轮廓的查找、表达、绘制、特性及匹配 c#版
作者:王先荣
前言
轮廓是构成任何一个形状的边界或外形线。前面讲了如何根据色彩及色彩的分布(直方图对比和模板匹配)来进行匹配,现在我们来看看如何利用物体的轮廓。包括以下内容:轮廓的查找、表达方式、组织方式、绘制、特性、匹配。
查找轮廓
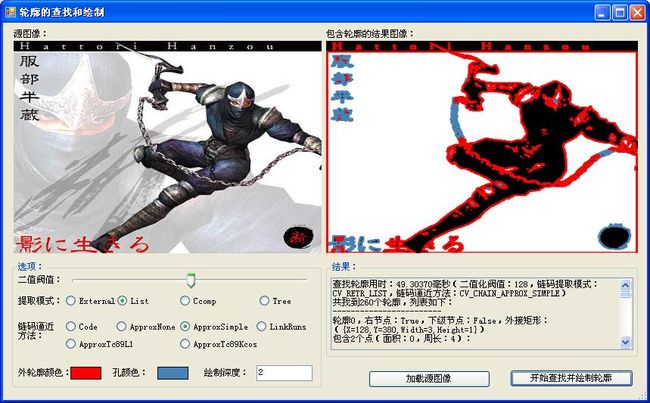
首先我们面对的问题是如何在图像中找到轮廓,OpenCv(EmguCv)为我们做了很多工作,我们的任务只是调用现成的函数而已。Image<TColor,TDepth>类的FindContours方法可以很方便的查找轮廓,不过在查找之前,我们需要将彩色图像转换成灰度图像,然后再将灰度图像转换成二值图像。代码如下所示:
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ -->Image<Bgr, Byte> imageSource = new Image<Bgr, byte>(sourceImageFileName); //获取源图像 Image<Gray, Byte> imageGray = imageSource.Convert<Gray, Byte>(); //将源图像转换成灰度图像 int thresholdValue = tbThreshold.Value; //用于二值化的阀值 Image<Gray, Byte> imageThreshold = imageGray.ThresholdBinary(new Gray(thresholdValue), new Gray(255d)); //对灰度图像二值化 Contour<Point> contour=imageThreshold.FindContours();
轮廓的表达方式
使用上面的代码可以得到图像的默认轮廓,但是轮廓在电脑中是如何表达的呢?在OpenCv(EmguCv)中提供了两类表达轮廓的方式:顶点的序列、Freeman链码。
1.顶点的序列
用多个顶点(或各点间的线段)来表达轮廓。假设要表达一个从(0,0)到(2,2)的矩形,
(1)如果用点来表示,那么依次存储的可能是:(0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(0,2),(0,1);
(2)如果用点间的线段来表达轮廓,那么依次存储的可能是:(0,0),(2,0),(2,2),(0,2)。
以下代码可以用来获取轮廓上的点:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
-->for (int i = 0; i < contour.Total; i++)
sbContour.AppendFormat("{0},", contour[i]);
2.Freeman链码
Freeman链码需要一个起点,以及从起点出发的一系列位移。每个位移有8个方向,从0~7分别指向从正北开始的8个方向。假设要用Freeman链码表达从(0,0)到(2,2)的矩形,可能的表示方法是:起点(0,0),方向链2,2,4,4,6,6,0,0。
EmguCv对Freeman链码的支持很少,我们需要做一系列的工作才能在.net中使用Freeman链码:
(1)获取Freeman链码
<!-- Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ -->//查找用Freeman链码表示的轮廓 Image<Gray,Byte> imageTemp=imageThreshold.Copy(); IntPtr storage = CvInvoke.cvCreateMemStorage(0); IntPtr ptrFirstChain = IntPtr.Zero; int total = CvInvoke.cvFindContours(imageTemp.Ptr, storage, ref ptrFirstChain, sizeof(MCvChain), mode, CHAIN_APPROX_METHOD.CV_CHAIN_CODE, new Point(0, 0));
(2)遍历Freeman链码上的点
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
-->//初始化Freeman链码读取
[DllImport("cv200.dll")]
public static extern void cvStartReadChainPoints(IntPtr ptrChain,IntPtr ptrReader);
//读取Freeman链码的点
[DllImport("cv200.dll")]
public static extern Point cvReadChainPoint(IntPtr ptrReader);
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.StructLayoutAttribute(System.Runtime.InteropServices.LayoutKind.Sequential, CharSet = System.Runtime.InteropServices.CharSet.Ansi)]
//定义链码读取结构
public struct MCvChainPtReader
{
//seqReader
public MCvSeqReader seqReader;
/// char
public byte code;
/// POINT->tagPOINT
public Point pt;
/// char[16]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.MarshalAsAttribute(System.Runtime.InteropServices.UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 16)]
public string deltas;
}
//将链码指针转换成结构
MCvChain chain=(MCvChain)Marshal.PtrToStructure(ptrChain,typeof(MCvChain));
//定义存放链码上点的列表
List<Point> pointList = new List<Point>(chain.total);
//链码读取结构
MCvChainPtReader chainReader = new MCvChainPtReader();
IntPtr ptrReader = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(sizeof(MCvSeqReader) + sizeof(byte) + sizeof(Point) + 16 * sizeof(byte));
Marshal.StructureToPtr(chainReader, ptrReader, false);
//开始读取链码
cvStartReadChainPoints(ptrChain, ptrReader);
int i = 0;
while (ptrReader != IntPtr.Zero && i < chain.total)
{
//依次读取链码上的每个点
Point p = cvReadChainPoint(ptrReader);
if (ptrReader == IntPtr.Zero)
break;
else
{
pointList.Add(p);
sbChain.AppendFormat("{0},", p);
i++;
}
}
imageResult.DrawPolyline(pointList.ToArray(), true, new Bgr(lblExternalColor.BackColor), 2);
需要注意的是:cvReadChainPoint函数似乎永远不会满足循环终止的条件,即ptrReader永远不会被置为null,这跟《学习OpenCv》和参考上不一致;我们需要用chain.total来辅助终止循环,读取了所有的点之后就可以罢手了。
轮廓之间的组织方式
在查找到轮廓之后,不同轮廓是怎么组织的呢?根据不同的选择,它们可能是:(1)列表;(2)双层结构;(3)树型结构。
从纵向上来看,列表只有一层,双层结构有一或者两层,树型结构可能有一层或者多层。
如果要遍历所有的轮廓,可以使用递归的方式,代码如下:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //遍历轮廓,并生成遍历结果
private void TravelContour(Contour<Point> contour,ref int total,ref StringBuilder sbContour)
{
if (contour != null)
{
sbContour.Append("------------------------\r\n");
sbContour.AppendFormat("轮廓{0},右节点:{1},下级节点:{2},外接矩形:({3})\r\n", total, contour.HNext != null, contour.VNext != null, contour.BoundingRectangle);
sbContour.AppendFormat("包含{0}个点(面积:{1},周长:{2}):\r\n", contour.Total, contour.Area, contour.Perimeter);
for (int i = 0; i < contour.Total; i++)
sbContour.AppendFormat("{0},", contour[i]);
sbContour.Append("\r\n");
total++;
if (contour.HNext != null)
TravelContour(contour.HNext, ref total, ref sbContour);
if (contour.VNext != null)
TravelContour(contour.VNext, ref total, ref sbContour);
}
}
轮廓的绘制
轮廓的绘制比较简单,用上面提到的方法取得轮廓的所有点,然后把这些点连接成一个多边形即可。
当然,对于用顶点序列表示的轮廓,用Image<TColor,TDepth>.Draw方法或者cvDrawContours函数可以很方便的绘制出轮廓。我发现,如果将参数max_level设置成2,可以绘制出所有的轮廓。
绘制轮廓的代码如下:
<!-- Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ -->Image<Bgr, Byte> imageResult = imageThreshold.Convert<Bgr, Byte>(); //结果图像 int maxLevel = 0; //绘制的轮廓深度 int.TryParse(txtMaxLevel.Text, out maxLevel); imageResult.Draw(contour, new Bgr(lblExternalColor.BackColor), new Bgr(lblHoleColor.BackColor), maxLevel, 2);
轮廓的特性 轮廓的特性有很多,下面一一介绍。
1.轮廓的多边形逼近
轮廓的多边形逼近指的是:使用多边形来近似表示一个轮廓。
多边形逼近的目的是为了减少轮廓的顶点数目。
多边形逼近的结果依然是一个轮廓,只是这个轮廓相对要粗旷一些。
可以使用Contour<Point>.ApproxPoly方法或者cvApproxyPoly函数来对轮廓进行多边形逼近,示例代码如下:
<!-- Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ -->contour = firstContour.ApproxPoly(double.Parse(txtApproxParameter.Text), 2, new MemStorage());
2.轮廓的关键点 轮廓的关键点是:轮廓上包含曲线信息比较多的点。关键点是轮廓顶点的子集。 可以使用cvFindDominantPoints函数来获取轮廓上的关键点,该函数返回的结果一个包含 关键点在轮廓顶点中索引 的序列。再次强调:是索引,不是具体的点。如果要得到关键点的具体坐标,可以用索引到轮廓上去找。 以下代码演示了如何获取轮廓上的关键点:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //得到关键点信息
private void GetDominantPointsInfo(Contour<Point> contour, ref StringBuilder sbContour, ref Image<Bgr, Byte> imageResult, double parameter1, double parameter2, double parameter3, double parameter4, Bgr dominantPointColor)
{
if (contour.Total > 2)
{
MemStorage storage = new MemStorage();
try
{
IntPtr ptrSeq = cvFindDominantPoints(contour.Ptr, storage.Ptr, (int)CV_DOMINANT.CV_DOMINANT_IPAN, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, parameter4);
Seq<int> seq = new Seq<int>(ptrSeq, storage);
sbContour.AppendFormat("{0}个关键点:\r\n", seq.Total);
for (int i = 0; i < seq.Total; i++)
{
int idx = seq[i]; //关键点序列中存储的数据 是 关键点在轮廓中所处位置的索引
Point p = contour[idx]; //得到关键点的坐标
sbContour.AppendFormat("{0}({1},{2}),", idx, p.X, p.Y);
imageResult.Draw(new CircleF(new PointF(p.X, p.Y), 3), dominantPointColor, -1);
}
sbContour.Append("\r\n");
}
catch (CvException ex)
{
sbContour.AppendFormat("在获取关键点时发生异常,错误描述:{0},错误源:{1},错误堆栈:{2}\r\n错误文件:{3},函数名:{4},行:{5},错误内部描述:{6}\r\n", ex.Message, ex.Source, ex.StackTrace, ex.FileName, ex.FunctionName, ex.Line, ex.ErrorStr);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
sbContour.AppendFormat("在获取关键点时发生异常,错误描述:{0},错误源:{1},错误堆栈:{2}\r\n", e.Message, e.Source, e.StackTrace);
}
finally
{
storage.Dispose();
}
}
}
3.轮廓的周长和面积
轮廓的周长可以用Contour<Point>.Perimeter属性或者cvArcLength函数来获取。
轮廓的面积可以用Contour<Point>.Area属性或者cvContourArea函数来获取。
4.轮廓的边界框
有三种常见的边界框:矩形、圆形、椭圆。
(1)矩形:在图像处理系统中提供了一种叫Rectangle的矩形,不过它只能表达边垂直或水平的特例;OpenCv中还有一种叫Box的矩形,它跟数学上的矩形一致,只要4个角是直角即可。
如果要获取轮廓的Rectangle,可以使用Contour<Point>.BoundingRectangle属性或者cvBoundingRect函数。
如果要获取轮廓的Box,可以使用Contour<Point>.GetMinAreaRect方法或者cvMinAreaRect2函数。
(2)圆形
如果要获取轮廓的圆形边界框,可以使用cvMinEnclosingCircle函数。
(3)椭圆
如果要获取轮廓的椭圆边界框,可以使用cvFitEllipse2函数。
下列代码演示了如何获取轮廓的各种边界框:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //得到边界框信息
private void GetEdgeInfo(Contour<Point> contour, string edge, ref StringBuilder sbContour, ref Image<Bgr, Byte> imageResult, Bgr edgeColor)
{
if (edge == "Rect")
//矩形
imageResult.Draw(contour.BoundingRectangle, edgeColor, 2);
else if (edge == "MinAreaRect")
{
//最小矩形
MCvBox2D box = CvInvoke.cvMinAreaRect2(contour.Ptr, IntPtr.Zero);
PointF[] points = box.GetVertices();
Point[] ps = new Point[points.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < points.Length; i++)
ps[i] = new Point((int)points[i].X, (int)points[i].Y);
imageResult.DrawPolyline(ps, true, edgeColor, 2);
}
else if (edge == "Circle")
{
//圆形
PointF center;
float radius;
CvInvoke.cvMinEnclosingCircle(contour.Ptr, out center, out radius);
imageResult.Draw(new CircleF(center, radius), edgeColor, 2);
}
else
{
//椭圆
if (contour.Total >= 6)
{
MCvBox2D box = CvInvoke.cvFitEllipse2(contour.Ptr);
imageResult.Draw(new Ellipse(box), edgeColor, 2);
}
else
sbContour.Append("轮廓点数小于6,不能创建外围椭圆。\r\n");
}
}
5.轮廓的矩
我们可以使用Contour<Point>.GetMoments方法或者cvMoments函数方便的得到轮廓的矩集,然后再相应的方法或函数获取各种矩。
特定的矩:MCvMoments.GetSpatialMoment方法、cvGetSpatialMoment函数
中心矩:MCvMoments.GetCentralMoment方法、cvGetCentralMoment函数
归一化中心矩:MCvMoments.GetNormalizedCentralMoment方法、cvGetNormalizedCentralMoment函数
Hu矩:MCvMoments.GetHuMoment方法、McvHuMoments.hu1~hu7字段、cvGetHuMoments函数
以下代码演示了如何获取轮廓的矩:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //得到各种矩的信息
private void GetMomentsInfo(Contour<Point> contour, ref StringBuilder sbContour)
{
//矩
MCvMoments moments = contour.GetMoments();
//遍历各种情况下的矩、中心矩及归一化矩,必须满足条件:xOrder>=0; yOrder>=0; xOrder+yOrder<=3;
for (int xOrder = 0; xOrder <= 3; xOrder++)
{
for (int yOrder = 0; yOrder <= 3; yOrder++)
{
if (xOrder + yOrder <= 3)
{
double spatialMoment = moments.GetSpatialMoment(xOrder, yOrder);
double centralMoment = moments.GetCentralMoment(xOrder, yOrder);
double normalizedCentralMoment = moments.GetNormalizedCentralMoment(xOrder, yOrder);
sbContour.AppendFormat("矩(xOrder:{0},yOrder:{1}),矩:{2:F09},中心矩:{3:F09},归一化矩:{4:F09}\r\n", xOrder, yOrder, spatialMoment, centralMoment, normalizedCentralMoment);
}
}
}
//Hu矩
MCvHuMoments huMonents = moments.GetHuMoment();
sbContour.AppendFormat("Hu矩 h1:{0:F09},h2:{1:F09},h3:{2:F09},h4:{3:F09},h5:{4:F09},h6:{5:F09},h7:{6:F09}\r\n", huMonents.hu1, huMonents.hu2, huMonents.hu3, huMonents.hu4, huMonents.hu5, huMonents.hu6, huMonents.hu7);
}
6.轮廓的轮廓树
轮廓树用来描述某个特定轮廓的内部特征。注意:轮廓树跟轮廓是一一对应的关系;轮廓树不用于描述多个轮廓之间的层次关系。
可以用函数cvCreateContourTree来构造轮廓树。
<!-- Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ -->IntPtr ptrTree1 = CvInvoke.cvCreateContourTree(contour1.Ptr, new MemStorage().Ptr, thresholdOfCreate);
7.轮廓的凸包和凸缺陷 轮廓的凸包和凸缺陷用于描述物体的外形。凸包和凸缺陷很容易获得,不过我目前不知道它们到底怎么使用。 如果要判断轮廓是否是凸的,可以用Contour<Point>.Convex属性和cvCheckContourConvexity函数。 如果要获取轮廓的凸包,可以用Contour<Point>.GetConvexHull方法或者cvConvexHull2函数,返回的是包含顶点的序列。 如果要获取轮廓的凸缺陷,可以用Contour<Point>.GetConvexityDefacts方法或者cvConvexityDefects函数。 注意:EmguCv将缺陷的单词拼写错了,defect才是缺陷。 以下代码演示了如何获取轮廓的凸包及凸缺陷:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //得到凸包及缺陷信息
private void GetConvexInfo(Contour<Point> contour,ref StringBuilder sbContour,ref Image<Bgr,Byte> imageResult)
{
if (!contour.Convex) //判断轮廓是否为凸
{
//凸包
Seq<Point> convexHull = contour.GetConvexHull(ORIENTATION.CV_CLOCKWISE);
//缺陷
Seq<MCvConvexityDefect> defects = contour.GetConvexityDefacts(new MemStorage(), ORIENTATION.CV_CLOCKWISE);
//显示信息
sbContour.AppendFormat("轮廓的凸包有{0}个点,依次为:", convexHull.Total);
Point[] points = new Point[convexHull.Total];
for (int i = 0; i < convexHull.Total; i++)
{
Point p = convexHull[i];
points[i] = p;
sbContour.AppendFormat("{0},", p);
}
sbContour.Append("\r\n");
imageResult.DrawPolyline(points, true, new Bgr(lblConvexColor.BackColor), 2);
MCvConvexityDefect defect;
sbContour.AppendFormat("轮廓有{0}个缺陷,依次为:\r\n", defects.Total);
for (int i = 0; i < defects.Total; i++)
{
defect = defects[i];
sbContour.AppendFormat("缺陷:{0},起点:{1},终点:{2},最深的点:{3},深度:{4}\r\n", i, defect.StartPoint, defect.EndPoint, defect.DepthPoint, defect.Depth);
}
}
else
sbContour.Append("轮廓是凸的,凸包和轮廓一样。\r\n");
}
8.轮廓的成对几何直方图
成对几何直方图的资料比较少,我是这么理解的。
(1)轮廓保存的是一系列的顶点,轮廓是由一系列线段组成的多边形。对于看起来光滑的轮廓(例如圆),只是线段条数比较多,线段长度比较短而已。实际上,电脑中显示的任何曲线都由线段组成。
(2)每两条线段之间都有一定的关系,包括它们(或者它们的延长线)之间的夹角,两条线段的夹角范围是:(0,180)。
(3)每两条线段上的点之间还有距离关系,包括最短(小)距离、最远(大)距离,以及平均距离。最大距离我用了一个偷懒的计算方法,我把轮廓外界矩形的对角线长度看作了最大距离。
(4)成对几何直方图所用的统计数据包括了夹角和距离。
可以用函数cvCalcPGH来计算轮廓的成对几何直方图,示例代码如下:
<!-- Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware) http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/ --> //生成成对几何直方图 Rectangle rect1 = contour1.BoundingRectangle; float maxDist1 = (float)Math.Sqrt(rect1.Width * rect1.Width + rect1.Height * rect1.Height); //轮廓的最大距离:这里使用轮廓矩形边界框的对角线长度 int[] bins1 = new int[] { 60, 20 }; RangeF[] ranges1 = new RangeF[] { new RangeF(0f, 180f), new RangeF(0f, maxDist1) }; //直方图第0维为角度,范围在(0,180),第2维为轮廓两条边缘线段的距离 DenseHistogram hist1 = new DenseHistogram(bins1, ranges1); CvInvoke.cvCalcPGH(contour1.Ptr, hist1.Ptr);
轮廓的匹配
如果要比较两个物体,可供选择的特征很多。如果要判断某个人的性别,可以根据他(她)头发的长短来判断,这很直观,在长发男稀有的年代准确率也很高。也可以根据这个人尿尿的射程来判断,如果射程大于0.50米,则是男性。总之,方法很多,不一而足。
我们在上文中得到了轮廓的这么多特征,它们也可以用于进行匹配。典型的轮廓匹配方法有:Hu矩匹配、轮廓树匹配、成对几何直方图匹配。
1.Hu矩匹配
轮廓的Hu矩对包括缩放、旋转和镜像映射在内的变化具有不变性。Contour<Point>.MatchShapes方法和cvMatchShapes函数可以很方便的实现对2个轮廓间的匹配。
2.轮廓树匹配
用树的形式比较两个轮廓。cvMatchContourTrees函数实现了轮廓树的对比。
3.成对几何直方图匹配
在得到轮廓的成对几何直方图之后,可以使用直方图对比的方法来进行匹配。如果您和我一样忘记了直方图的对比方式,可以看看我写的另一篇文章《颜色直方图的计算、显示、处理、对比及反向投影(How to Use Histogram? Calculate, Show, Process, Compare and BackProject)》。
各种轮廓匹配的示例代码如下:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> //开始匹配
private void btnStartMatch_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//准备轮廓(这里只比较最外围的轮廓)
Image<Bgr, Byte> image1 = new Image<Bgr, byte>((Bitmap)pbImage1.Image);
Image<Bgr, Byte> image2 = new Image<Bgr, byte>((Bitmap)pbImage2.Image);
Image<Gray, Byte> imageGray1 = image1.Convert<Gray, Byte>();
Image<Gray, Byte> imageGray2 = image2.Convert<Gray, Byte>();
Image<Gray, Byte> imageThreshold1 = imageGray1.ThresholdBinaryInv(new Gray(128d), new Gray(255d));
Image<Gray, Byte> imageThreshold2 = imageGray2.ThresholdBinaryInv(new Gray(128d), new Gray(255d));
Contour<Point> contour1 = imageThreshold1.FindContours(CHAIN_APPROX_METHOD.CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, RETR_TYPE.CV_RETR_EXTERNAL);
Contour<Point> contour2 = imageThreshold2.FindContours(CHAIN_APPROX_METHOD.CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, RETR_TYPE.CV_RETR_EXTERNAL);
/*if (contour1.Perimeter / 50 > 2 && contour2.Perimeter / 50 > 2)
{
contour1 = contour1.ApproxPoly(contour1.Perimeter / 50, 2, new MemStorage()); //对轮廓进行多边形逼近(参数设为轮廓周长的1/50)
contour2 = contour2.ApproxPoly(contour2.Perimeter / 50, 2, new MemStorage());
}*/
//进行匹配
string result = "";
if (rbHuMoments.Checked)
result = MatchShapes(contour1, contour2); //Hu矩匹配
else if (rbContourTree.Checked)
result = MatchContourTrees(contour1, contour2); //轮廓树匹配
else if (rbPGH.Checked)
result = MatchPghHist(contour1, contour2); //成对几何直方图匹配
txtResult.Text += result;
}
//Hu矩匹配
private string MatchShapes(Contour<Point> contour1, Contour<Point> contour2)
{
//匹配方法
CONTOURS_MATCH_TYPE matchType = rbHuI1.Checked ? CONTOURS_MATCH_TYPE.CV_CONTOUR_MATCH_I1 : (rbHuI2.Checked ? CONTOURS_MATCH_TYPE.CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I2 : CONTOURS_MATCH_TYPE.CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I3);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
//匹配
double matchValue = contour1.MatchShapes(contour2, matchType);
sw.Stop();
double time = sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds;
return string.Format("Hu矩匹配({0:G}),结果:{1:F05},用时:{2:F05}毫秒\r\n", matchType, matchValue, time);
}
//轮廓树匹配
private string MatchContourTrees(Contour<Point> contour1, Contour<Point> contour2)
{
//生成轮廓树
double thresholdOfCreate = double.Parse(txtThresholdOfCreateContourTrees.Text); //生成轮廓树的阀值
IntPtr ptrTree1 = CvInvoke.cvCreateContourTree(contour1.Ptr, new MemStorage().Ptr, thresholdOfCreate);
IntPtr ptrTree2 = CvInvoke.cvCreateContourTree(contour2.Ptr, new MemStorage().Ptr, thresholdOfCreate);
//匹配
double thresholdOfMatch = double.Parse(txtThresholdOfMatchContourTrees.Text); //比较轮廓树的阀值
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
double matchValue = CvInvoke.cvMatchContourTrees(ptrTree1, ptrTree2, MATCH_CONTOUR_TREE_METHOD.CONTOUR_TREES_MATCH_I1, thresholdOfMatch);
sw.Stop();
double time = sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds;
return string.Format("轮廓树匹配(生成轮廓树的阀值:{0},比较轮廓树的阀值:{1}),结果:{2:F05},用时:{3:F05}毫秒\r\n", thresholdOfCreate, thresholdOfMatch, matchValue, time);
}
//成对几何直方图匹配
private string MatchPghHist(Contour<Point> contour1, Contour<Point> contour2)
{
//生成成对几何直方图
Rectangle rect1 = contour1.BoundingRectangle;
float maxDist1 = (float)Math.Sqrt(rect1.Width * rect1.Width + rect1.Height * rect1.Height); //轮廓的最大距离:这里使用轮廓矩形边界框的对角线长度
int[] bins1 = new int[] { 60, 20 };
RangeF[] ranges1 = new RangeF[] { new RangeF(0f, 180f), new RangeF(0f, maxDist1) }; //直方图第0维为角度,范围在(0,180),第2维为轮廓两条边缘线段的距离
DenseHistogram hist1 = new DenseHistogram(bins1, ranges1);
CvInvoke.cvCalcPGH(contour1.Ptr, hist1.Ptr);
Rectangle rect2 = contour2.BoundingRectangle;
float maxDist2 = (float)Math.Sqrt(rect2.Width * rect2.Width + rect2.Height * rect2.Height);
int[] bins2 = new int[] { 60, 20 };
RangeF[] ranges2 = new RangeF[] { new RangeF(0f, 180f), new RangeF(0f, maxDist2) };
DenseHistogram hist2 = new DenseHistogram(bins2, ranges2);
CvInvoke.cvCalcPGH(contour2.Ptr, hist2.Ptr);
//匹配
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
double compareResult;
HISTOGRAM_COMP_METHOD compareMethod = rbHistCorrel.Checked ? HISTOGRAM_COMP_METHOD.CV_COMP_CORREL : (rbHistChisqr.Checked ? HISTOGRAM_COMP_METHOD.CV_COMP_CHISQR : (rbHistIntersect.Checked ? HISTOGRAM_COMP_METHOD.CV_COMP_INTERSECT : HISTOGRAM_COMP_METHOD.CV_COMP_BHATTACHARYYA));
if (rbHistEmd.Checked)
{
//EMD
//将直方图转换成矩阵
Matrix<Single> matrix1 = FormProcessHist.ConvertDenseHistogramToMatrix(hist1);
Matrix<Single> matrix2 = FormProcessHist.ConvertDenseHistogramToMatrix(hist2);
compareResult = CvInvoke.cvCalcEMD2(matrix1.Ptr, matrix2.Ptr, DIST_TYPE.CV_DIST_L2, null, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero);
matrix1.Dispose();
matrix2.Dispose();
}
else
{
//直方图对比方式
hist1.Normalize(1d);
hist2.Normalize(1d);
compareResult = CvInvoke.cvCompareHist(hist1.Ptr, hist2.Ptr, compareMethod);
}
sw.Stop();
double time = sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds;
return string.Format("成对几何直方图匹配(匹配方式:{0}),结果:{1:F05},用时:{2:F05}毫秒\r\n", rbHistEmd.Checked ? "EMD" : compareMethod.ToString("G"), compareResult, time);
}
通过以上代码,可以计算出两个轮廓对比的值,但是这些值具体代表什么意义呢?实际上,我目前还不清楚,需要进行大量的试验才行。