Android内存优化:ArrayMap
通常我们在使用key-value存储数据时,随手就会打出HashMap的代码,当数据量较小时,还可以,当数量比较多的时候,如果是PC机上,也还说得过去,但是如果使用设备是手机等移动设备,这是就要慎重了。因为手机的内存非常宝贵,不像PC那样不计后果的使用,内存使用不当很容易就会引起OOM的问题。那Android开发团队,也为我们找到了HashMap的替代品ArrayMap。
官方对ArrayMap也有说明:它不是一个适应大数据的数据结构,相比传统的HashMap速度要慢,因为查找方法是二分法,并且当你删除或者添加数据时,会对空间重新调整,在使用大量数据时,效率并不明显,低于50%。
所以ArrayMap是牺牲了时间换区空间。在写手机app时,适时的使用ArrayMap,会给内存使用带来可观的提升。
那HashMap和ArrayMap到底不同在哪呢,个人总结有以下方面:
1、存储方式不同。
HashMap内部有一个HashMapEntry<K, V>[]对象,每一个键值对都存储在这个对象里,当使用put方法添加键值对时,就会new一个HashMapEntry对象
@Override public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
int hash = secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
//先查找有没有对应的key值,如果有,就改写value,并返回改写前的value值:oldValue
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
if (size++ > threshold) {
//扩容,双倍
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}
//创建对象存储键值对
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
table[index] = new HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hash, table[index]);
}
ArrayMap的存储中没有Entry这个东西,他是由两个数组来维护的
int[] mHashes;
Object[] mArray;
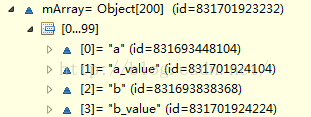
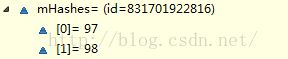
mHashes数组中保存的是每一项的HashCode值,mArray中就是键值对,每两个元素代表一个键值对,前面保存key,后面的保存value,我们看看下面代码的结果
arraymap = new HashMap<String, String>();
a.put("a", "a_value");
a.put("b", "b_value");执行上面代码后,arraymap中的存储是这样的
是不是能清楚地看到ArrayMap的存储了,这种存储在put代码中如下
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
2、添加数据时扩容时的处理不一样
先来看看HashMap
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
doubleCapacity进行双倍扩容,它的代码中有这么一句话
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] newTable = makeTable(newCapacity);最终,这个newTable将作为扩容后的新对象返回,那么makeTable做了什么呢,如下:
private HashMapEntry<K, V>[] makeTable(int newCapacity) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") HashMapEntry<K, V>[] newTable
= (HashMapEntry<K, V>[]) new HashMapEntry[newCapacity];
table = newTable;
threshold = (newCapacity >> 1) + (newCapacity >> 2); // 3/4 capacity
return newTable;
}
我们清楚地看到,这里进行了new操作,重新创建对象,开销很大。
那么ArrayMap呢,看看吧
//如果容量不够
if (mSize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = mSize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize+(mSize>>1))
: (mSize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
//分配数组
allocArrays(n);
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + mSize + " to 0");
//特别注意这,是copy,而不是new,效率提升
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
//释放无用空间,收缩数组
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
ArrayMap用的是copy数据,所以效率相对要高。
3、ArrayMap提供了数组收缩的功能,在clear或remove后,会重新收缩数组,是否空间
4、ArrayMap采用二分法查找(见 android.support.v4.util.ContainerHelpers中的binarySearch方法)