对Spring中MappingSqlQueryWithParameters、SqlQuery等的一些理解
MappingSqlQueryWithParameters、SqlQuery等都是在Spring的org.springframework.jdbc.object包中。从包名object中也可以看出来这里面放的是对象,主要是查询对象。顾名思义,就是将查询这个操作封装成了一个对象,这里面包括查询所使用的sql语句、参数、参数类型、查询结果等。这样这个查询操作对象就是可以重复使用的,下次可以直接使用这个对象,不需要再重新构造sql语句,重新赋值参数,重新查询,重新rowMapper等。
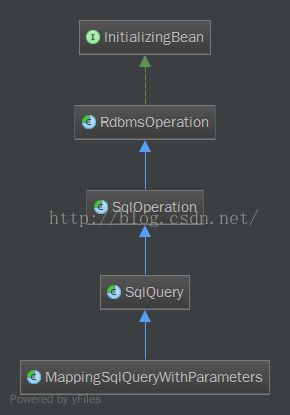
首先看一下类图:
从类图中可以看出MappingSqlQueryWithParameters继承字SqlQuery,SqlQuery继承SqlOperation,SqlOperation继承RdbmsOperation
MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类比较简单,主要是实现了SqlQuery中的
protected RowMapper<T> newRowMapper(Object[] parameters, Map context)虚函数。在该函数中创建了一个实现了RowMapper<T>的类RowMapperImpl的对象并返回。RowMapperImpl是在MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类中定义的内部类。
/**
* Implementation of RowMapper that calls the enclosing
* class's {@code mapRow} method for each row.
*/
protected class RowMapperImpl implements RowMapper<T> {
private final Object[] params;
private final Map context;
/**
* Use an array results. More efficient if we know how many results to expect.
*/
public RowMapperImpl(Object[] parameters, Map context) {
this.params = parameters;
this.context = context;
}
//该类的mapRow方法实现就是调用MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类中的mapRow方法
//因此继承MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类的子类需要实现mapRow方法。
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return MappingSqlQueryWithParameters.this.mapRow(rs, rowNum, this.params, this.context);
}
}
可以看出该类的mapRow方法实现就是调用MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类中的mapRow方法。因此继承MappingSqlQueryWithParameters类的子类只需要实现mapRow方法就好,不需要再实现一个继承RowMapper<T>接口的类,省下了一些代码量,这就是该类相比SqlQuery类的作用。
下面我们来看一下SqlQuery类。该类的作用主要是提供了很多形式的Excute函数和executeByNamedParam函数来分别执行sql语句,包括匿名参数的和命名参数的。
另外在此基础上又提供了各种形式的findObject和findObjectByNamedParam函数来提供对单个对象的查询操作。
这个类里面最终调用的查询函数有两个,分别是:
/**
* Central execution method. All un-named parameter execution goes through this method.
* @param params parameters, similar to JDO query parameters.
* Primitive parameters must be represented by their Object wrapper type.
* The ordering of parameters is significant.
* @param context contextual information passed to the {@code mapRow}
* callback method. The JDBC operation itself doesn't rely on this parameter,
* but it can be useful for creating the objects of the result list.
* @return a List of objects, one per row of the ResultSet. Normally all these
* will be of the same class, although it is possible to use different types.
*/
public List<T> execute(Object[] params, Map context) throws DataAccessException {
//验证传进来的sql参数
validateParameters(params);
//调用newRowMapper函数生成RowMapper<T>具体类的对象
RowMapper<T> rowMapper = newRowMapper(params, context);
//调用相关的JdbcTemplate类的query函数来执行查询
return getJdbcTemplate().query(newPreparedStatementCreator(params), rowMapper);
}
/**
* Central execution method. All named parameter execution goes through this method.
* @param paramMap parameters associated with the name specified while declaring
* the SqlParameters. Primitive parameters must be represented by their Object wrapper
* type. The ordering of parameters is not significant since they are supplied in a
* SqlParameterMap which is an implementation of the Map interface.
* @param context contextual information passed to the {@code mapRow}
* callback method. The JDBC operation itself doesn't rely on this parameter,
* but it can be useful for creating the objects of the result list.
* @return a List of objects, one per row of the ResultSet. Normally all these
* will be of the same class, although it is possible to use different types.
*/
public List<T> executeByNamedParam(Map<String, ?> paramMap, Map context) throws DataAccessException {
//验证传进来的sql参数
validateNamedParameters(paramMap);
//解析sql语句,找到每个占位符和命名参数的位置,对于命名参数记录其在sql语句中的名称以及其起始和终止位置,
//并记录匿名参数以及命名参数的个数,以及占位符的总个数。将所有这些参数解析出来后构造成ParsedSql对象进行保存
//但是合法的sql语句中不允许即出现命名参数占位符和匿名参数占位符。这个会在下面的buildValueArray函数中进行校验
ParsedSql parsedSql = getParsedSql();
//将paramMap封装为MapSqlParameterSource类对象
MapSqlParameterSource paramSource = new MapSqlParameterSource(paramMap);
//将sql语句中的命名参数占位符替换为JDBC占位符?形式。并且如果给的参数值是数组或列表类型的话,就把命名参数展开成所需要数目的?占位符
//详细处理情况可以参考substituteNamedParameters函数
String sqlToUse = NamedParameterUtils.substituteNamedParameters(parsedSql, paramSource);
//将Map形式的参数转换为数组形式的参数
Object[] params = NamedParameterUtils.buildValueArray(parsedSql, paramSource, getDeclaredParameters());
//调用newRowMapper函数生成RowMapper<T>具体类的对象
RowMapper<T> rowMapper = newRowMapper(params, context);
//调用相关的JdbcTemplate类的query函数来执行查询
return getJdbcTemplate().query(newPreparedStatementCreator(sqlToUse, params), rowMapper);
}
只需要理解了这两个函数,SqlQuery类就算是理解了。
在excuteByNameParam函数中调用的getParsedSql函数以及NamedParameterUtils的substituteNamedParameters函数需要深入了解下。设计和处理的都是很巧妙的。
getParsedSql函数本身比较简单,主要调用了NamedParameterUtils的parseSqlStatement函数。那么下面我们就来主要看看NamedParameterUtils的parseSqlStatement还有substituteNamedParameters函数吧。
parseSqlStatement函数如下:
/**
* Parse the SQL statement and locate any placeholders or named parameters.
* Named parameters are substituted for a JDBC placeholder.
* @param sql the SQL statement
* @return the parsed statement, represented as ParsedSql instance
*/
public static ParsedSql parseSqlStatement(final String sql) {
Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null");
Set<String> namedParameters = new HashSet<String>();
String sqlToUse = sql;
List<ParameterHolder> parameterList = new ArrayList<ParameterHolder>();
char[] statement = sql.toCharArray();
int namedParameterCount = 0;
int unnamedParameterCount = 0;
int totalParameterCount = 0;
int escapes = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < statement.length) {
int skipToPosition = i;
//将sql转换成char数据,进行逐个字符的遍历处理
while (i < statement.length) {
//从i位置开始跳过sql语句中的注释和引号,返回跳过后sql语句下个待处理的位置
//如果i开始的位置不是注释或引号的开始,则会直接返回i,因为i就是待处理的位置
//具体查看skipCommentsAndQuotes是如何处理的
skipToPosition = skipCommentsAndQuotes(statement, i);
//表明当前i位置不需要跳过
if (i == skipToPosition) {
break;
}
//直接跳过注释或者引号,到下一个待处理的位置
else {
i = skipToPosition;
}
}
//表明处理到了sql语句的结尾处,已经处理完成
if (i >= statement.length) {
break;
}
char c = statement[i];
if (c == ':' || c == '&') {
//j指向i的下一个字符
int j = i + 1;
//如果是::,是Postgres的关键字,代表的是类型转换操作符,后面不是参数,直接跳过
if (j < statement.length && statement[j] == ':' && c == ':') {
// Postgres-style "::" casting operator - to be skipped.
i = i + 2;
continue;
}
String parameter = null;
if (j < statement.length && c == ':' && statement[j] == '{') {
// :{x} style parameter
while (j < statement.length && !('}' == statement[j])) {
j++;
if (':' == statement[j] || '{' == statement[j]) {
throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException("Parameter name contains invalid character '" +
statement[j] + "' at position " + i + " in statement: " + sql);
}
}
if (j >= statement.length) {
throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException(
"Non-terminated named parameter declaration at position " + i + " in statement: " + sql);
}
if (j - i > 3) {
parameter = sql.substring(i + 2, j);
//将命名参数名称加入namedParameters,并返回当前命名参数的个数
namedParameterCount = addNewNamedParameter(namedParameters, namedParameterCount, parameter);
//将命名参数封装成ParameterHolder对象加入parameterList,包括参数的名称,参数在sqlToUse中的起始和终止位置,
//并返回当前参数的总个数。其中escapes表示遍历到当前位置时statement的转义字符的个数。
//因为要在起始位置和终止位置中减掉其大小。因为在sqlToUse中会过滤掉转义字符
totalParameterCount = addNamedParameter(parameterList, totalParameterCount, escapes, i, j + 1, parameter);
}
j++;
}
else {
//在命名参数内进行遍历,直到命名参数分割符处
while (j < statement.length && !isParameterSeparator(statement[j])) {
j++;
}
if (j - i > 1) {
parameter = sql.substring(i + 1, j);
//将命名参数名称加入namedParameters,并返回当前命名参数的个数
namedParameterCount = addNewNamedParameter(namedParameters, namedParameterCount, parameter);
//将命名参数封装成ParameterHolder对象加入parameterList,并返回当前参数的总个数
totalParameterCount = addNamedParameter(parameterList, totalParameterCount, escapes, i, j, parameter);
}
}
//i跳到分割符处,因为后面还要i++,所以这里要=j-1
i = j - 1;
}
else {
//判断是否转义字符
if (c == '\\') {
int j = i + 1;
if (j < statement.length && statement[j] == ':') {
// this is an escaped : and should be skipped
sqlToUse = sqlToUse.substring(0, i - escapes) + sqlToUse.substring(i - escapes + 1);
escapes++;
i = i + 2;
continue;
}
}
if (c == '?') {
unnamedParameterCount++;
totalParameterCount++;
}
}
i++;
}
//构造ParsedSql对象
ParsedSql parsedSql = new ParsedSql(sqlToUse);
for (ParameterHolder ph : parameterList) {
parsedSql.addNamedParameter(ph.getParameterName(), ph.getStartIndex(), ph.getEndIndex());
}
parsedSql.setNamedParameterCount(namedParameterCount);
parsedSql.setUnnamedParameterCount(unnamedParameterCount);
parsedSql.setTotalParameterCount(totalParameterCount);
return parsedSql;
}这里面用到的skipCommentsAndQuotes函数是用来跳过当前位置开始的注释或者是引号符,然后返回注释或者引号结束的位置。
/**
* Skip over comments and quoted names present in an SQL statement
* @param statement character array containing SQL statement
* @param position current position of statement
* @return next position to process after any comments or quotes are skipped
*/
private static int skipCommentsAndQuotes(char[] statement, int position) {
for (int i = 0; i < START_SKIP.length; i++) {
//判断statement的position位置是不是和START_SKIP定义的一些字符相等,如果不相等,下面直接返回
if (statement[position] == START_SKIP[i].charAt(0)) {
boolean match = true;
for (int j = 1; j < START_SKIP[i].length(); j++) {
if (!(statement[position + j] == START_SKIP[i].charAt(j))) {
match = false;
break;
}
}
if (match) {
int offset = START_SKIP[i].length();
for (int m = position + offset; m < statement.length; m++) {
//注释符或引号要成对出现,所以直接跟STOP_SKIP[i]进行比较
if (statement[m] == STOP_SKIP[i].charAt(0)) {
boolean endMatch = true;
int endPos = m;
for (int n = 1; n < STOP_SKIP[i].length(); n++) {
if (m + n >= statement.length) {
// last comment not closed properly
return statement.length;
}
if (!(statement[m + n] == STOP_SKIP[i].charAt(n))) {
endMatch = false;
break;
}
endPos = m + n;
}
if (endMatch) {
// found character sequence ending comment or quote
return endPos + 1;
}
}
}
// character sequence ending comment or quote not found
return statement.length;
}
}
}
return position;
}另外一个substituteNamedParameters函数如下:
/**
* Parse the SQL statement and locate any placeholders or named parameters. Named
* parameters are substituted for a JDBC placeholder, and any select list is expanded
* to the required number of placeholders. Select lists may contain an array of
* objects, and in that case the placeholders will be grouped and enclosed with
* parentheses. This allows for the use of "expression lists" in the SQL statement
* like: <br /><br />
* {@code select id, name, state from table where (name, age) in (('John', 35), ('Ann', 50))}
* <p>The parameter values passed in are used to determine the number of placeholders to
* be used for a select list. Select lists should be limited to 100 or fewer elements.
* A larger number of elements is not guaranteed to be supported by the database and
* is strictly vendor-dependent.
* @param parsedSql the parsed representation of the SQL statement
* @param paramSource the source for named parameters
* @return the SQL statement with substituted parameters
* @see #parseSqlStatement
*/
public static String substituteNamedParameters(ParsedSql parsedSql, SqlParameterSource paramSource) {
String originalSql = parsedSql.getOriginalSql();
StringBuilder actualSql = new StringBuilder();
List paramNames = parsedSql.getParameterNames();
int lastIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.size(); i++) {
String paramName = (String) paramNames.get(i);
int[] indexes = parsedSql.getParameterIndexes(i);
int startIndex = indexes[0];
int endIndex = indexes[1];
//将originalSql上一个位置到本次命名参数位置之间的字符串加入到actualSql中。
//因为命名参数在下面要替换或者展开为占位符?
actualSql.append(originalSql, lastIndex, startIndex);
if (paramSource != null && paramSource.hasValue(paramName)) {
Object value = paramSource.getValue(paramName);
//获取参数具体的值,因为传过来的命名参数的值有可能是SqlParameterValue对象
if (value instanceof SqlParameterValue) {
value = ((SqlParameterValue) value).getValue();
}
//如果对象是集合,就需要将sql语句的命名参数进行替换为和集合中值个数对应的占位符?
if (value instanceof Collection) {
Iterator entryIter = ((Collection) value).iterator();
int k = 0;
while (entryIter.hasNext()) {
if (k > 0) {
actualSql.append(", ");
}
k++;
Object entryItem = entryIter.next();
//如果集合中的每个值又是个对象数组,说明最终是诸如“(name, age) in (('John', 35), ('Ann', 50))”
//这样的情形,需要在sql语句中将每个集合中的数组元素对应成(?,?,...)这样的形式,每个元组中占位符的个数和Object[]数组的大小相等
//最终整个该命名参数会替换为((?,?,...),(?,?,...),...)的形式,元组的个数和集合大小相等
if (entryItem instanceof Object[]) {
Object[] expressionList = (Object[]) entryItem;
actualSql.append("(");
for (int m = 0; m < expressionList.length; m++) {
if (m > 0) {
actualSql.append(", ");
}
actualSql.append("?");
}
actualSql.append(")");
}
//集合中的每个对象就是单个的对象,那么每个集合中的对象元素就替换为?,
//最终整个该命名参数会替换为(?,?,...)的形式,占位符的个数和集合大小相等
else {
actualSql.append("?");
}
}
}
//参数值不是集合,直接将命名参数替换为?
else {
actualSql.append("?");
}
}
//如果paramSource不包含当前的命名参数,直接将命名参数替换为?
else {
actualSql.append("?");
}
lastIndex = endIndex;
}
actualSql.append(originalSql, lastIndex, originalSql.length());
return actualSql.toString();
}
理解了这些,SqlQuery类也就能够理解了。
SqlQuery又继承自RdbmsOperation类。这个类主要定义了Query Object的一些基本属性和操作方法。
其中validateParameters、validateNamedParameters函数分别被SqlQuery中的execute和executeByNamedParam函数调用,用来验证参数。
在validateParameters、validateNamedParameters这两个函数中,都用到了declaredParameters属性。该属性表示了sql参数的定义,包括参数的名称、类型等。
因此在创建SqlQuery相关对象的时候,应该先赋值declaredParameters属性。然后才能使用excute或者executeByNamedParam等函数。可以调用setTypes、declareParameter、setParameters等函数来赋值declaredParameters属性。