Android-自定义view之无所不能的path
自定义view之无所不能的path
UI给我了五张图片,我感觉太浪费了,自定义view完全可以做而且适配起来更加的方便
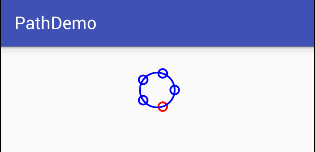
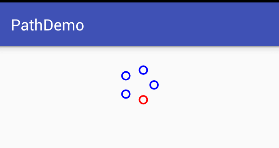
最终实现效果
需要知道技术点
在实现这个过程之前,我们需要了解path的一系列的原理(如果你了解path的用法直接跳过)
PathMeasure(是一个用来测量Path的类,主要有以下方法)
- setPath、 isClosed 和 getLength
这三个方法都如字面意思一样,非常简单,这里就简单是叙述一下,不再过多讲解。
setPath 是 PathMeasure 与 Path 关联的重要方法,效果和 构造函数 中两个参数的作用是一样的。
isClosed 用于判断 Path 是否闭合,但是如果你在关联 Path 的时候设置 forceClosed 为 true 的话,这个方法的返回值则一定为true。
getLength 用于获取 Path 的总长度
- getSegment
//返回值(boolean) 判断截取是否成功 true 表示截取成功,结果存入dst中,false 截取失败,不会改变dst中内容
//startD 开始截取位置距离 Path 起点的长度 取值范围: 0 <= startD < stopD <= Path总长度
//stopD 结束截取位置距离 Path 起点的长度 取值范围: 0 <= startD < stopD <= Path总长度
//dst 截取的 Path 将会添加到 dst 中 注意: 是添加,而不是替换
//startWithMoveTo 起始点是否使用 moveTo 用于保证截取的 Path 第一个点位置不变
//如果 startD、stopD 的数值不在取值范围 [0, getLength] 内,或者 startD == stopD 则返回值为 false,不会改变 dst 内容。
//如果在安卓4.4或者之前的版本,在默认开启硬件加速的情况下,更改 dst 的内容后可能绘制会出现问题,请关闭硬件加速或者给 dst 添加一个单个操作,例如: dst.rLineTo(0, 0)
boolean getSegment (float startD, float stopD, Path dst, boolean startWithMoveTo)
- getPosTan
/*这个方法是用于得到路径上某一长度的位置以及该位置的正切值: 参数 作用 备注 返回值(boolean) 判断获取是否成功 true表示成功,数据会存入 pos 和 tan 中, false 表示失败,pos 和 tan 不会改变 distance 距离 Path 起点的长度 取值范围: 0 <= distance <= getLength pos 该点的坐标值 坐标值: (x==[0], y==[1]) tan 该点的正切值 正切值: (x==[0], y==[1]) */
boolean getPosTan (float distance, float[] pos, float[] tan)- getMatrix
这个方法是用于得到路径上某一长度的位置以及该位置的正切值的矩阵:
/* 返回值(boolean) 判断获取是否成功 true表示成功,数据会存入matrix中,false 失败,matrix内容不会改变 distance 距离 Path 起点的长度 取值范围: 0 <= distance <= getLength matrix 根据 falgs 封装好的matrix 会根据 flags 的设置而存入不同的内容 flags 规定哪些内容会存入到matrix中 可选择 POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG(位置) ANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG(正切) */
boolean getMatrix (float distance, Matrix matrix, int flags)实现
通过path得到一个园,然后将圆分割5份
Path pathCircle = new Path();
pathCircle.addCircle(with / 2, hight / 2, hight / 2 - pading - radius, Path.Direction.CW);通过PathMeasure的getPosTan方法得到等分点在圆上的坐标,然后判断当前的状态,给选中的状态圆不同的颜色值
float[] position = new float[2];
for (int index = 0; index < 5; index++) {
if (currentPosition == index) {
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
} else {
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
}
float allLength = pathMeasure.getLength();
distance = (allLength / 5) * (index + 1);
pathMeasure.getPosTan(distance, position, tan);
canvas.drawCircle(position[0], position[1], radius, paint);
}实现完以后我们发现问题,圆的位置每个圆环的位置和效果图不是一样的,那是为什么呢?
其实在path添加大圆的时候我们只能控制path路径的轨迹方向,并不能指定其开始位置,而且现在我们写死了很多变量:颜色,圆环数等*
解决办法:那我们用arc(圆弧)去画指定其实位置;通过指定要属性实现动态添加属性;
优化
画出圆弧,指定开始位置为正上方及时-90°
Path pathCircle = new Path();
RectF rectF = new RectF(pading + radius, pading + radius, with - pading - radius, hight - pading - radius);
pathCircle.arcTo(rectF, -90, 359);
通过自定义属性动态指定参数
// 宽
private int with;
// 高
private int hight;
// 间距
private int pading;
// 小圆环半径
private int radius;
// 圆环宽度
private int paintWith;
// 圆环数
private int pie;
// 当前选中圆环
private int currentPosition;
// 正常颜色
private int normalColor;
// 选中颜色
private int clickColor;
// 画笔
private Paint paint;
public ProgressCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView);
pading = a.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_pading, 0);
radius = a.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_radius, 10);
paintWith = a.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_paintWith, 4);
pie = a.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_pie, 5);
currentPosition = a.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_currentPosition, 0);
normalColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_normalColor, Color.BLUE);
clickColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.ProgressCircleOldView_clickColor, Color.RED);
a.recycle();
initPaint();
}对应的xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="ProgressCircleOldView">
<!--间距-->
<attr name="pading" format="dimension"/>
<!--小圆环半径-->
<attr name="radius" format="dimension"/>
<!--圆环宽度-->
<attr name="paintWith" format="dimension"/>
<!--圆环数-->
<attr name="pie" format="integer"/>
<!--当前选中圆环-->
<attr name="currentPosition" format="integer"/>
<!--正常颜色-->
<attr name="normalColor" format="color"/>
<!-- 选中颜色-->
<attr name="clickColor" format="color"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>得到坐标点,画出圆
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
float[] position = new float[2];
float[] tan = new float[2];
float distance;
Path pathCircle = new Path();
RectF rectF = new RectF(pading + radius, pading + radius, with - pading - radius, hight - pading - radius);
pathCircle.arcTo(rectF, -90, 359);
PathMeasure pathMeasure = new PathMeasure(pathCircle, false);
for (int index = 0; index < pie; index++) {
if (currentPosition == index) {
paint.setColor(clickColor);
} else {
paint.setColor(normalColor);
}
float allLength = pathMeasure.getLength();
distance = (allLength / pie) * (index);
pathMeasure.getPosTan(distance, position, tan);
canvas.drawCircle(position[0], position[1], radius, paint);
}
}
到这里我们基本已经完成了这个需求了但是估计大家还是没有讲PathMeasure没有很好的理解,所以就有了下面的扩展
扩展
上面的效果在很多场景中我们都能用到,不如加载、经度显示等;其实通过动画我们也可以实现,但是自定义view也是可以的,而且它的效率更高,
灵活性更加好,功能也可以做的更加强大,主要是你实现起来还很简单哦!
其实上面的矩形和圆轨迹都是走的同样的逻辑,不过是path添加了不同的图形,所以你可以自由发挥哦,所以就拿上面的圆形进度为例子来讲解了
path给定一个图形
Path path = new Path();
path.addCircle(600, 400, 100, Path.Direction.CCW);
通过比getPosTan得到位置和偏移量
// 按照比例获取
progress = progress < 1 ? progress + 0.0005 : 0;
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
paint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
measure.getPosTan((int) (measure.getLength() * progress), position, tan);
通过得到的点坐标画出箭头
Path path1 = new Path();
path1.moveTo(position[0] - 20, position[1] + 20);
path1.lineTo(position[0], position[1]);
path1.lineTo(position[0] + 20, position[1] + 20);
// 是否闭合,闭合就是三角形了
path1.close();通过tan得到箭头的偏移量
Path path2 = new Path();
float degrees = (float) (Math.atan2(tan[1], tan[0]) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
matrix.setRotate(degrees + 90, position[0], position[1]);
path2.addPath(path1, matrix);通过getSegment得到进度上截取的弧线,链接箭头
// 进度线
measure.getSegment(-1000, (int) (measure.getLength() * progress), path2, true);
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawPath(path2, paint);
最后不断的刷新界面重画
/** * 绘制panth上每一个点的位置 * 带箭头的进度框 * * @param canvas */
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
private void PaintMatr(Canvas canvas) {
paint.setStrokeWidth(10);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
Path path = new Path();
path.addCircle(600, 400, 100, Path.Direction.CCW);
PathMeasure measure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
// 按照比例获取
progress = progress < 1 ? progress + 0.0005 : 0;
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
paint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
measure.getPosTan((int) (measure.getLength() * progress), position, tan);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
// 箭头
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
Path path1 = new Path();
path1.moveTo(position[0] - 20, position[1] + 20);
path1.lineTo(position[0], position[1]);
path1.lineTo(position[0] + 20, position[1] + 20);
// 是否闭合,闭合就是三角形了
path1.close();
Path path2 = new Path();
float degrees = (float) (Math.atan2(tan[1], tan[0]) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
matrix.setRotate(degrees + 90, position[0], position[1]);
path2.addPath(path1, matrix);
// 进度线
measure.getSegment(-1000, (int) (measure.getLength() * progress), path2, true);
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawPath(path2, paint);
invalidate();
}到这里你也是path就完事了 no no no其实path还能结合SVG( 是一种矢量图,内部用的是 xml 格式化存储方式存储这操作和数据,你完全可以将 SVG 看作是 Path 的各项操作简化书写后的存储格式)
svg和path的结合
SVG 是一种矢量图,内部用的是 xml 格式化存储方式存储这操作和数据,你完全可以将 SVG 看作是 Path 的各项操作简化书写后的存储格式
他们结合能创找出很多意想不到的东西,有兴趣的同学可以自己去研究一下
SVG解析成Path的解析库
github开源库
项目源码地址*戳我
带卡片滑动结合地址*戳我