Java 入门 之 字符串与异常处理
本节主要要求掌握,字符串的常见方法(字符串转字符数组、字符串的比较函数、提取索引位置字符、将字符串转换为一个字节数组(???),返回字符串索引、去掉字符串前面的空格、从字符串中提取子串、大小写转换、替换字符串中的子串、判断字符串首末字符)。了解 String 与 StringBuffer、String Builder 的区别。以及,Try、Catch、Throw 用以实现异常捕获的基本格式。
字符串的初始化
String str1 = "abc"; // 更节省空间
String str2 = new String("abc");
字符串转字符数组 String.toCharArray();
字符串的比较函数 String.equals(String);
提取索引位置字符 char String.charAt(int);
将字符串转换为一个字节数组 getBytes(String); ?
返回字符索引 String.indexOf(String); // 有则返回相应位置,没有则返回 -1
去掉字符串前面的空格 trim();
从字符串中提取子串 subString;
大小写转换 toLowerCase,toUpperCase;
替换字符串中的一个字符 replace
判断字符串首末字符 endwith,startwith
注:
String 型数据内容不可更改,StringBuffer、StringBuilder 型数据可以更改。
StringBuilder 在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候,速度快于 StringBuffer ,涉及线程安全的环境,优先使用StringBuffer 。
StringBuffer 的常见方法为 Insert、append。
字符串常见代码示例:
package String_Pack;
public class String_Class {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
StringBuffer myStrB = new StringBuffer();
myStrB.append("Hello");
myStrB.insert(2, "tttiii");
byte[] b = new byte[100];
// System.out.println(getBytes(myStrB));
System.out.println(myStrB.indexOf("iii"));
System.out.println(myStrB);
}
}
异常的初始化和实例化
Exc e = null; // 初始化
e = new Exc(); // 实例化
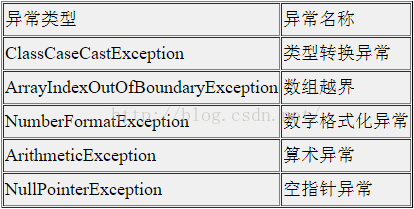
常见的异常
Try/Catch Block 异常格式
try{
; //可能出现异常的代码段
}
Catch(Exception e){
; // 捕获异常
}
finally {
; // 最终一定会执行的代码段
}
Try/Catch Block 代码示例
package Try_Catch_Pack;
class MyExc{
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
}
public class Try_Catch {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int tmp = 0;
MyExc myExc = null;
// myExc = new MyExc(); // 注释掉就是空指针异常了
try {
tmp = myExc.a/myExc.b;
System.out.println(tmp);
}
catch (NullPointerException e1) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.err.println("空指针异常"+e1);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.err.println("算术异常:"+e2);
}
finally{
System.out.println("退出!");
}
}
}
定义方法时使用 throw 关键字声明,表示方法不处理异常,只抛给调用者处理。
例子:
public void tell throw Exception { ... }
如果主方法出现了异常,则交给 JVM 处理。
Try/Catch + Throw Block 异常格式
try{
throw new Exception("实例化异常");
}
Catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
自定义异常
自定义异常,即直接继承 Exception 类即可完成。
代码示例
package Self_Def_Exp;
class myExp extends Exception{
public myExp(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
public class Self_Def_Exp {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
throw new myExp("自定义异常!");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
代码输出:
自定义异常类名+(输出字符串)自定义异常 。