数据结构之哈弗曼编码的(Huffman Coding)加密解密压缩
Huffman树又叫最优二叉树,它的特点是带权路径最短。
Huffman树的一个重要应用是Huffman编码,Huffman编码是长度最短的前缀编码。即给定要传送的字符的权值,根据权值求出Huffman编码,它一定是前缀编码(指任意字符的编码都不是另一个字符编码的前缀),并且在传送过程由字符组成的文字时,编码长度最小。
因此Huffman编码可以对文字进行加密解密还有压缩。加密的工作就是将文字转换为编码,解密工作是将编码转换为文字,如何转换本文不做详解(严蔚敏的《数据结构》书中有代码)。那么如何进行压缩?当字符转变为编码,如果数字编码用char数组存储,则size并未减少。因此我们考虑用位操作。
由于编码完成后,码的形式是0和1组成的串,因此按位存储比原来将节省空间,假设平均编码长度为5位(若平均编码长度超过8位则没有压缩效果了,毕竟char是一个字节,但不可能超过8位,因为根据Huffman编码性质编码长的出现频率低,编码短的出现频率高,后面结果也得到了验证),则64位8个字节可以存储12.8个字符,而char只能存储8个字符。因此文字得到了压缩。
整个程序执行过程如图所示:

其中最难的是writeFile,利用位操作将编码组合在一起并写入文件,这里我们定义一个Unit单元,它包含64位数据,每次编码塞满64位数据,则写入文件。
按照上面的思想,写成的代码如下:
#include <IOSTREAM>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string.h>
#include <FSTREAM>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
const int maxNum = 56; //字符的种类数,只统计 A-Z a-z . , \n 空格 一共56种
int Frequent[maxNum+1] = { 0 }; //字符出现的频率,0号元素不用
typedef unsigned __int64 Dcode;
char mapPrint[maxNum+1];
char *readFileName = "test.txt"; //读的文件名称
char *writeFileName = "test2.dat"; //写的文件名称
typedef struct HCBinary
{
Dcode binaryCode; //哈弗曼编码的二进制表示方法
int length; //编码长度
}HCBinary;
HCBinary code[maxNum+1];
typedef struct Unit
{
Dcode content;
int remain;
}Unit;
Unit tempUnit;
typedef struct
{
int weight;
int parent, lchild, rchild;
int flag;
}HTNode, *HuffmanTree;
void select(HuffmanTree &HT, int dest, int &s1, int &s2)//选择两个最小的元素,获得它们的位置
{
int min1 = 999999; //先让min1,min2为一个足够大的数
int min2 = 999999;
int tempS1 = 0; //用来记录位置
int tempS2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= dest; i++)
{
if (HT[i].flag == 1) //说明已经被用过,则直接跳到下一个
{
continue;
}
else
{
if (HT[i].weight <= min2)
{
if (HT[i].weight <= min1)
{
min2 = min1;
tempS2 = tempS1;
min1 = HT[i].weight;
tempS1 = i;
}
else
{
min2 = HT[i].weight;
tempS2 = i;
}
}
}
}
s1 = tempS1;
s2 = tempS2;
HT[s1].flag = HT[s2].flag = 1;
}
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree &HT, char** &HC, int *w, int n) //哈弗曼编码,其实就是填表的过程
{
int c, f, m, i;
int start;
int s1, s2;
HuffmanTree p;
char * cd;
if (n <= 1)
{
exit(0);
}
m = 2 * n - 1; //根据哈弗曼树的性质,可得总结点数m=2n-1
HT = new HTNode[m + 1]; //0号元素不用
for (p = HT + 1, i = 1; i <= n; i++, ++p, ++w) //先初始化所有叶子节点
{
p->weight = *(w+1); //由于0号元素是不用的所以要加1
p->lchild = 0;
p->rchild = 0;
p->parent = 0;
}
for (; i <= m; ++i, ++p) //初始化其他节点
{
p->weight = 0;
p->lchild = 0;
p->rchild = 0;
p->parent = 0;
}
for (i = n + 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
select(HT, i - 1, s2, s1); //选择两个最小的元素,获得它们的位置
HT[s1].parent = i;
HT[s2].parent = i;
HT[i].lchild = s1;
HT[i].rchild = s2;
HT[i].weight = HT[s1].weight + HT[s2].weight;
}
HC = new char*[n + 1];
cd = new char[n];
cd[n - 1] = '\0';
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
start = n - 1;
for (c = i, f = HT[i].parent; f != 0; c = f, f = HT[f].parent)
{
if (HT[f].lchild == c)
cd[--start] = '0';
else
cd[--start] = '1';
}
HC[i] = new char[n - start];
strcpy_s(HC[i],n-start,&cd[start]);
}
delete cd;
}
void getBinaryCode(char** HC) //获取56种哈弗曼编码的二进制,存储在code中
{
int i;
int j;
Dcode ZERO = 0;
Dcode ONE = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= 56; i++)
{
for (j = 0; HC[i][j] != '\0'; j++)
{
if (HC[i][j] == '1')
{
code[i].binaryCode <<= 1; //必须要先移动再或
code[i].binaryCode = ONE | code[i].binaryCode;
}
if (HC[i][j] == '0')
{
code[i].binaryCode <<= 1;
}
code[i].length++;
}
}
}
void init() //初始化
{
tempUnit.content = 0;
tempUnit.remain = 64;
int i;
for (i = 1; i<=26; i++)
{
mapPrint[i] = 'A' + i-1;
}
for (; i<=52; i++)
{
mapPrint[i] = 'a' + i - 26-1;
}
mapPrint[53] = ',';
mapPrint[54] = '.';
mapPrint[55] = '\n';
mapPrint[56] = ' ';
}
void computeFrequent() //计算字符出现的频率
{
int i;
fstream fp(readFileName, ios::in);
if (!fp)
{
cout << "can't open the file." << endl;
exit(0);
}
char ch;
while (ch=fp.get(), !fp.eof())
{
if (ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z')
{
Frequent[ch - 'A'+1]++;
}
else if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')
{
Frequent[ch - 'a'+ 26+1]++;
}
else if (ch == ',')
{
Frequent[53]++;
}
else if (ch == '.')
{
Frequent[54]++;
}
else if (ch == '\n')
{
Frequent[55]++;
}
else //其他字符都当做空格
{
Frequent[56]++;
}
}
fp.close();
}
void writeUnit(fstream &file,int i)
{
Dcode temp = 0;
if (tempUnit .remain == code[i].length) //若单元中剩余位置大小等于code长度
{
tempUnit .content <<= code[i].length;
tempUnit .content |= code[i].binaryCode;
file.write((char*)(&tempUnit .content), sizeof(tempUnit .content)); //将单元整个写入
tempUnit .remain = 64; //初始化该单元
tempUnit .content = 0;
}
else if (tempUnit .remain>code[i].length) //若单元中剩余位置大小大于code长度,将code放入单元中
{
tempUnit .content <<= code[i].length;
tempUnit .content |= code[i].binaryCode;
tempUnit .remain = tempUnit .remain - code[i].length;
return;
}
else //若单元中剩余位置大小小于code长度,将部分code放入单元,则要先将部分code写入单元,在将单元写入文件后,将其余code写入单元
{
tempUnit .content <<= tempUnit .remain;
temp = code[i].binaryCode >> (code[i].length - tempUnit .remain);
tempUnit .content |= temp;
file.write((char*)(&tempUnit .content), sizeof(tempUnit .content));
tempUnit .content = 0;
temp = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF; //不用数了,16个F
temp<<=(code[i].length - tempUnit .remain);
temp = ~temp;//求反
temp |= code[i].binaryCode;
tempUnit .content |= temp;
tempUnit .remain = 64 - (code[i].length - tempUnit .remain);
}
}
void writeFile()
{
int i;
fstream readFp(readFileName,ios::in);
fstream writeFp(writeFileName, ios::out | ios::binary);
if (!readFp||!writeFp)
{
cout << "can not open the file!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
char ch;
while (ch=readFp.get(),!readFp.eof())
{
if (ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z')
{
writeUnit(writeFp,ch - 'A'+1);
}
else if (ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z')
{
writeUnit(writeFp,ch - 'a' + 26 + 1);
}
else if (ch == ',')
{
writeUnit(writeFp,53);
}
else if (ch == '.')
{
writeUnit(writeFp,54);
}
else if (ch == '\n')
{
writeUnit(writeFp,55);
}
else //空格或其他字符君当作空格
{
writeUnit(writeFp,56);
}
}
if (tempUnit.remain != 64) //说明,还有一个单元没有被写入,将剩余的写入
{
//FIXME:这样会导致多写入0,那么如果有哈弗曼编码位00..,就会出错
tempUnit.content <<= tempUnit.remain;
writeFp.write((char*)(&tempUnit.content), sizeof(tempUnit.content));
}
readFp.close();
writeFp.close();
}
void Decode(HuffmanTree &HT) //解码过程
{
int f = 2 * maxNum - 1;
int c = 0;
int i;
fstream readFp(writeFileName, ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!readFp)
{
cout << "can not open the file." << endl;
exit(0);
}
Dcode one = 0;
Dcode temp = 0;
Dcode temp2 = 0;
one = 0x8000000000000000;
while (!readFp.eof())
{
readFp.read((char*)(&temp2), sizeof(Dcode));
if (readFp.fail())
{
break;
}
for (i = 0; i<64; i++) //根据得到的0,1从根节点往下,直到叶子节点输出相应字符
{
temp = temp2&one;
if (temp == 0)
{
c = HT[f].lchild;
}
else
{
c = HT[f].rchild;
}
f = c;
temp2 <<= 1;
if (HT[c].lchild == 0 && HT[c].rchild == 0)
{
cout << mapPrint[c];
f = 2 * maxNum - 1;
c = 0;
}
}
}
readFp.close();
}
int main()
{
init();
//int n=56;
computeFrequent();
HuffmanTree HT;
char** HC;
HuffmanCoding(HT, HC, Frequent, 56);
cout << "字符" << setw(20) << "出现频率" << setw(25) << "哈弗曼编码" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= maxNum; i++)
{
cout << mapPrint[i] << setw(20) << Frequent[i] << setw(25) << HC[i] << endl;
}
getBinaryCode(HC);
writeFile();
cout << "开始解码:"<<endl;
Decode(HT);
return 0;
} 程序的执行结果如下图:
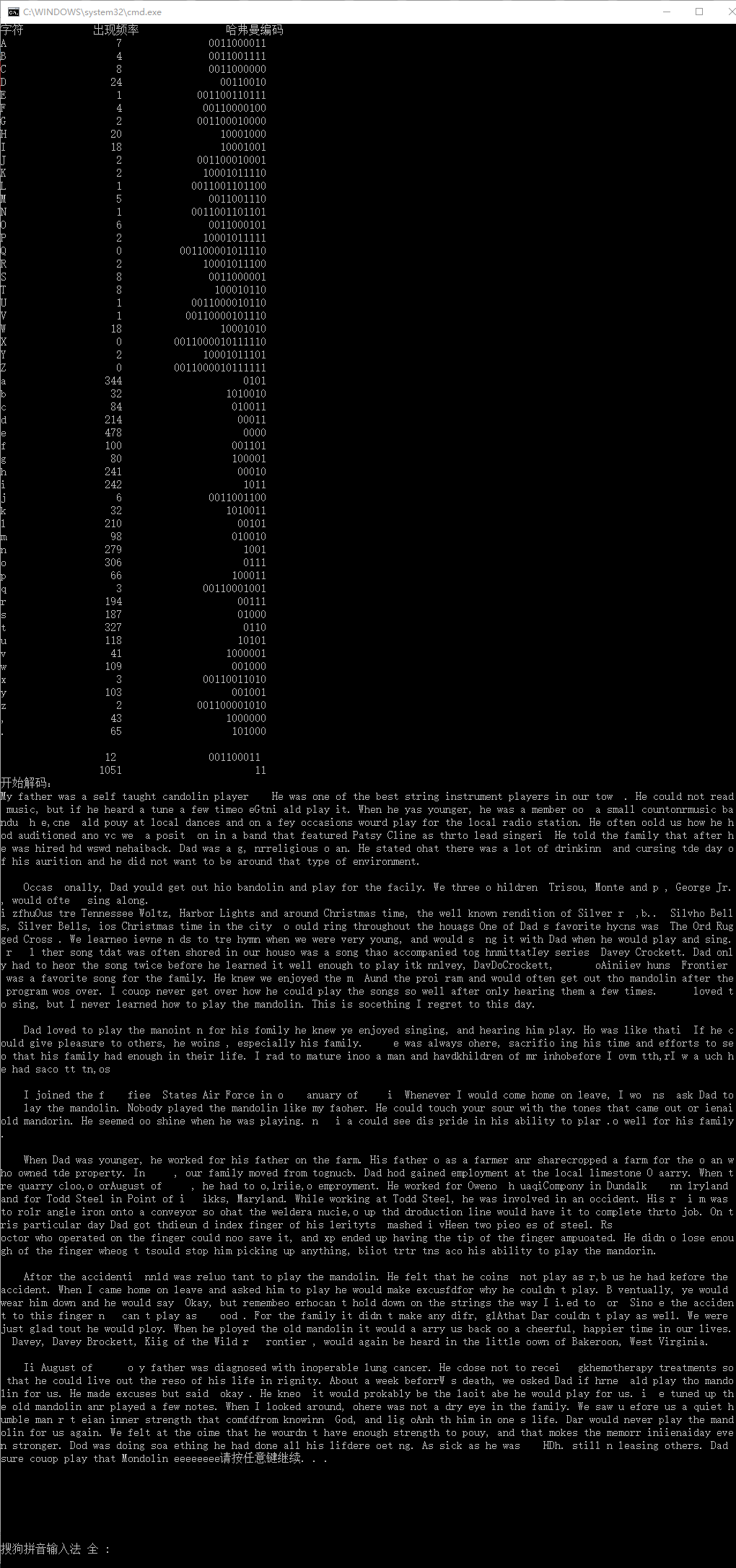
![]()
可以看到整篇文章的确进行了压缩(从6KB->3KB)。这里出现了一个小问题,最后多输出了eeeeeeee。由于我们是以64位为一个单元进行写入的,当最后一个单元不满64时,我们以0进行填充,而e的编码为0000,所以最后一个单元剩余的内容都被解析成了e。
解决方法可以在增加一个字符“截止符”,并和其他字符一起计算Huffman码,当写完最后一个单元的时候将截止符也写入,解码过程中若碰到“截止符”则跳出函数,不再解码。