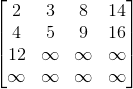《算法导论》笔记 第6章 总结与思考
【完整代码】
template<typename Type>
class CHeap{
private:
Type *A;
int heapSize;
int length;
inline int left(int x) { return x<<1; }
inline int right(int x) { return x<<1|1; }
inline int parent(int x) { return x>>1; }
public:
CHeap(){}
CHeap(Type B[],int n) {
init(B,n);
}
void init(Type B[],int n) {
A = B;
length = n;
heapSize = 0;
}
void heapSort() {
buildMaxHeap();
for (int i=length;i>=2;i--) {
swap(A[1],A[i]);
heapSize--;
maxHeapify(1);
}
}
void maxHeapify(int i) {
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l <= heapSize && A[l] > A[largest]) largest = l;
if (r <= heapSize && A[r] > A[largest]) largest = r;
if (largest != i) {
swap(A[i],A[largest]);
maxHeapify(largest);
}
}
void maxHeapify_NonRecursive(int i) {
while (true) {
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l <= heapSize && A[l] > A[largest]) largest = l;
if (r <= heapSize && A[r] > A[largest]) largest = r;
if (largest == i) break;
swap(A[i],A[largest]);
i = largest;
}
}
void buildMaxHeap() {
heapSize = length;
for (int i=length/2;i>=1;i--) {
maxHeapify(i);
}
}
Type heapMaximum() {
return A[1];
}
Type heapExtractMax() {
if (heapSize < 1) return 0;
int max = A[1];
A[1] = A[heapSize--];
maxHeapify(1);
return max;
}
void heapIncreaseKey(int i,Type key) {
if (key < A[i]) return;
A[i] = key;
while (i>1 && A[parent(i)] < A[i]) {
swap(A[i],A[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
void maxHeapInsert(Type key) {
heapSize++;
A[heapSize] = key;
heapIncreaseKey(heapSize,key);
}
void heapDeleteMax(int i) {
if (i<1||i>heapSize) return;
A[i] = A[heapSize--];
maxHeapify(i);
}
void minHeapify(int i) {
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l <= heapSize && A[l] < A[smallest]) smallest = l;
if (r <= heapSize && A[r] < A[smallest]) smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(A[i],A[smallest]);
minHeapify(smallest);
}
}
void minHeapify_NonRecursive(int i) {
while (true) {
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l <= heapSize && A[l] < A[smallest]) smallest = l;
if (r <= heapSize && A[r] < A[smallest]) smallest = r;
if (smallest == i) break;
swap(A[i],A[smallest]);
i = smallest;
}
}
void buidMinHeap() {
heapSize = length;
for (int i=length/2;i>=1;i--) {
minHeapify(i);
}
}
Type heapMinimum() {
return A[1];
}
Type heapExtractMin() {
if (heapSize < 1) return 0;
int min = A[1];
A[1] = A[heapSize--];
minHeapify(1);
return min;
}
void heapDecreaseKey(int i,Type key) {
if (key > A[i]) return;
A[i] = key;
while (i>1 && A[parent(i)] > A[i]) {
swap(A[i],A[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
void minHeapInsert(Type key) {
heapSize++;
A[heapSize] = key;
heapDecreaseKey(heapSize,key);
}
void heapDeleteMin(int i) {
if (i<1||i>heapSize) return;
A[i] = A[heapSize--];
minHeapify(i);
}
};
【思考题】
6-1 用插入方法建堆
a) 当输入数组相同时,过程BUILD_MAX_HEAP和BUILD_MAX_HEAP'产生的堆是否总是一样的?是的给出证明;否则给出反例。
不一样哦。
n = 9
A = <5 3 17 10 84 19 6 22 9>
BUILD_MAX_HEAP:84 22 19 10 3 17 6 5 9
BUILE_MAX_HEAP':84 22 19 17 10 5 6 3 9
b) 证明:最坏情况下,BUILD_MAX_HEAP'要用⊙(nlgn)时间来建成一个含n个元素的堆。
执行一次MAX_HEAP_INSERT最坏的时间为⊙(logn)。BUILD_MAX_HEAP'中执行了n次,因此复杂度为⊙(nlogn)
6-2 对d叉堆的分析
a) 如何在一个数组中表示一个d叉堆?
A[(x-1)*d+2]、A[(x-1)*d+2+1]...A[(x-1)*d+2+k-1] 表示第i个结点的d叉堆第k个子结点。
b) 含n个元素的d叉堆的高度是多少?
![]()
c) 给出d叉堆的EXTRACT_MAX的一个有效实现,并用d和n表示出它的运行时间。
Type heapExtractMax() {
if (heapSize < 1) return 0;
int max = A[1];
A[1] = A[heapSize--];
maxHeapify(1);
return max;
}时间
d) 给出d叉堆最大堆的INSERT的一个有效实现,并用d和n表示出它的运行时间。
void maxHeapInsert(Type key) {
heapSize++;
A[heapSize] = key;
heapIncreaseKey(heapSize,key);
}
e) 给出INCREASE_KEY(A,i,k)的一个有效实现,该过程首先执行A[i]=max(A[i],k),并相应地更新d叉最大堆的结构。请用d和n表示出它的运行时间。
void heapIncreaseKey(int i,Type key) {
if (key > A[i]) A[i] = key;
while (i>1 && A[parent(i)] < A[i]) {
swap(A[i],A[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
时间 ![]()
template <typename Type>
class CDHeap{
private:
Type *A;
int d;
int heapSize;
int length;
inline int son(int x,int k) { return (x-1)*d+2+k; }
inline int parent(int x) { return (x-2)/d+1; }
public:
CDHeap(){}
CDHeap(Type B[],int n,int dd) {
init(B,n,dd);
}
void init(Type B[],int n,int dd) {
A = B;
length = n;
d = dd;
heapSize = 0;
}
void maxHeapify(int x) {
int largest = x;
for (int i=0;i<d;i++) {
int k = son(x,i);
if (k <= heapSize && A[k] > A[largest]) largest = k;
}
if (largest != x) {
swap(A[x],A[largest]);
maxHeapify(largest);
}
}
void buildMaxHeap() {
heapSize = length;
for (int i=length/d;i>=1;i--) {
maxHeapify(i);
}
}
Type heapMaximum() {
return A[1];
}
Type heapExtractMax() {
if (heapSize < 1) return 0;
int max = A[1];
A[1] = A[heapSize--];
maxHeapify(1);
return max;
}
void heapIncreaseKey(int i,Type key) {
if (key > A[i]) A[i] = key;
while (i>1 && A[parent(i)] < A[i]) {
swap(A[i],A[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
void maxHeapInsert(Type key) {
heapSize++;
A[heapSize] = key;
heapIncreaseKey(heapSize,key);
}
void heapSort() {
buildMaxHeap();
for (int i=length;i>=2;i--) {
swap(A[1],A[i]);
heapSize--;
maxHeapify(1);
}
}
};
6-3 Young氏矩阵
a) 画一个包含元素{9,16,3,2,4,8,5,14,12}的4X4Young氏矩阵。
b) 讨论一个mXn的Young氏矩阵,如果Y[1,1]=OO,则Y为空;如果Y[m,n]<OO,则Y是满的(包含mXn个元素)。
1、当Y[1,1]=OO时,由Young氏矩阵的性质可知,A[1,1]右侧的元素 >= OO,下侧的元素 >= OO,因此A[1,1]的右侧和下侧均为OO。
对Y[1,2...n]做同样的分析,可知矩阵中所有元素均为OO,表示矩阵中不存在元素。
2、当Y[m,n]<OO时,由Young氏矩阵的性质可知,A[m,n]左侧和上侧元素 <= A[m][n] < OO。
对Y[m,1...n-1]做同样的分析,可知矩阵中所有元素均小于OO,矩阵中不存在空位置,所以矩阵是满的。
c) 给出一个在非空mXn的Young氏矩阵上实现EXTRACT_MIN的算法,使其运行时间为O(m+n)。
将存在于(1,1)中的最小元素取出。用OO代替,将OO与右边或下边更小的元素进行交换,直至到达正确的位置。
由于元素只能向右或向下移动,F(i,j) = F(i-1,j) or F(i,j-1)。
令p = n+m,,因此F(p) = F(p-1) + O(1),运行时间为O(m+n)。
void extractYoungs(int x,int y) {
int sx = x;
int sy = y;
if (x < n && matrix[x+1][y] < matrix[sx][sy]) {
sx = x + 1;
sy = y;
}
if (y < m && matrix[x][y+1] < matrix[sx][sy]) {
sx = x;
sy = y + 1;
}
if (sx != x || sy != y) {
swap(matrix[x][y],matrix[sx][sy]);
extractYoungs(sx,sy);
}
}
int extractMin() {
int ret = matrix[1][1];
matrix[1][1] = INF;
extractYoungs(1,1);
return ret;
}
d) 说明如何在O(m+n)的时间内,将一个新元素插入到一个未满的 mXn Young氏矩阵中。
将元素替换掉矩阵中最大的元素A[n][m],循环将其与左侧或上侧更大的元素交换,维护矩阵性质。
void insertYoungs(int x,int y) {
int lx = x;
int ly = y;
if (x > 1 && matrix[x-1][y] > matrix[lx][ly] ) {
lx = x - 1;
ly = y;
}
if (y > 1 && matrix[x][y-1] > matrix[lx][ly]) {
lx = x;
ly = y - 1;
}
if (lx != x || ly != y) {
swap(matrix[x][y],matrix[lx][ly]);
insertYoungs(lx,ly);
}
}
void insert(int x) {
if (matrix[n][m]!=INF) return;
matrix[n][m]=x;
insertYoungs(n,m);
}
e)在不用其他排序算法帮助的情况下,说明利用 nXn Young氏矩阵对n^2个数排序的运行时间为O(n^3)。
将n^2个数插入矩阵:O(n+n)*O(n^2) = O(n^3)
取出矩阵中的最小元素n^2次:O(n+n)*O(n^2) = O(n^3)
因此排序运行时间为 O(2*n^3) = O(n^3)
f) 给出一个运行时间为O(m+n)的算法,来决定一个给定的数是否存在于一个给定的 mXn Young氏矩阵内。
从(1,m)左上角开始查找c,若小于c,则向下找;若大于c,则向左找。越界时则不存在。
pair<int,int> find(int c) {
int x = 1,y = m;
while (x <= n && y >= 1) {
if (matrix[x][y] == c) return make_pair(x,y);
if (matrix[x][y] < c) x++;
if (matrix[x][y] > c) y--;
}
return make_pair(0,0);
}
Young氏矩阵完整代码:
const int MAXN = 100;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
class CYoungs{
private:
int n,m;
int matrix[MAXN][MAXN];
void extractYoungs(int x,int y) {
int sx = x;
int sy = y;
if (x < n && matrix[x+1][y] < matrix[sx][sy]) {
sx = x + 1;
sy = y;
}
if (y < m && matrix[x][y+1] < matrix[sx][sy]) {
sx = x;
sy = y + 1;
}
if (sx != x || sy != y) {
swap(matrix[x][y],matrix[sx][sy]);
extractYoungs(sx,sy);
}
}
void insertYoungs(int x,int y) {
int lx = x;
int ly = y;
if (x > 1 && matrix[x-1][y] > matrix[lx][ly] ) {
lx = x - 1;
ly = y;
}
if (y > 1 && matrix[x][y-1] > matrix[lx][ly]) {
lx = x;
ly = y - 1;
}
if (lx != x || ly != y) {
swap(matrix[x][y],matrix[lx][ly]);
insertYoungs(lx,ly);
}
}
public:
CYoungs() {}
void init(int a,int b) {
n = a;
m = b;
memset(matrix,INF,sizeof matrix);
}
int extractMin() {
int ret = matrix[1][1];
matrix[1][1] = INF;
extractYoungs(1,1);
return ret;
}
void insert(int x) {
if (matrix[n][m]!=INF) return;
matrix[n][m]=x;
insertYoungs(n,m);
}
pair<int,int> find(int c) {
int x = 1,y = m;
while (x <= n && y >= 1) {
if (matrix[x][y] == c) return make_pair(x,y);
if (matrix[x][y] < c) x++;
if (matrix[x][y] > c) y--;
}
return make_pair(0,0);
}
void showMatrix() {
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++) {
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};