POJ 3194 (DFS)
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 2643 | Accepted: 1540 |
Description
An equidivision of an n × n square array of cells is a partition of the n2 cells in the array in exactly n sets, each one with n contiguous cells. Two cells are contiguous when they have a common side.
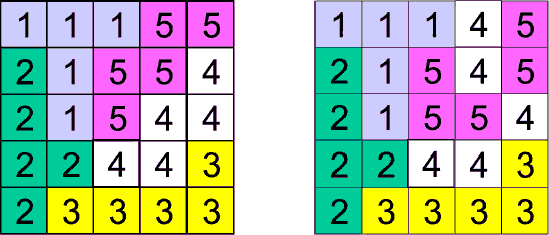
A good equidivision is composed of contiguous regions. The figures show a good and a wrong equidivision for a 5 × 5 square:
Note that in the second example the cells labeled with 4 describe three non-contiguous regions and cells labeled with 5 describe two non-contiguous regions. You must write a program that evaluates if an equidivision of the cells in a square array is good or not.
Input
It is understood that a cell in an n × n square array is denoted by a pair (i, j), with 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n. The input file contains several test cases. Each test case begins with a line indicating n, 0 < n < 100, the side of the square array to be partitioned. Next, there are n − 1 lines, each one corresponding to one partition of the cells of the square, with some non-negative integer numbers. Consecutive integers in a line are separated with a single blank character. A line of the form
a1a2a3a4…
means that cells denoted with the pairs (a1, a2), (a3, a4), … belong to one of the areas in the partition. The last area in the partition is defined by those cells not mentioned in the n − 1 given lines. If a case begins with n = 0 it means that there are no more cases to analyze.
Output
For each test case good must be printed if the equidivision is good, in other case, wrong must be printed. The answers for the different cases must preserve the order of the input.
Sample Input
2 1 2 2 1 5 1 1 1 2 1 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 4 2 4 1 5 1 3 1 4 5 5 2 5 3 5 5 5 4 2 5 3 4 3 5 4 3 4 4 5 1 1 1 2 1 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 4 2 4 5 5 2 5 3 5 5 5 4 2 4 1 4 3 5 4 3 4 4 0
Sample Output
wrong good wrong
题意+解题思路:
一道简单的DFS被题目说的神乎其神。。
其实就是看n个数是不是都各自相连。
用一个t来标记一下总共有几块区域即可。
算法:
DFS
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,a[101][101],map[101][101];
int dir[4][2]={-1,0,0,-1,0,1,1,0};
int inside(int x, int y)
{
if (x>0 && x<=n && y>0 && y<=n)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void find(int x, int y)
{
int i;
map[x][y]=1;
for (i=0; i<4; i++)
if (a[x+dir[i][0]][y+dir[i][1]]==a[x][y] && map[x+dir[i][0]][y+dir[i][1]]==0 && inside(x+dir[i][0],y+dir[i][1]))
find(x+dir[i][0],y+dir[i][1]);
}
int main ()
{
int i,j,x,y,t;
while(scanf("%d",&n))
{
if (n==0) break;
t=0;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
//if (n==1)
//{
// cout<<"good"<<endl;
// continue;
//}
for (i=1; i<n; i++)
{
for (j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
a[x][y]=i;
}
}
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
for (j=1; j<=n; j++)
if (map[i][j]==0)
{
find(i,j);
t++;
}
if (t==n)
cout<<"good"<<endl;
else
cout<<"wrong"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}