HDU 3338 Kakuro Extension
Problem Description
If you solved problem like this, forget it.Because you need to use a completely different algorithm to solve the following one.
Kakuro puzzle is played on a grid of "black" and "white" cells. Apart from the top row and leftmost column which are entirely black, the grid has some amount of white cells which form "runs" and some amount of black cells. "Run" is a vertical or horizontal maximal one-lined block of adjacent white cells. Each row and column of the puzzle can contain more than one "run". Every white cell belongs to exactly two runs — one horizontal and one vertical run. Each horizontal "run" always has a number in the black half-cell to its immediate left, and each vertical "run" always has a number in the black half-cell immediately above it. These numbers are located in "black" cells and are called "clues".The rules of the puzzle are simple:
1.place a single digit from 1 to 9 in each "white" cell
2.for all runs, the sum of all digits in a "run" must match the clue associated with the "run"
Given the grid, your task is to find a solution for the puzzle.

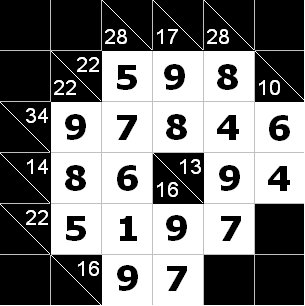
Picture of the first sample input Picture of the first sample output
Kakuro puzzle is played on a grid of "black" and "white" cells. Apart from the top row and leftmost column which are entirely black, the grid has some amount of white cells which form "runs" and some amount of black cells. "Run" is a vertical or horizontal maximal one-lined block of adjacent white cells. Each row and column of the puzzle can contain more than one "run". Every white cell belongs to exactly two runs — one horizontal and one vertical run. Each horizontal "run" always has a number in the black half-cell to its immediate left, and each vertical "run" always has a number in the black half-cell immediately above it. These numbers are located in "black" cells and are called "clues".The rules of the puzzle are simple:
1.place a single digit from 1 to 9 in each "white" cell
2.for all runs, the sum of all digits in a "run" must match the clue associated with the "run"
Given the grid, your task is to find a solution for the puzzle.


Picture of the first sample input Picture of the first sample output
Input
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n,m ≤ 100) — the number of rows and columns correspondingly. Each of the next n lines contains descriptions of m cells. Each cell description is one of the following 7-character strings:
.......— "white" cell;
XXXXXXX— "black" cell with no clues;
AAA\BBB— "black" cell with one or two clues. AAA is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding vertical run, or XXX if there is no associated vertical run. BBB is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding horizontal run, or XXX if there is no associated horizontal run.
The first row and the first column of the grid will never have any white cells. The given grid will have at least one "white" cell.It is guaranteed that the given puzzle has at least one solution.
.......— "white" cell;
XXXXXXX— "black" cell with no clues;
AAA\BBB— "black" cell with one or two clues. AAA is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding vertical run, or XXX if there is no associated vertical run. BBB is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding horizontal run, or XXX if there is no associated horizontal run.
The first row and the first column of the grid will never have any white cells. The given grid will have at least one "white" cell.It is guaranteed that the given puzzle has at least one solution.
Output
Print n lines to the output with m cells in each line. For every "black" cell print '_' (underscore), for every "white" cell print the corresponding digit from the solution. Delimit cells with a single space, so that each row consists of 2m-1 characters.If there are many solutions, you may output any of them.
Sample Input
6 6 XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 028\XXX 017\XXX 028\XXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 022\022 ....... ....... ....... 010\XXX XXX\034 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\014 ....... ....... 016\013 ....... ....... XXX\022 ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXX\016 ....... ....... XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 5 8 XXXXXXX 001\XXX 020\XXX 027\XXX 021\XXX 028\XXX 014\XXX 024\XXX XXX\035 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX 007\034 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\043 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\030 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX
Sample Output
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 5 8 9 _ _ 7 6 9 8 4 _ 6 8 _ 7 6 _ 9 2 7 4 _ _ _ 7 9 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 9 9 1 1 8 6 _ _ 1 7 7 9 1 9 _ 1 3 9 9 9 3 9 _ 6 7 2 4 9 2 _
网络流最大流,注意左右都有的要拆点。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<bitset>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1e2 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int m, n, U[maxn][maxn], L[maxn][maxn], f[maxn][maxn][2], ans[maxn][maxn];
char s[maxn][maxn][9];
struct MaxFlow
{
#define maxe 1000010 //边数
#define maxp 20010 //点数
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
struct Edges
{
int to, flow;
Edges(){}
Edges(int to, int flow) :to(to), flow(flow){}
}edge[maxe];
int first[maxp], next[maxe], dis[maxp], tot, work[maxp], n;
void clear(int x){ n = x; tot = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) first[i] = -1; }
void AddEdge(int s, int t, int flow)
{
edge[tot] = Edges(t, 0); next[tot] = first[s]; first[s] = tot++;
edge[tot] = Edges(s, flow); next[tot] = first[t]; first[t] = tot++;
}
bool bfs(int s, int t)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) dis[i] = -1;
queue<int> p; p.push(s); dis[s] = 0;
while (!p.empty())
{
int q = p.front(); p.pop();
for (int i = first[q]; i != -1; i = next[i])
{
if (edge[i ^ 1].flow&&dis[edge[i].to] == -1)
{
p.push(edge[i].to);
dis[edge[i].to] = dis[q] + 1;
if (dis[t] != -1) return true;
}
}
}
return dis[t] != -1;
}
int dfs(int s, int t, int low)
{
if (s == t) return low;
for (int &i = work[s]; i >= 0; i = next[i])
{
if (dis[s] + 1 == dis[edge[i].to] && edge[i ^ 1].flow)
{
int x = dfs(edge[i].to, t, min(low, edge[i ^ 1].flow));
if (x)
{
edge[i].flow += x; edge[i ^ 1].flow -= x;
return x;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int s, int t)
{
int maxflow = 0, inc = 0;
while (bfs(s, t))
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) work[i] = first[i];
while (inc = dfs(s, t, INF)) maxflow += inc;
}
return maxflow;
}
}solve;
int get(char a, char b, char c)
{
return a * 100 + b * 10 + c - '0' * 111;
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) scanf("%s", s[i][j]), L[i][j] = U[i][j] = 0;
solve.clear(2 * n * m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (s[i][j][3] != 'X')
{
if (s[i][j][3] == '\\')
{
f[i][j][0] = s[i][j][0] == 'X' ? 0 : get(s[i][j][0], s[i][j][1], s[i][j][2]);
f[i][j][1] = s[i][j][4] == 'X' ? 0 : get(s[i][j][4], s[i][j][5], s[i][j][6]);
if (f[i][j][0]) U[i][j] = i;
if (f[i][j][1]) L[i][j] = j;
}
else
{
U[i][j] = U[i - 1][j]; L[i][j] = L[i][j - 1];
f[U[i][j]][j][0]--; f[i][L[i][j]][1]--;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (s[i][j][3] != 'X')
{
if (s[i][j][3] == '\\')
{
if (f[i][j][0]) solve.AddEdge((i - 1 + n)*m + j, 2 * n * m + 1, f[i][j][0]);
if (f[i][j][1]) solve.AddEdge(0, (i - 1) * m + j, f[i][j][1]);
}
else
{
solve.AddEdge((i - 1) * m + L[i][j], (i - 1) * m + j, 8);
solve.AddEdge((i - 1) * m + j, (U[i][j] - 1 + n) * m + j, 8);
}
}
}
solve.dinic(0, 2 * n * m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (s[i][j][3] != '.') printf("_ ");
else printf("%d ", solve.edge[solve.first[(i - 1)*m + j]].flow + 1);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}