Python数据可视化matplotlib(三)——绘制基本的图表
Python数据可视化matplotlib(三)——绘制基本的图表
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
% matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.style as psl
psl.use('_classic_test')
基本图表绘制 plt.plot()
图表类别:线形图、柱状图、密度图,以横纵坐标两个维度为主
同时可延展出多种其他图表样式
plt.plot(kind=‘line’, ax=None, figsize=None, use_index=True, title=None, grid=None, legend=False,
style=None, logx=False, logy=False, loglog=False, xticks=None, yticks=None, xlim=None, ylim=None,
rot=None, fontsize=None, colormap=None, table=False, yerr=None, xerr=None, label=None, secondary_y=False, **kwds)
线性表
Series直接生成图表
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000),index=pd.date_range('1/1/2010',periods=1000))
ts = ts.cumsum()
ts.plot(kind='line', #图表类型
color='r',
style='-gx',
alpha=0.5,
use_index=True, #是否使用数据中给出的index
rot=0, # 旋转刻度标签
ylim=[-50, 50],
yticks=list(range(-50, 50,10)),
title='time series',
legend=True,
label='cad')
plt.grid(True, linestyle = "--",color = "gray", linewidth = "0.5",axis = 'both') # 网格
# Series.plot():series的index为横坐标,value为纵坐标
# kind → line,bar,barh...(折线图,柱状图,柱状图-横...)
# label → 图例标签,Dataframe格式以列名为label
# style → 风格字符串,这里包括了linestyle(-),marker(.),color(g)
# color → 颜色,有color指定时候,以color颜色为准
# alpha → 透明度,0-1
# use_index → 将索引用为刻度标签,默认为True
# rot → 旋转刻度标签,0-360
# grid → 显示网格,一般直接用plt.grid
# xlim,ylim → x,y轴界限
# xticks,yticks → x,y轴刻度值
# figsize → 图像大小
# title → 图名
# legend → 是否显示图例,一般直接用plt.legend()
# 也可以 → plt.plot()
Dataframe直接生成图表
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4), index = ts.index, columns=list('abcd'))
df = df.cumsum()
df.plot(style='--.',
alpha=0.8,
ylim=[-100,100],
figsize=(10,8),
grid=True,
yticks=list(range(-100, 125,25)),
title='text',
subplots=True, #是否将每个系列分成不同的子图
)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', axis='both')
# subplots → 是否将各个列绘制到不同图表,默认False
# 也可以 → plt.plot(df)
柱状图与堆叠图
直接生成图
# 柱状图与堆叠图
# plt.xkcd() #漫画风格
fig,axes=plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(12,12))
s = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0,10,16), index=list('abcdfeghjklmnopq'))
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 3), columns=['a', 'b','c'])
#单系列柱状图
s.plot(kind='bar',ax=axes[0],grid=True,legend=True,label='s', alpha=0.6)
#多系列柱状图
df.plot(kind='bar', ax=axes[1],colormap='Reds_r')
#多系列堆叠图
df.plot(kind='bar',ax=axes[2],colormap='Blues_r', stacked=True)
# stacked → 堆叠
df.plot.barh(ax = axes[3],grid = True,stacked=True,colormap = 'BuGn_r')
# 新版本plt.plot.柱状图 plt.bar()
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
x = np.arange(10)
y1 = np.random.rand(10)
y2 = np.random.rand(10)
plt.bar(x, y1, width = 0.8, facecolor = 'green', edgecolor= 'black', yerr = y1*0.1)
plt.bar(x, -y2, width = 0.8, facecolor = 'yellow', edgecolor= 'black', yerr = y2*0.1)
# x,y参数:x,y值
# width:宽度比例
# facecolor柱状图里填充的颜色、edgecolor是边框的颜色
# left-每个柱x轴左边界,bottom-每个柱y轴下边界 → bottom扩展即可化为甘特图 Gantt Chart
# align:决定整个bar图分布,默认left表示默认从左边界开始绘制,center会将图绘制在中间位置
# xerr/yerr :x/y方向error bar 误差值
for i, j in zip(x, y1):
plt.text(i-0.2, j+0.1, '%.2f'%j, color='blue')
for i, j in zip(x, y2):
plt.text(i, -j-0.2, '%.2f'%j, color='blue')
# 给图添加text
# zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。
外嵌图表
# 外嵌图表plt.table()
''' table(cellText=None, cellColours=None,cellLoc='right', colWidths=None,rowLabels=None, rowColours=None, rowLoc='left', colLabels=None, colColours=None, colLoc='center',loc='bottom', bbox=None) '''
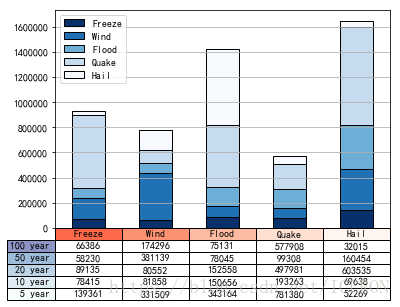
data = [[ 66386, 174296, 75131, 577908, 32015],
[ 58230, 381139, 78045, 99308, 160454],
[ 89135, 80552, 152558, 497981, 603535],
[ 78415, 81858, 150656, 193263, 69638],
[139361, 331509, 343164, 781380, 52269]]
columns=('Freeze', 'Wind', 'Flood', 'Quake', 'Hail')
rows = ['%d year'% x for x in (100, 50, 20, 10, 5)]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=('Freeze', 'Wind', 'Flood', 'Quake', 'Hail'),
index=rows)
print(df)
df.plot(kind='bar', grid=True, colormap='Blues_r',stacked=True,
edgecolor='black',rot=0)
#创建堆叠图
plt.table(cellText = data,
cellLoc = 'center',
cellColours = None,
rowLabels = rows,
rowColours = plt.cm.BuPu(np.linspace(0, 0.5,5))[::-1], # BuPu可替换成其他colormap
colLabels = columns,
colColours = plt.cm.Reds(np.linspace(0, 0.5,5))[::-1],
rowLoc='right',
loc='bottom')
# cellText:表格文本
# cellLoc:cell内文本对齐位置
# rowLabels:行标签
# colLabels:列标签
# rowLoc:行标签对齐位置
# loc:表格位置 → left,right,top,bottom
plt.xticks([])
Freeze Wind Flood Quake Hail
100 year 66386 174296 75131 577908 32015
50 year 58230 381139 78045 99308 160454
20 year 89135 80552 152558 497981 603535
10 year 78415 81858 150656 193263 69638
5 year 139361 331509 343164 781380 52269
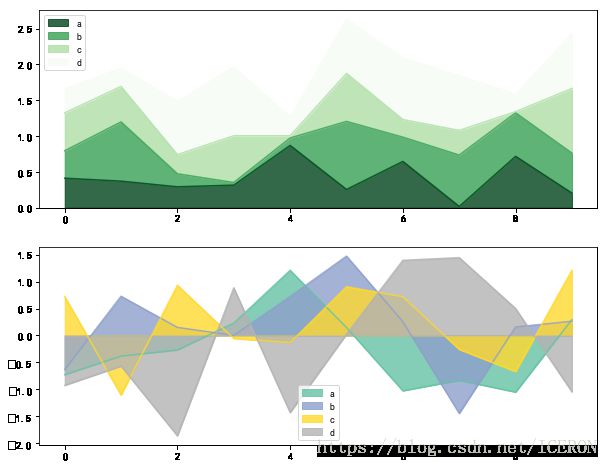
面积图,填图, 饼图
面积图 plt.plot.area()
# 面积图plt.plot.area()
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,1,figsize = (10,8))
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 4), columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4), columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
df1.plot.area(colormap = 'Greens_r', alpha = 0.8, ax = axes[0])
df2.plot.area(stacked=False ,colormap = 'Set2',alpha=0.8, ax = axes[1])
# 使用Series.plot.area()和DataFrame.plot.area()创建面积图
# stacked:是否堆叠,默认情况下,区域图被堆叠
# 为了产生堆积面积图,每列必须是正值或全部负值!
# 当数据有NaN时候,自动填充0,所以图标签需要清洗掉缺失值
填图
# 填图
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10,8))
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 500)
y1 = np.sin(4 * np.pi * x) * np.exp(-5 * x)
y2 = -np.sin(4 * np.pi * x) * np.exp(-5 * x)
axes[0].fill(x, y1, 'r', label = 'y1', alpha = 0.5)
axes[0].fill(x, y2, 'g',alpha = 0.5,label= 'y2')
# 对函数与坐标轴之间的区域进行填充,使用fill函数
# 也可写成:plt.fill(x, y1, 'r',x, y2, 'g',alpha=0.5)
x = np.linspace(0, 5 * np.pi, 1000)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.sin(2 * x)
axes[1].fill_between(x, y1, y2, color ='b',alpha=0.5,label='area')
# 填充两个函数之间的区域,使用fill_between函数
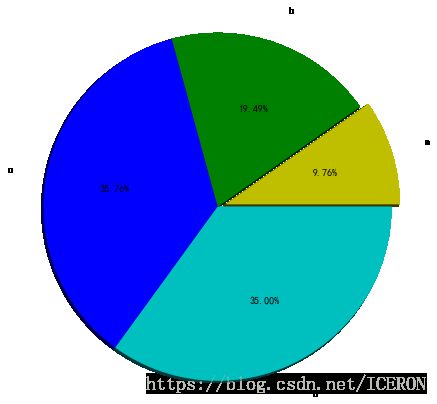
饼图
# 饼图 plt.pie()
''' plt.pie(x, explode=None, labels=None, colors=None, autopct=None, pctdistance=0.6, shadow=False, labeldistance=1.1, startangle=None, radius=None, counterclock=True, wedgeprops=None, textprops=None, center=(0, 0), frame=False, hold=None, data=None) '''
s = pd.Series(3 * np.random.rand(4), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], name='series')
plt.axis('equal') # 保证长宽相等
plt.pie(s,
explode = [0.1,0,0,0],
labels = s.index,
colors=['y', 'g', 'b', 'c'],
autopct='%.2f%%',
pctdistance=0.6,
labeldistance = 1.2,
shadow = True,
startangle=0,
radius=2,
frame=False)
print(s)
# 第一个参数:数据
# explode:指定每部分的偏移量
# labels:标签
# colors:颜色
# autopct:饼图上的数据标签显示方式
# pctdistance:每个饼切片的中心和通过autopct生成的文本开始之间的比例
# labeldistance:被画饼标记的直径,默认值:1.1
# shadow:阴影
# startangle:开始角度
# radius:半径
# frame:图框
# counterclock:指定指针方向,顺时针或者逆时针
a 0.783335
b 1.564125
c 2.870229
d 2.809502
Name: series, dtype: float64
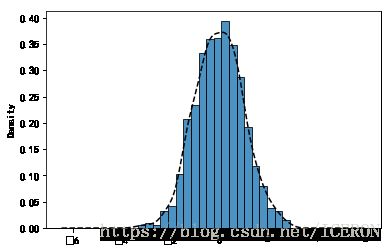
直方图
直方图+密度图
# 直方图+密度图
''' plt.hist(x, bins=10, range=None, normed=False, weights=None, cumulative=False, bottom=None, histtype='bar', align='mid', orientation='vertical',rwidth=None, log=False, color=None, label=None, stacked=False, hold=None, data=None, **kwargs) '''
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000))
s.hist(bins = 20,
histtype = 'bar',
align = 'mid',
orientation = 'vertical',
alpha=0.8,
normed =True,
edgecolor = 'black')
# bin:箱子的宽度
# normed 标准化
# histtype 风格,bar,barstacked,step,stepfilled
# orientation 水平还是垂直{‘horizontal’, ‘vertical’}
# align : {‘left’, ‘mid’, ‘right’}, optional(对齐方式)
s.plot(kind='kde',style='k--')
# 密度图
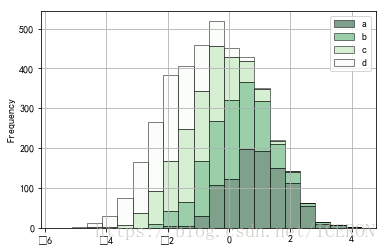
堆叠直方图
# 堆叠直方图
plt.figure(num=1)
df = pd.DataFrame({'a': np.random.randn(1000) + 1, 'b': np.random.randn(1000),
'c': np.random.randn(1000) - 1, 'd': np.random.randn(1000)-2},
columns=['a', 'b', 'c','d'])
df.plot.hist(stacked=True,
bins=20,
colormap='Greens_r',
alpha=0.5,
grid=True,
edgecolor='black')
# 使用DataFrame.plot.hist()和Series.plot.hist()方法绘制
# stacked:是否堆叠
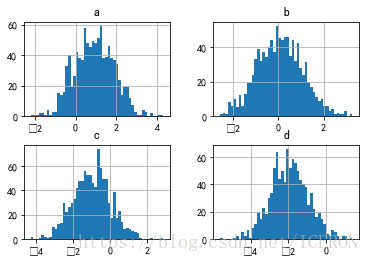
df.hist(bins=50)
# 生成多个直方图
散点图
散点图 plt.scatter()
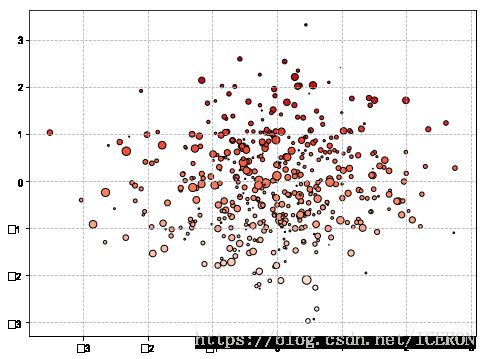
#plt.scatter()
# plt.scatter(x, y, s=20, c=None, marker='o', cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None,
# alpha=None, linewidths=None, verts=None, edgecolors=None, hold=None, data=None, **kwargs)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
plt.scatter(x,y,marker='.',
s=np.random.randn(1000)*100,
cmap='Reds',
c=y,
edgecolor='black')
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--')
# s:散点的大小
# c:散点的颜色
# vmin,vmax:亮度设置,标量
# cmap:colormap
矩阵散点图
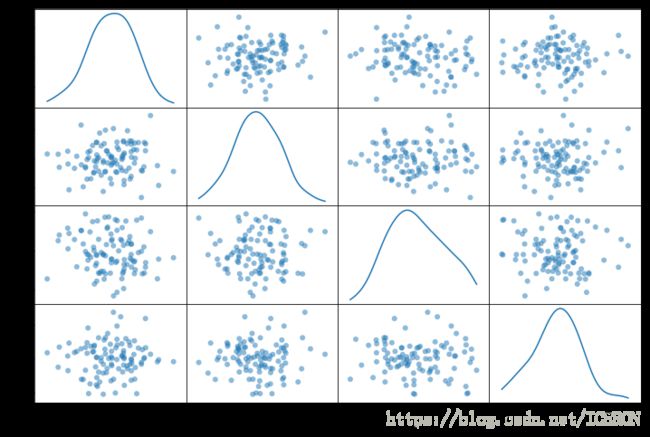
# pd.scatter_matrix()散点矩阵
# pd.scatter_matrix(frame, alpha=0.5, figsize=None, ax=None,
# grid=False, diagonal='hist', marker='.', density_kwds=None, hist_kwds=None, range_padding=0.05, **kwds)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(100,4),columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(df,figsize=(12,8),
marker='o',
diagonal='kde',
range_padding=0.2)
# diagonal:({‘hist’, ‘kde’}),必须且只能在{‘hist’, ‘kde’}中选择1个 → 每个指标的频率图
# range_padding:(float, 可选),图像在x轴、y轴原点附近的留白(padding),该值越大,留白距离越大,图像远离坐标原点
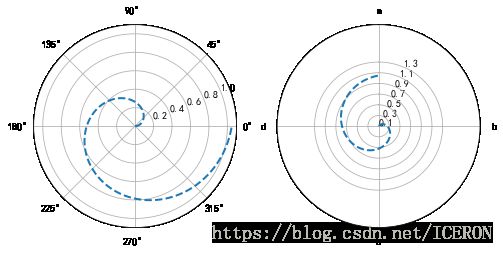
极坐标图
- 调用subplot()创建子图时通过设置projection=‘polar’,便可创建一个极坐标子图,然后调用plot()在极坐标子图中绘图
创建简单的极坐标图
#创建极坐标轴
s = pd.Series(np.arange(20))
theta = np.arange(0, 2*np.pi, 0.02)
#print(theta)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
ax1=plt.subplot(121,projection='polar')
ax2 = plt.subplot(122)
# 创建极坐标子图
# 还可以写:ax = fig.add_subplot(111,polar=True)
ax1.plot(s, linestyle='--',marker='.', lw=2)
ax2.plot(s, linestyle='--',marker='.', lw=2)
ax1.plot(theta, theta*3, linestyle='--', lw=1)
ax2.plot(theta, theta*3, linestyle='--', lw=1)
plt.grid()
# 创建极坐标图,参数1为角度(弧度制),参数2为value
# lw → 线宽
极坐标图的参数设置
# 极坐标参数设置
theta=np.arange(0,2*np.pi,0.02)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
ax1= plt.subplot(121, projection='polar')
ax2= plt.subplot(122, projection='polar')
ax1.plot(theta,theta/6,'--',lw=2)
ax2.plot(theta,theta/6,'--',lw=2)
# 创建极坐标子图ax
ax2.set_theta_direction(-1)
# set_theta_direction():坐标轴正方向,默认逆时针
ax2.set_thetagrids(np.arange(0.0, 360.0, 90),['a','b','c','d'])
ax2.set_rgrids(np.arange(0.2,2,0.4))
# set_thetagrids():设置极坐标角度网格线显示及标签 → 网格和标签数量一致
# set_rgrids():设置极径网格线显示,其中参数必须是正数
ax2.set_theta_offset(np.pi/2)
# set_theta_offset():设置角度偏移,逆时针,弧度制
ax2.set_rlim(0.2,1.2)
ax2.set_rmax(2)
ax2.set_rticks(np.arange(0.1, 1.5, 0.2))
# set_rlim():设置显示的极径范围
# set_rmax():设置显示的极径最大值
# set_rticks():设置极径网格线的显示范围
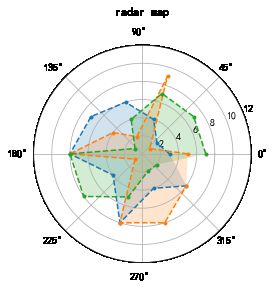
雷达图
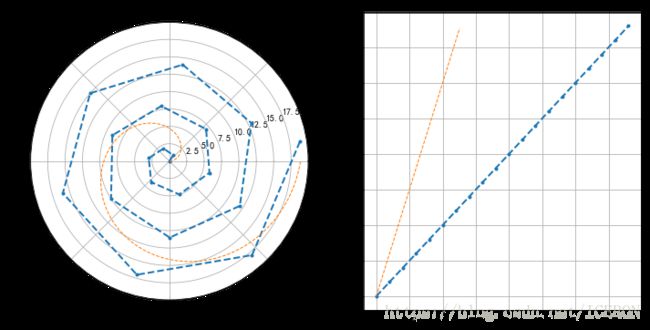
# 雷达图1 - 极坐标的折线图/填图 - plt.plot()
plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
ax1= plt.subplot(111, projection='polar')
ax1.set_title('radar map\n') # 创建标题
ax1.set_rlim(0,12)
data1 = np.random.randint(1,10,10)
data2 = np.random.randint(1,10,10)
data3 = np.random.randint(1,10,10)
theta=np.arange(0,2*np.pi,2*np.pi/10)
# 创建数据
ax1.plot(theta,data1,'.--',label='data1')
ax1.fill(theta,data1,alpha=0.2)
ax1.plot(theta,data2,'.--',label='data2')
ax1.fill(theta,data2,alpha=0.2)
ax1.plot(theta,data3,'.--',label='data3')
ax1.fill(theta,data3,alpha=0.2)
# 绘制雷达线
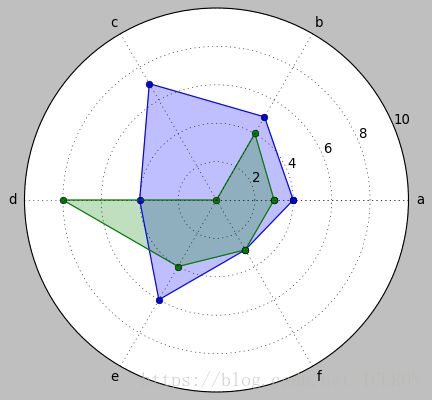
# 雷达图2 - 极坐标的折线图/填图 - plt.polar()
# 首尾闭合
labels = np.array(['a','b','c','d','e','f']) # 标签
dataLenth = 6 # 数据长度
data1 = np.random.randint(0,10,6)
data2 = np.random.randint(0,10,6) # 数据
angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, dataLenth, endpoint=False) # 分割圆周长
data1 = np.concatenate((data1, [data1[0]])) # 闭合
data2 = np.concatenate((data2, [data2[0]])) # 闭合
angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) # 闭合
plt.polar(angles, data1, 'o-', linewidth=1) #做极坐标系
plt.fill(angles, data1, alpha=0.25)# 填充
plt.polar(angles, data2, 'o-', linewidth=1) #做极坐标系
plt.fill(angles, data2, alpha=0.25)# 填充
plt.thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels) # 设置网格、标签
plt.ylim(0,10) # polar的极值设置为ylim
(0, 10)
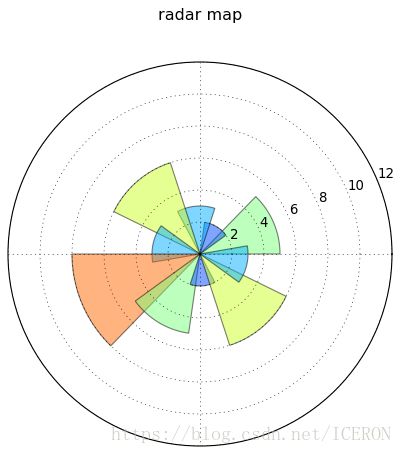
极轴图
# 极轴图 - 极坐标的柱状图
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6), facecolor='White')
ax1= plt.subplot(111, projection='polar')
ax1.set_title('radar map\n') # 创建标题
ax1.set_rlim(0,12)
data = np.random.randint(1,10,10)
theta=np.arange(0,2*np.pi,2*np.pi/10)
# 创建数据
bar = ax1.bar(theta,data,alpha=0.5)
for r,bar in zip(data, bar):
bar.set_facecolor(plt.cm.jet(r/10.)) # 设置颜色
plt.thetagrids(np.arange(0.0, 360.0, 90), []) # 设置网格、标签(这里是空标签,则不显示内容)
箱型图
箱型图:又称为盒须图、盒式图、盒状图或箱线图,是一种用作显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图
- 包含一组数据的:最大值、最小值、中位数、上四分位数(Q3)、下四分位数(Q1)、异常值
1.中位数 → 一组数据平均分成两份,中间的数
2.上四分位数Q1 → 是将序列平均分成四份,计算(n+1)/4与(n-1)/4两种,一般使用(n+1)/4
3.下四分位数Q3 → 是将序列平均分成四份,计算(1+n)/4*3=6.75
4.内限 → T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+1.5IQR,最小值区间Q1-1.5IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
5.外限 → T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+3IQR,最小值区间Q1-3IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
6.异常值 → 内限之外 - 中度异常,外限之外 - 极度异常
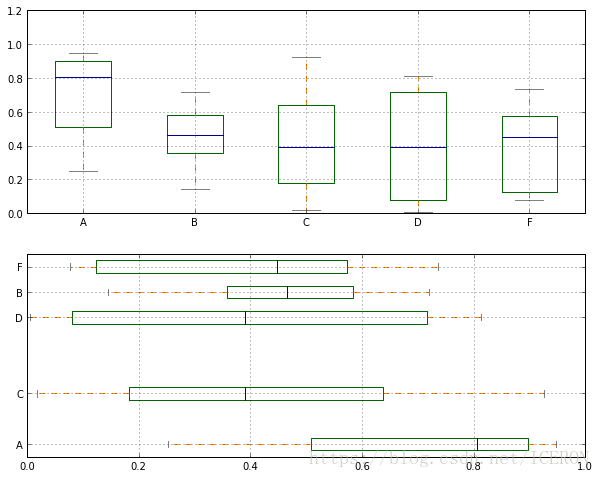
plt.plot.box(),plt.boxplot()
plt.plot.box()绘制
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 8))
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 5), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'F'])
color = dict(boxes='DarkGreen', whiskers='DarkOrange', medians='DarkBlue', caps='Gray')
# 箱型图着色
# boxes → 箱线
# whiskers → 分位数与error bar横线之间竖线的颜色
# medians → 中位数线颜色
# caps → error bar横线颜色
df.plot.box(ylim=[0, 1.2],
grid=True,
color=color,
ax=axes[0])
# color:样式填充
df.plot.box(vert=False,
positions=[1, 7, 3, 6, 8],
ax = axes[1],
grid = True,
color = color)
# vert:是否垂直,默认True
# position:箱型图占位,在这里指数据中的ABCDF列分别位于第几个占位
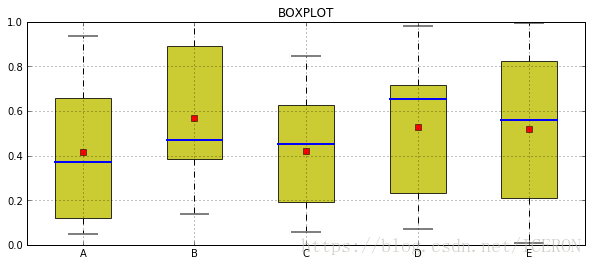
# plt.boxplot()绘制
# plt.boxplot()绘制
# pltboxplot(x, notch=None, sym=None, vert=None, whis=None, positions=None, widths=None, patch_artist=None, bootstrap=None,
# usermedians=None, conf_intervals=None, meanline=None, showmeans=None, showcaps=None, showbox=None, showfliers=None, boxprops=None,
# labels=None, flierprops=None, medianprops=None, meanprops=None, capprops=None, whiskerprops=None, manage_xticks=True, autorange=False,
# zorder=None, hold=None, data=None)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 5), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
f = df.boxplot(sym='o', # 异常点的形状
vert=True, # 是否垂直
whis=1.5, # IQR默认1.5也可以设置区间比如[5,95],代表强制上下边缘为数据95%和5%位置
patch_artist=True, # 上下四分位框内是否填充,True为填充
meanline=False, showmeans=True, # 是否有均值线,及其形状
showbox=True, # 是否显示箱线
showcaps=True, # 是否显示边缘线
showfliers=True, # 是否显示异常值
notch=False, # 中间箱体是否缺口
return_type='dict' # 返回类型为字典
)
plt.title('BOXPLOT')
for box in f['boxes']:
box.set( color='black', linewidth=1)
box.set(facecolor='y', alpha=0.8) # 当箱体的选择不填充颜色的时候,就没有facecolor这个参数
for whisker in f['whiskers']:
whisker.set(color='k', linewidth=1, linestyle='--')
for cap in f['caps']:
cap.set(color='gray', linewidth=2)
for median in f['medians']:
median.set(color='b', linewidth=2)
for flier in f['fliers']:
flier.set(marker='o', color='y', alpha=0.5)
# plt.boxplot()绘制
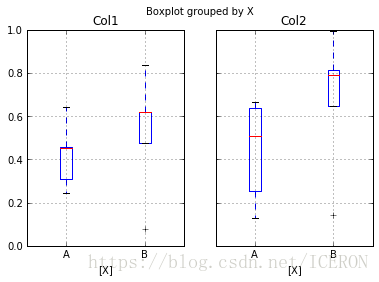
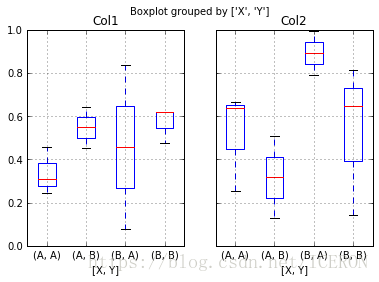
# 分组汇总
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,2), columns=['Col1', 'Col2'] )
df['X'] = pd.Series(['A','A','A','A','A','B','B','B','B','B'])
df['Y'] = pd.Series(['A','B','A','B','A','B','A','B','A','B'])
print(df.head())
df.boxplot(by = 'X')
df.boxplot(column=['Col1','Col2'], by=['X','Y'])
# columns:按照数据的列分子图
# by:按照列分组做箱型图
Col1 Col2 X Y
0 0.243543 0.663692 A A
1 0.643759 0.126715 A B
2 0.457961 0.639223 A A
3 0.451694 0.508668 A B
4 0.307339 0.255042 A A