iOS数据持久化存储 (1)-- Plist 、归档、NSUserDefaults、NSFileManager
iOS数据持久化存储(1)
iOS 数据持久化存储方式有很多,博主今天只跟大家分享以下四种方法:
Plist文件、归档、NSUserDefaults 和NSFileManager
一、Plist文件
在做 iOS 开发时,经常用到plist文件, 那plist文件是什么呢? 它全名是:Property List,属性列表文件,它是一种用来存储串行化后的对象的文件。属性列表文件的扩展名为.plist ,因此通常被称为 plist文件。文件是 json 或 xml格式的。
Plist文件通常用于储存用户设置,也可以用于存储捆绑的信息。
Plist文件可以存放的数据类型:NSString、NSArray、NSDictionary、NSData、NSNumber等。
在开发过程中,有时候需要把程序的一些配置保存下来,或者游戏数据等等。 这时候需要写入 Plist数据。写入的plist文件会生成在对应程序的沙盒目录里。
//字典写入plist文件
NSString * plistPath=@"/Users/lisary/Desktop/test/dic.plist";
NSDictionary * dic=@{@"one":@[@"wwo",@3,@"d"],@"two":@{@"1":@"kk"}};
[dic writeToFile:plistPath atomically:NO];
//读取plist文件内容
NSDictionary * outDic=[NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:plistPath];
NSLog(@"%@",outDic);
//数组写入plist文件
NSArray * array=@[@"one",@{@"1":@[@"w",@"e"]},@8];
NSString * arrayPath=@"/Users/lisary/Desktop/test/array.plist";
[array writeToFile:arrayPath atomically:NO];
//
NSArray * outArray=[NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:arrayPath];
NSLog(@"%@",outArray);
二、归档
归档也叫序列化,是将文件存在硬盘,解档是从硬盘还原。归档和解档的操作正好相反的,但是要注意的是:他们属性的key一定要保持一致。
第1种、使用属性列表进行归档
如果对象是NSString,NSDictionary,NSArray,NSData或者NSNumber,可以使用writeToFile:atomically方法将数据写到文件,注意这种方式是明文
sample:
NSArray *array = @[@"abc",@"123",@23.4];
if ([array writeToFile:@"text.plist" atomically:YES])
{
NSLog(@"success");
}
NSArray *arr2=[NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:@"text.plist"];
NSLog(@"%@",arr2);
第2种、NSKeyedArchiver--对象归档,数据会加密
1)、对于NSArray或者NSDictionary sample code:
/***归档对象****/
NSArray *array = @[@"abc",@"123",@23.4];
NSString *homePath = NSHomeDirectory();
NSString *path = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test.arc"];
// BOOL success = [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:array toFile:path];
BOOL success=[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:array toFile:path];
if (success) {
NSLog(@"archive success");
}
/***解归档****/
NSArray *array2 =[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path];
NSLog(@"%@",array2);
结果:
success
2013-12-28 22:14:25.353 ArchiverDemo1[1206:303] (
abc,
123,
"23.4"
)
2)、如果是其他类型的对象存储到文件,可以利用NSKeyedArchiver类创建带键的档案来完成
NSString *homePath = NSHomeDirectory();
NSString *path = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"archiver2.archiv"];
NSMutableData *data = [NSMutableData data];
NSKeyedArchiver *archiver = [[NSKeyedArchiver alloc] initForWritingWithMutableData:data];
NSArray *array = @[@"jack",@"tom"];
[archiver encodeInt:100 forKey:@"age"];
[archiver encodeObject:array forKey:@"names"];
[archiver finishEncoding];
[archiver release];
BOOL success = [data writeToFile:path atomically:YES];
if (success) {
NSLog(@"archive success");
}
/***解归档对象**/
NSData *data2 = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSKeyedUnarchiver *unArchiver = [[NSKeyedUnarchiver alloc] initForReadingWithData:data2];
int age = [unArchiver decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
NSArray *names = [unArchiver decodeObjectForKey:@"names"];
[unArchiver release];
NSLog(@"age=%d,names=%@",age,names);
对属性编码,归档的时候会调用
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder
//对属性解码,解归档调用
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder
//对属性编码,归档的时候会调用
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder {
[aCoder encodeInt:_age forKey:AGE];
[aCoder encodeObject:_name forKey:NAME];
[aCoder encodeObject:_email forKey:EMAIL];
[aCoder encodeObject:_password forKey:PASSWORD];
}
//对属性解码,解归档调用
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder {
self = [super init];
if (self != nil) {
_age = [aDecoder decodeIntForKey:AGE];
self.name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:NAME];
self.email = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:EMAIL];
self.password = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:PASSWORD];
}
return self;
}
第3种:NSUserDefaults
sample code:
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:authData forKey:@"SinaWeiboAuthData"];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] synchronize];
三、NSUserDefaults
上面也提到了NSUserDefaults,这里需要补充的是,使用NSUserDefaults存数的数据最终保存在了什么地方。
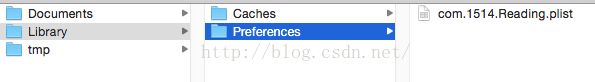
iOS应用产生的内容,如图像、文件、缓存内容等都必须存储在自己的沙盒内。默认情况下,每个沙盒含有3个文件夹:Documents, Library 和 tmp。Library包含Caches、Preferences目录。
Documents:苹果建议将程序创建产生的文件以及应用浏览产生的文件数据保存在该目录下,iTunes备份和恢复的时候会包括此目录
Library:存储程序的默认设置或其它状态信息;
Library/Caches:存放缓存文件,保存应用的持久化数据,用于应用升级或者应用关闭后的数据保存,不会被itunes同步,所以为了减少同步的时间,可以考虑将一些比较大的文件而又不需要备份的文件放到这个目录下。
tmp:提供一个即时创建临时文件的地方,但不需要持久化,在应用关闭后,该目录下的数据将删除,也可能系统在程序不运行的时候清除。
而使用NSUserDefaults存数的数据最终保存在 Library --> Preferences --> xxx.plist.
四、NSFileManager
NSFileManager中包含了用来查询单词库目录、创建、重命名、删除目录以及获取/设置文件属性的方法(可读性,可编写性等等)。
每个程序都会有它自己的沙盒,通过它你可以阅读/编写文件。写入沙盒的文件在程序的进程中将会保持稳定,即便实在程序更新的情况下。
如下所示,你可以在沙盒中定位文件目录:
NSError *error; // 创建文件管理器 NSFileManager *fileMgr = [NSFileManagerdefaultManager]; //指向文件目录 NSString *documentsDirectory= [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents"]; //创建一个目录 [[NSFileManager defaultManager] createDirectoryAtPath: [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/myFolder", NSHomeDirectory()] attributes:nil]; //创建一个文件 NSString *filePath= [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"file1.txt"]; NSString *str= @"iPhoneDeveloper Tips\nhttp://iPhoneDevelopTips,com"; [str writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error]; NSLog(@"Documentsdirectory: %@", [fileMgr contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:documentsDirectoryerror:&error]);
//1.文件重命名 //通过移动该文件对文件重命名 NSString *filePath2= [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"file2.txt"]; if ([fileMgr moveItemAtPath:filePath toPath:filePath2 error:&error] != YES) NSLog(@"Unable to move file: %@", [error localizedDescription]); NSLog(@"Documentsdirectory: %@", [fileMgr contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:documentsDirectoryerror:&error]); //2.删除一个文件 if ([fileMgr removeItemAtPath:filePath2 error:&error] != YES) NSLog(@"Unable to delete file: %@", [error localizedDescription]); NSLog(@"Documentsdirectory: %@", [fileMgr contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:documentsDirectoryerror:&error]);
一旦文件被删除了,正如你所预料的那样,文件目录就会被自动清空。
相关代码:
//1.遍历某个文件夹路径下的目录
//创建到一个NSFileManager单例对象
NSFileManager * defaultManager=[NSFileManager defaultManager];
//浅度遍历
NSString * onePath=@"/Users/lisary/Desktop/test";
NSError * error=nil;
NSArray * files=[defaultManager contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:onePath error:&error];
//深度遍历
NSArray * files1=[defaultManager subpathsOfDirectoryAtPath:onePath error:&error];
//2.NSFileHandle 读写文件( setValueForKey//写文件)
NSString * path=@"/Users/zhang_guang_yang/Desktop/test/test.txt";
//以只读的形式打开文件
NSFileHandle * fh=[NSFileHandle fileHandleForReadingAtPath:path];
//以读写方式开打<span style="font-size: 13.3333px; font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">开文件</span>
NSFileHandle * fh1=[NSFileHandle fileHandleForUpdatingAtPath:path];
//以只写方式打<span style="font-size: 13.3333px; font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">开文件</span>
NSFileHandle * fh2=[NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:path];
//写操作
[fh1 seekToFileOffset:0];
NSString * contents=@"content";
NSData * cData=[contents dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[fh1 writeData:cData];
//同步磁盘文件
[fh1 synchronizeFile];
//关闭文件
[fh closeFile];
[fh1 closeFile];
[fh2 closeFile];