hibernate中一种可替代联合主键的设计模式
有如下设计:
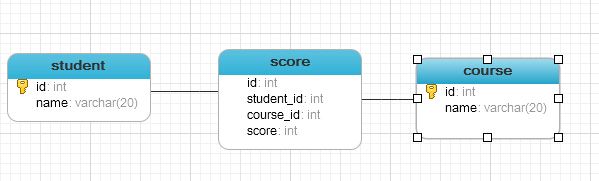
存在这样的表结构 学生表、课程表和分数表。
我们可以这样设计,一个学生对应多门课程,一门课程对应多个学生,他们之间是多对多的关系。我们可以建立一个中间表来关联他们,而此时恰巧有一个分数表来帮我充当这2个表的中间表的关系。
我们来分析一下,分数和学生,课程之间是这样的对应关系。一个具体的分数是某个学生、某门课程下的分数,是通过唯一的学生id和唯一的课程id来标识的。
所以,我们可以在score表上设置联合主键(student_id 和course_id),但是联合主键有其不必要的复杂性,我们完全可以通过以下方式,来方便他的设计。
我们在score表中设计一个主键id,在设计一个外键student_id 和course_id.关系图如下
建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `student` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(20) default NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 PACK_KEYS=0;
CREATE TABLE `course` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(20) default NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 PACK_KEYS=0;
CREATE TABLE `score` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `student_id` int(11) default NULL, `course_id` int(11) default NULL, `score` int(3) default NULL, KEY `student_id` (`student_id`), KEY `course_id` (`course_id`), CONSTRAINT `score_fk2` FOREIGN KEY (`course_id`) REFERENCES `course` (`id`), CONSTRAINT `score_fk1` FOREIGN KEY (`student_id`) REFERENCES `student` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 PACK_KEYS=0;
对应的类文件语句如下:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Student entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "student", catalog = "hibernate")
public class Student implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set<Score> scores = new HashSet<Score>(0);
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Student() {
}
/** minimal constructor */
public Student(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
/** full constructor */
public Student(Integer id, String name, Set<Score> scores) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.scores = scores;
}
// Property accessors
@Id
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "name", length = 20)
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "student")
public Set<Score> getScores() {
return this.scores;
}
public void setScores(Set<Score> scores) {
this.scores = scores;
}
}
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Course entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "course", catalog = "hibernate")
public class Course implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set<Score> scores = new HashSet<Score>(0);
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Course() {
}
/** minimal constructor */
public Course(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
/** full constructor */
public Course(Integer id, String name, Set<Score> scores) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.scores = scores;
}
// Property accessors
@Id
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "name", length = 20)
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "course")
public Set<Score> getScores() {
return this.scores;
}
public void setScores(Set<Score> scores) {
this.scores = scores;
}
}
import javax.persistence.AttributeOverride;
import javax.persistence.AttributeOverrides;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.EmbeddedId;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Score entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "score", catalog = "hibernate")
public class Score implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private ScoreId id;
private Course course;
private Student student;
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Score() {
}
/** minimal constructor */
public Score(ScoreId id) {
this.id = id;
}
/** full constructor */
public Score(ScoreId id, Course course, Student student) {
this.id = id;
this.course = course;
this.student = student;
}
// Property accessors
@EmbeddedId
@AttributeOverrides({ @AttributeOverride(name = "id", column = @Column(name = "id", nullable = false)), @AttributeOverride(name = "studentId", column = @Column(name = "student_id")), @AttributeOverride(name = "courseId", column = @Column(name = "course_id")), @AttributeOverride(name = "score", column = @Column(name = "score")) })
public ScoreId getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(ScoreId id) {
this.id = id;
}
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "course_id", insertable = false, updatable = false)
public Course getCourse() {
return this.course;
}
public void setCourse(Course course) {
this.course = course;
}
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "student_id", insertable = false, updatable = false)
public Student getStudent() {
return this.student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
}