解答,但我写不好,之后用搜索来写了,阶段很好划分,每一列为一个阶段,对于每个点都能推出下一列的三个点的状态(水面可以更新下一列的两个点的状态),直接更新即可。
PS:输入中的空格可能不止一个,所以接收数据的时候要小心
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
#define inf (-((1<<30)-1))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
char opt[105][1005];//格子的类型
int value[105][1005];//格子的数值
int dp[1005];
int n,m,k;
void dfs(int x,int y,int v,int ki,int money,int pre)//深度x,第y列,当前速度v,下水ki,当前收益money,第pre列下水
{
if(x==1&&y!=pre)
{
dp[y]=max(dp[y],dp[pre]+money);
return;
}
if(ki>=k) return;
if(y>=m) return;
money+=(opt[x][y]=='$'?value[x][y]:0);
int vi=(x!=1?(opt[x][y]!='$'?value[x][y]:0):0);
for(int i=-1;i<=1;++i)
{
int pos=x+v+vi+i;
if(pos<=1)
dfs(1,y+1,0,0,money,pre);
else
{
if(pos>n) pos=n;
dfs(pos,y+1,v+vi+i,ki+1,money,pre);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char c;
for(; ~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);)
{
if(n+m+k==0) break;
//接收输入
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
{
for(int j=1; j<=m; ++j)
{
for(;c=getchar();)
if(c=='v'||c=='$') break;
opt[i][j]=c;
scanf("%d",&value[i][j]);
}
}
dp[1]=0;
for(int i=2;i<=m;++i) dp[i]=inf;
for(int i=1;i<m;++i)
if(dp[i]!=inf)
dfs(1,i,0,0,0,i);//深度x,第y列,当前速度v,下水ki,当前收益money,第pre列下水
printf("%d\n",dp[m]+(opt[1][m]=='$'?value[1][m]:0));
}
return 0;
}来源: http://blog.csdn.net/ACM_Ted