【物联网(IoT)开发】使用 Arduino 和 Python在 Bluemix 上开发一个 IoT 应用程序之控制LED灯开关
上篇“【物联网(IoT)开发】Arduino 入门 Hello World(LED闪烁)”只是通过将一段程序烧录到Arduino开发板上控制LEC闪烁,没有任何连网动作,也就是说断开网络提供电源依然还可以工作。本文将介绍如何开发一个应用程序,以便使用适用于物联网 (Internet of Things, IoT) 的技术。我们的应用程序通过串口收集数据,将其存储在一个 Web 服务器上,然后在网页上实时显式结果,并可以在网页上控制LED的开关。
构建一个类似的应用程序的前提条件
对于第 1 部分,您需要:
一个 Bluemix 帐户,您还没有? 点击这里注册,已经有,点击这里登录;
对 HTML(超文本标记语言)的基本了解;
对CSS (层叠样式表)的基本了解;
对JavaScript(一种直译式脚本语言)的基本了解;
对Python 编程的基本了解;
对MySQL数据库及管理工具的基本了解;
对SQL语言的基本了解;
对于第 2 部分,您需要:一个 Arduino NANO 或其他兼容 Arduino 的主板
可选:Arduino Ethernet Shield
一个LED灯(发光二极管)
一些母母跳线(female-female jumper wire)
Python 2.7.x
我提供了所有必要代码,但对这些技术的基本了解有助于您理解有关的细节,但不是必须如此。
也无需拥有使用 Arduino 或任何其他类型的微型控制器主板的经验。
步骤 1. 创建您的Python应用程序
- 1、在 Bluemix 用户界面中,转至“仪表板”。
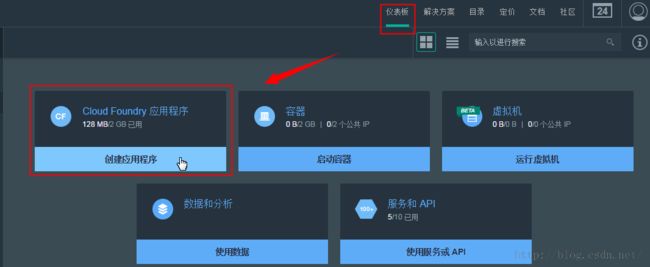
- 2、单击创建应用程序。

- 3、单击 Web,然后按照指导经验来选择入门模板,指定名称以及选择编码方式。

- 输入应用程序名称
- 应用程序名称是唯一的,接下来要通过它做为二级域名来访问你的应用!
- 点击完成之后,需要等待一会儿,然后可以看到下图的界面

- 这时就可以访问你刚刚创建的应用了。如下图:
步骤 2. 添加数据库服务
- 可以通过单击 Bluemix 用户界面中应用程序“概述”上的添加服务或 API,将服务添加到应用程序中。也可以使用 cf 命令行界面。请参阅处理应用程序的可用选项。
- 在服务列表中选择数据库(ClearDB MySQL Database)

- 您可以指定服务的名称,也可以使用默认的;

如果你事先已经创建了数据库服务,也可以直接绑定:
获取服务信息
进入自己的应用程序》概述页面,找到已经添加的服务,点击“显示凭证”,可以查看服务的具体信息:
拿到凭证,我们就可以通过MySQL的客户端管理工具来连接管理数据库了:
1、连接数据库
如果你还没有安装Navicat for MySQL管理工具,请参考:MySQL学习(二)图形界面管理工具Navicat for MySQL安装和使用
2、创建数据表
注意:我们是没有权限创建数据库的,只能用默认创建好的;
只需要创建一张非常简单的表,来保存状态和控制命令
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `led_status`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `led_status`;
CREATE TABLE `led_status` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`status` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`control` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of led_status
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `led_status` VALUES ('1', '0', '0');
步骤 3. 准备开发环境及硬件环境
有关开发环境搭建的细节,请参考下面的文章:
《Python入门》Windows 7下Python Web开发环境搭建笔记
《Python入门》第一个Python Web程序——简单的Web服务器
《Python入门》Linux 下 Python Web开发环境搭建笔记【物联网(IoT)开发】Arduino IDE(集成开发环境)下载及安装
【物联网(IoT)开发】Arduino NANO,UNO 驱动安装
本文使用的硬件环境非常简单,请参考:
【物联网(IoT)开发】Arduino 入门 Hello World(LED闪烁)
步骤 4.编写代码
1、下载初始Hello World示例代码
你可以下载入门示例参考,也可以完全自己写!
进入您的应用程序,点击左侧的开始编码,在右侧点击“下载入门模板代码”。
也可以通过添加Git来下载代码。
2、使其在本地运行
1、将下载的入门模板代码解压到一个目录,打开命令行窗口,切换到这个目录下
可以看出代码结构是很简单的;
2、执行命令:python server.py
3、在浏览器中访问:http://localhost:8000/
3、编写代码
本文涉及到三部分代码
1)、烧录到Arduino开发板上的代码,用于接收串口的命令控制LED状态,并实时输出LED的状态
String blink_flag = "1";
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin 13 as an output.
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
String rx_buffer;
rx_buffer=Serial.readString();
if (rx_buffer.length() == 1){
blink_flag = rx_buffer;
}
if (blink_flag.compareTo("1")){
digitalWrite(2, LOW); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
//delay(1000); // wait for a second
}else{
digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
//delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(blink_flag);
delay(100);
}
2)、运行在本地计算机用于收集LED状态上传到Bluemix云平台上和从Bluemix云平台上接收命令并将控制命令通过串口发送给Anduino
文件:sendSamples.py
import serial, httplib
import os #Python的标准库中的os模块包含普遍的操作系统功能
import re #引入正则表达式对象
import urllib #用于对URL进行编解码
import sys #提供了许多函数和变量来处理 Python 运行时环境的不同部分.
# 调试函数,用于输出对象的属性及属性值
def getAllAttrs(obj):
strAttrs = ''
for o in dir(obj):
strAttrs = strAttrs + o + ' := ' + str(getattr(obj, o)) + '\r\n'
return strAttrs;
# Sends the reading to the webserver using a POST request
def sendRequest(reading):
headers = {"Content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
conn = httplib.HTTPConnection("localhost:8000")
conn.request("POST", "/ledsave", "id="+reading, headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
print response.status, response.reason
data = response.read()
conn.close()
# Creates an array of numbers based on the string
# If there's any problem on the string, returns (_,False)
def parseNumbers(s):
numbers = []
success = True
s = s.split(" ")
for number in s:
try:
numbers.append(int(number))
except ValueError:
success = False
return (numbers, success)
## Establish connection to the serial port that your arduino
## is connected to.
serialPorts=['COM5','COM7']
for port in serialPorts:
try:
print "Trying to connect to Arduino on",port
device = serial.Serial(port, 9600, timeout=2)
break
except:
print "Failed to connect on",port
exit(1)
print "Arduino is ready!"
numberOfSamples = 0
currentAcceleration = [0,0,0]
auxString = ""
# Keep reading everything sent by the Arduino
while 1:
c = ''
auxString = ''
# Verifies if there's something to read in the buffer
while device.inWaiting():
# Reads a character
c=device.read()
# If its not the end of the line yet, keep appending chars to the string
if(c != '\r' and c != '\n' and c != ','):
auxString = str(c)
# If we reached the end of the line, parse the numbers read
elif (c == ','):
auxString = ""
if auxString != '':
print auxString
sendRequest(auxString)
surl = 'http://localhost:8000/ledcontrol'
resContent = ''
try:
response = urllib.urlopen(surl)
resContent = response.read()
if (auxString != resContent):
device.write(resContent)
except:
info = sys.exc_info()
resContent = getAllAttrs(info[0]) + getAllAttrs(info[1]) # 获取异常的详细信息
print resContent
device.close()
3)、运行在Bluemix上,实时显示LED状态提供控制界面
Web服务:server.py
# coding=utf-8
import os # Python的标准库中的os模块包含普遍的操作系统功能
import re # 引入正则表达式对象
import MySQLdb
import sys # 提供了许多函数和变量来处理 Python 运行时环境的不同部分.
import cgi
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
# 调试函数,用于输出对象的属性及属性值
def getAllAttrs(obj):
strAttrs = ''
for o in dir(obj):
strAttrs = strAttrs + o + ' := ' + str(getattr(obj, o)) + '<br />'
return strAttrs;
try:
from SimpleHTTPServer import SimpleHTTPRequestHandler as Handler
from SocketServer import TCPServer as Server
except ImportError:
from http.server import SimpleHTTPRequestHandler as Handler
from http.server import HTTPServer as Server
# 自定义处理程序,用于处理HTTP请求
class TransHTTPHandler(Handler):
# 处理GET请求
def do_GET(self):
# 页面输出模板字符串
templateStr = '<html><head><title>pytrans</title></head><body>%s</body></html>'
# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象
pattern = re.compile(r'/ledinfo')
# 使用Pattern匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
match = pattern.match(self.path)
if match:
resContent = ''
try:
# conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='us-cdbr-iron-east-04.cleardb.net',user='b7de64a29b1f49',passwd='64701d27',db='ad_fd4a422d117d69b',port=3306)
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost', user='root', passwd='root', db='pyiotled', port=3306)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SET NAMES UTF8')
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM led_status')
rows = cur.fetchall()
rowIdx = 0
for row in rows:
rowIdx += 1;
resContent += row[1]
cur.close()
conn.close()
except MySQLdb.Error, e:
print "Mysql Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1])
self.protocal_version = 'HTTP/1.1' # 设置协议版本
self.send_response(200) # 设置响应状态码
self.send_header("Content-type", "text/html") # 设置响应头
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(resContent) # 输出响应内容
else:
pattern = re.compile(r'/ledcontrol')
# 使用Pattern匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
match = pattern.match(self.path)
if match:
resContent = ''
try:
# conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='us-cdbr-iron-east-04.cleardb.net',user='b7de64a29b1f49',passwd='64701d27',db='ad_fd4a422d117d69b',port=3306)
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost', user='root', passwd='root', db='pyiotled', port=3306)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SET NAMES UTF8')
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM led_status')
rows = cur.fetchall()
rowIdx = 0
for row in rows:
rowIdx += 1;
resContent += row[2]
cur.close()
conn.close()
except MySQLdb.Error, e:
print "Mysql Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1])
self.protocal_version = 'HTTP/1.1' # 设置协议版本
self.send_response(200) # 设置响应状态码
self.send_header("Content-type", "text/html") # 设置响应头
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(resContent) # 输出响应内容
else:
# /voteinfo 之外的请求,交给底层去处理
if self.path == "":
self.path = '/index.html'
fStatic = self.send_head()
if fStatic:
try:
self.copyfile(fStatic, self.wfile)
finally:
fStatic.close()
# 处理POST请求
def do_POST(self):
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象
pattern = re.compile(r'/ledsave')
# 使用Pattern匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
match = pattern.match(self.path)
datas = self.rfile.read(int(self.headers['content-length']))
print datas
ids = datas.split("=")
id = 0
if len(ids) == 2:
id = int(ids[1])
print id
if match:
resContent = ''
try:
# conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='us-cdbr-iron-east-04.cleardb.net',user='b7de64a29b1f49',passwd='64701d27',db='ad_fd4a422d117d69b',port=3306)
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost', user='root', passwd='root', db='pyiotled', port=3306)
cur = conn.cursor()
print str(id)
cur.execute("UPDATE led_status SET `status`='" + str(id) + "' WHERE id=1")
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
except MySQLdb.Error, e:
print "Mysql Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1])
self.protocal_version = 'HTTP/1.1' # 设置协议版本
self.send_response(200) # 设置响应状态码
self.send_header("Content-type", "text/html") # 设置响应头
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(resContent) # 输出响应内容
else:
# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象
pattern = re.compile(r'/ledcontrol')
# 使用Pattern匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
match = pattern.match(self.path)
#datas = self.rfile.read(int(self.headers['content-length']))
print datas
ids = datas.split("=")
id = 0
if len(ids) == 2:
id = int(ids[1])
print id
if match:
resContent = ''
try:
print 'a'
# conn=MySQLdb.connect(host='us-cdbr-iron-east-04.cleardb.net',user='b7de64a29b1f49',passwd='64701d27',db='ad_fd4a422d117d69b',port=3306)
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost', user='root', passwd='root', db='pyiotled', port=3306)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("UPDATE led_status SET `control`='" + str(id) + "' WHERE id=1")
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
except MySQLdb.Error, e:
print "Mysql Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1])
self.protocal_version = 'HTTP/1.1' # 设置协议版本
self.send_response(200) # 设置响应状态码
self.send_header("Content-type", "text/html") # 设置响应头
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(resContent) # 输出响应内容
else:
# /ledsave 之外的请求,返回错误信息
self.protocal_version = 'HTTP/1.1' # 设置协议版本
self.send_response(500) # 设置响应状态码
self.send_header("Content-type", "text/html") # 设置响应头
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write("非法请求") # 输出响应内容
# Read port selected by the cloud for our application
PORT = int(os.getenv('PORT', 8000))
# #改变当前目录到 static 目录
os.chdir('static')
httpd = Server(("", PORT), TransHTTPHandler)
try:
print("Start serving at port %i" % PORT)
httpd.serve_forever() ##设置一直监听并接收请求
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass # 按Ctrl+C退出服务
httpd.server_close()
前端页面:index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>【物联网(IoT)开发】使用 Arduino 和 Python在 Bluemix 上开发一个 IoT 应用程序之控制LED灯开关 - 无知人生,记录点滴</title>
<style>
body {
margin:0; padding:0;
}
a{
text-decoration:none;
color:black;
}
div.div_id {
float:left;
clear:left;
width:60px;
height:27px;
border-bottom:solid 1px #808080;
text-align:center;
line-height:27px;
}
div.div_item {
float:left;
clear:none;
width:260px;
height:27px;
border-bottom:solid 1px #808080;
text-align:left;
line-height:27px;
}
div.div_radio {
float:left;
clear:none;
width:60px;
height:27px;
border-bottom:solid 1px #808080;
text-align:left;
line-height:27px;
display:none;
}
div.div_num {
float:left;
clear:right;
width:260px;
height:27px;
border-bottom:solid 1px #808080;
text-align:left;
line-height:27px;
display:none;
}
</style>
<script src="jquery.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<SCRIPT language=javascript>
$(document).ready(function(){
setInterval(loadLedStatus,1000);
});
//通过AJAX加载LED状态信息
function loadLedStatus(){
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "ledinfo",
dataType:"html",
async: false,
success: function(data){
if (data == "1"){
$("#divctnr").html("<img src=\"led1.png\" />");
$("#button1").hide();
$("#button2").show();
}else{
$("#divctnr").html("<img src=\"led0.png\" />");
$("#button2").hide();
$("#button1").show();
}
console.log(data);
},
error: function(data){
console.log(data);
console.log( "加载LED信息失败: " + data.responseText );
}
});
}
//通过AJAX调用后台保存LED信息
function execControl(status){
$("#button1").hide();
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "ledcontrol",
dataType:"html",
data: {"id":status},
success: function(data){
console.log(data);
},
error: function(data){
console.log(data);
console.log( "命令发送失败: " + data.responseText );
}
});
}
</SCRIPT>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<a href="http://blog.csdn.net/testcs_dn" target="_blank" title="无知人生,记录点滴 不积硅步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海……">
<img src="banner.png" border=0 />
</a>
</div>
<div style="width:640px; height:40px; border-bottom:solid 1px #808080;text-align:center;">
<a href="http://blog.csdn.net/testcs_dn/article/details/49965993"><h3>您可以在这里监控和控制LED灯的点亮或关闭</h3></a>
</div>
<table id="Wrapper" style="padding: 0px; margin: 0px; min-height:300px; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">
<tr>
<td>
<form>
<div id="divctnr"></div>
</form>
</td>
<td>
<div style="width:640px; height:40px; text-align:center; float:left; clear:both; margin-top:15px;">
<input type="button" id="button1" name="button1" value="点亮" onclick="execControl(1)" style="display:none; width:200px; height:45px; font-size:36px; font-weight:bold;" />
<input type="button" id="button2" name="button2" value="关闭" onclick="execControl(0)" style="display:none; width:200px; height:45px; font-size:36px; font-weight:bold;" />
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<hr />
<div style="margin:auto; text-align:center; line-height:28px;">
云服务器:<a href="https://console.ng.bluemix.net/home/" target="_blank" title="IBM Bluemix 数字创新平台" style="">
IBM Bluemix 数字创新平台
</a><br />
服务提供:<a href="https://www.ibm.com/smarterplanet/us/en/ibmwatson/developercloud/language-translation/api/v2/#introduction" target="_blank" title="IBM Watson Developer Cloud" style="">
IBM Watson Developer Cloud
</a>
</div>
<div style="margin:auto; text-align:center; line-height:28px;">
<a href="http://blog.csdn.net/testcs_dn" target="_blank" title="无知人生,记录点滴 不积硅步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海……" style="">
Powered by:testcs_dn(微wx笑)<br />
无知人生,记录点滴 不积硅步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海……
</a>
</div>
<br /><br /><br />
<div id="divout"></div>
</body>
</html>
步骤 5. 本地运行访问测试
运行
运行Web服务,执行命令:python server.py
运行发送状态接收命令的服务,执行命令:phthon sendSamples.py
当然,你也可以直接在PyCharm等工具中调试运行。
访问
启动调试后会自动打开浏览器窗口:
点亮状态:显示关闭按钮
步骤 6. 上传应用程序
登录到 Bluemix™ 后,可以使用 cf push 命令来上传应用程序。
开始之前,您必须:- 1、安装 Cloud Foundry 命令行界面。

- 请根据自己使用的操作系统下载对应的版本;我使用的是Windows 7 64位操作系统,
- 下载Binaries版本的不需要安装,直接解压到Windows目录就可以了。

- 依次点击仪表板》jstrans(您创建的应用程序名称)》开始编码,可以查看属于自己的命令;如下图:
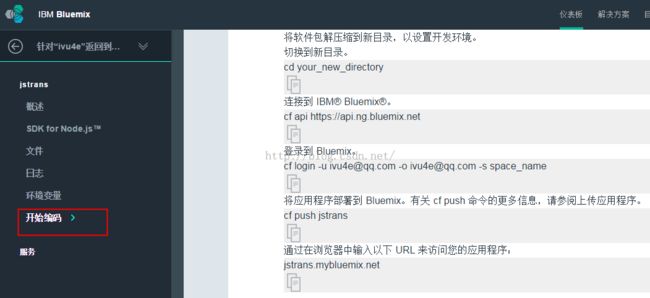
- 2、连接到 Bluemix。
- 打开命令提示符窗口:开始》运行,输入“cmd”,回车
- 执行:cf api https://api.ng.bluemix.net,如下图:

- 3、登录到 Bluemix。
- 注意,这里要换成对应你自己账户的命令!
cf login -u [email protected] -o [email protected] -s ivu4e
4、发出 cf push 命令时,cf 命令行界面将提供使用 buildpack 来构建并运行应用程序的 Bluemix 环境的工作目录。
步骤 7. 做个小小的测试
通过仪表板进入您刚刚创建的应用页面,点击左侧的概述,右侧顶部会显示:您的应用程序正在运行。
这时应用程序路径是带链接可以访问的,点击链接就可以访问刚刚发布的应用程序了。
注意:本地测试时收集数据、获取状态和控制命令等都是使用的本地的URL地址,上传到Bluemix之前要将其改为你创建的应用的URL地址。
结束语
本文提供了一个可用来开发许多 IoT 应用程序的框架。在这里,我们使用了一个连接到 Arduino 的LED,将LED的状态发送到 Web 服务器,并实时显示LED的状态,而且可以通过Web页面来控制LED的状态。尽管这是一个使用 Bluemix 和 Arduino 的特定示例,但您也可以使用本文介绍的原理来创建其他许多应用程序。
===========文档信息============
版权声明:非商用自由转载-保持署名-注明出处
署名(BY) :testcs_dn(微wx笑)
文章出处:[无知人生,记录点滴](http://blog.csdn.net/testcs_dn)




