- SQL Server_查询某一数据库中的所有表的内容
qq_42772833
SQLServer数据库sqlserver
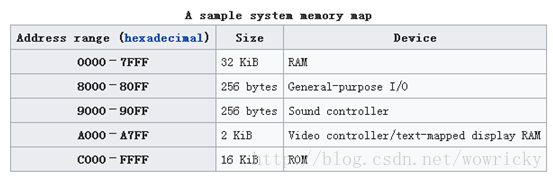
1.查看所有表的表名要列出CrabFarmDB数据库中的所有表(名),可以使用以下SQL语句:USECrabFarmDB;--切换到目标数据库GOSELECTTABLE_NAMEFROMINFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLESWHERETABLE_TYPE='BASETABLE';对这段SQL脚本的解释:SELECTTABLE_NAME:这个语句的作用是从查询结果中选择TABLE_NAM
- libyuv之linux编译
jaronho
Linuxlinux运维服务器
文章目录一、下载源码二、编译源码三、注意事项1、银河麒麟系统(aarch64)(1)解决armv8-a+dotprod+i8mm指令集支持问题(2)解决armv9-a+sve2指令集支持问题一、下载源码到GitHub网站下载https://github.com/lemenkov/libyuv源码,或者用直接用git克隆到本地,如:gitclonehttps://github.com/lemenko
- ARM中断处理过程
落汤老狗
嵌入式linux
一、前言本文主要以ARM体系结构下的中断处理为例,讲述整个中断处理过程中的硬件行为和软件动作。具体整个处理过程分成三个步骤来描述:1、第二章描述了中断处理的准备过程2、第三章描述了当发生中的时候,ARM硬件的行为3、第四章描述了ARM的中断进入过程4、第五章描述了ARM的中断退出过程本文涉及的代码来自3.14内核。另外,本文注意描述ARM指令集的内容,有些sourcecode为了简短一些,删除了T
- ARM驱动学习之基础小知识
JT灬新一
ARM嵌入式arm开发学习
ARM驱动学习之基础小知识•sch原理图工程师工作内容–方案–元器件选型–采购(能不能买到,价格)–原理图(涉及到稳定性)•layout画板工程师–layout(封装、布局,布线,log)(涉及到稳定性)–焊接的一部分工作(调试阶段板子的焊接)•驱动工程师–驱动,原理图,layout三部分的交集容易发生矛盾•PCB研发流程介绍–方案,原理图(网表)–layout工程师(gerber文件)–PCB板
- ARM驱动学习之5 LEDS驱动
JT灬新一
嵌入式C底层arm开发学习单片机
ARM驱动学习之5LEDS驱动知识点:•linuxGPIO申请函数和赋值函数–gpio_request–gpio_set_value•三星平台配置GPIO函数–s3c_gpio_cfgpin•GPIO配置输出模式的宏变量–S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT注意点:DRIVER_NAME和DEVICE_NAME匹配。实现步骤:1.加入需要的头文件://Linux平台的gpio头文件#include//三
- ARM驱动学习之4小结
JT灬新一
嵌入式C++arm开发学习linux
ARM驱动学习之4小结#include#include#include#include#include#defineDEVICE_NAME"hello_ctl123"MODULE_LICENSE("DualBSD/GPL");MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET");staticlonghello_ioctl(structfile*file,unsignedintcmd,unsignedlo
- Python编译器
鹿鹿~
Python编译器Pythonpython开发语言后端
嘿嘿嘿我又来了啊有些小盆友可能不知道Python其实是有编译器的,也就是PyCharm。你们可能会问到这个是干嘛的又不可以吃也不可以穿好像没有什么用,其实你还说对了这个还真的不可以吃也不可以穿,但是它用来干嘛的呢。用来编译你所打出的代码进行运行(可能这里说的有点不对但是只是个人认为)现在我们来说说PyCharm是用来干嘛的。PyCharm是一种PythonIDE,带有一整套可以帮助用户在使用Pyt
- ARM V8 base instruction -- Debug instructions
xiaozhiwise
Assemblyarm
/**Debuginstructions*/BRK#imm16进入monitormodedebug,那里有on-chipdebugmonitorcodeHLT#imm16进入haltmodedebug,连接有外部调试硬件
- Armv8.3 体系结构扩展--原文版
代码改变世界ctw
ARM-TEE-Androidarmv8嵌入式arm架构安全架构芯片TrustzoneSecureboot
快速链接:.ARMv8/ARMv9架构入门到精通-[目录]付费专栏-付费课程【购买须知】:个人博客笔记导读目录(全部)TheArmv8.3architectureextensionTheArmv8.3architectureextensionisanextensiontoArmv8.2.Itaddsmandatoryandoptionalarchitecturalfeatures.Somefeat
- ARMv8 Debug
__pop_
ARMv8ARM64架构linux运维
内容来自DEN0024A_v8_architecture_PG.pdf本质ARMv8Debug是什么历史在ARMv4开始被引入,并已发展成一系列广泛的调试(debug1)和跟踪(trace)功能ARMv6和ARMv7-a新增了自托管调试(debug2)和性能评测(trace-enhance)ARMv8处理器提供硬件功能侵入式:调试工具能够对核心活动提供显著级别的控制非侵入式:以非侵入性方式收集有关
- 【ARM Cortex-M 系列 2.3 -- Cortex-M7 Debug event 详细介绍】
主公讲 ARM
#ARM系列arm开发debugevent
请阅读【嵌入式开发学习必备专栏】文章目录Cortex-M7DebugeventDebugeventsCortex-M7Debugevent在ARMCortex-M7架构中,调试事件(DebugEvent)是由于调试原因而触发的事件。一个调试事件会导致以下几种情况之一发生:进入调试状态:如果启用了停滞调试(HaltingDebug),一个调试事件会使处理器在调试状态下停滞。通过将DHCSR.C_DE
- ARMV8体系结构简介:概述
简单同学
ARMV8体系结构ARMV8
1.前言本文主要概括的介绍ARMV8体系结构定义了哪些内容,概括的说:ARM体系结构定义了PE的行为,不会定义具体的实现ARM体系结构也定义了debug体系结构和trace体系结构ARM体系结构采用RISC指令集(1)长度一致的寄存器;(2)load/store架构,数据处理操作只能对寄存器内容进行处理,不会直接对内存的内容进行处理;(3)简单寻址方式,load/store地址来源于寄存器或指令域
- [实验室服务器使用]使用VSCode、PyCharm、MobaXterm和CMD连接远程服务器
YuanDaima2048
工具使用服务器vscodepycharmcmd代理模式机器学习实验
文章总览:YuanDaiMa2048博客文章总览实验室服务器使用:使用VSCode、PyCharm、MobaXterm和CMD连接远程服务器在进行实验室工作时,远程连接服务器是常见的需求之一。本篇文章根据个人的一些使用介绍使用不同工具连接服务器的方法,并提供优化功能,使服务器能够使用本机代理的说明。准备服务器账号信息Host(主机):10.XXX.XX.XXXPort(端口):[SSHPort]U
- HarmonyOS开发实战( Beta5.0)搜索框热搜词自动切换
让开,我要吃人了
OpenHarmonyHarmonyOS鸿蒙开发harmonyos华为鸿蒙移动开发鸿蒙系统前端开发语言
鸿蒙HarmonyOS开发往期必看:HarmonyOSNEXT应用开发性能实践总结最新版!“非常详细的”鸿蒙HarmonyOSNext应用开发学习路线!(从零基础入门到精通)介绍本示例介绍使用TextInput组件与Swiper组件实现搜索框内热搜词自动切换。效果图预览使用说明页面顶部搜索框内热搜词条自动切换,编辑搜索框时自动隐藏。实现思路使用TextInput实现搜索框TextInput({te
- HarmonyOS Next鸿蒙扫一扫功能实现
JohnLiu_
HarmonyOSNextharmonyos华为扫一扫鸿蒙
直接使用的是华为官方提供的api,封装成一个工具类方便调用。import{common}from'@kit.AbilityKit';import{scanBarcode,scanCore}from'@kit.ScanKit';exportnamespaceScanUtil{exportasyncfunctionstartScan(context:common.Context):Promise{if
- 鲲鹏 ARM 架构 麒麟 Lylin v10 安装 Nginx (离线)
焚木灵
arm开发架构nginx服务器
最近做一个银行的项目,银行的服务器是鲲鹏ARM架构的服务器,并且是麒麟v10的系统,这里记录一下在无法访问外网安装Nginx的方法。其他文章:鲲鹏ARM架构麒麟Lylinv10安装Mysql8.3(离线)-CSDN博客鲲鹏ARM架构麒麟Lylinv10安装Node和NVM(离线)-CSDN博客鲲鹏ARM架构麒麟Lylinv10安装Pm2(离线)-CSDN博客鲲鹏ARM架构麒麟Lylinv10安装P
- 【鸿蒙应用】总结一下ArkUI
读心悦
鸿蒙基础鸿蒙应用
ArkUI是HarmonyOS应用界面的UI开发框架,提供了简洁的UI语法、UI组件、动画机制和事件交互等等UI开发基础,以此满足应用开发者对UI界面开发的需求。组件是界面搭建的最小单位,开发者通过多种组件的组合构成完整的界面。页面是ArkUI最小的调度分隔单位,开发者可以将应用设计为多个功能页面,每一个页面进行单独的文件管理,并且通过页面路由API完成页面之间的调度管理,以此来实现应用内功能的解
- python环境安装 pip不能用的问题 pycharm的模板字符
卓越小Y
python学习pythonpycharmpip
学习初衷今天是九月一号,也就是开学日,做大人的也要适当开下学,享受下仪式感。以往都是存储在笔记本的,但是几台电脑,经常很多资料乱成一团,写成博客,方便让有心学习的朋友少走一些弯路。属于自己的开学季也出发了python环境安装和一些小问题环境搭建环境安装添加变量名为PYTHON_HOME地址:安装文件的路径path路径(%代表引用设置好的变量)一般我们会添加一个环境PYTHON_HOME然后指向我们
- 基于高通主板的ARM架构服务器
问就是想睡觉
arm开发服务器运维
一、ARM架构服务器的崛起(一)市场需求推动消费市场寒冬,全球消费电子需求下行,服务器成半导体核心动力之一。Arm加速布局服务器领域,如9月推出NeoverseV2。长久以来,x86架构主导服务器市场,现面临挑战。Arm2008年入服务器领域,虽因性能与生态问题未大突破,但近几年重新冲刺。(二)技术创新引领Arm的Neoverse平台不断发展。2018年推出参考架构,2020年衍生出E、N、V系列
- GEO数据的下载和处理|GEO数据转换为Gene symbol|GEO注释文件提取symbol|查看样本标签|查看GEO数据疾病或正常|生物信息基础
Red Red
生信小技巧学习笔记生物信息r语言GEO数据库数据库
GEO数据的下载和处理|GEO数据转换为Genesymbol|GEO注释文件提取symbol|查看样本标签|查看GEO数据疾病或正常|生物信息基础数据的下载和处理首先在GEO数据库中通过GSEID找到相关数据,然后下载txt文件。数据读取与处理。#设置工作路径,也就是你的分析数据存放以及要保存到地方setwd(dir="C:\\Users\\LiaoMinzhen\\PycharmProjects
- 【开发环境搭建】Macbook M1搭建Java开发环境
weixin_44329069
java开发语言
JDK安装与配置下载并安装JDK:ARM64DMG安装包下载链接:JDK21forMac(ARM64)。双击下载的DMG文件,按照提示安装JDK。配置环境变量:打开终端,使用vim编辑.bash_profile文件:vim~/.bash_profile在文件中添加以下内容来设置JAVA_HOME:exportJAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/j
- 深入了解树莓派5:性能与功能的全面升级
像风一样自由2020
树莓派ubuntu
深入了解树莓派5:性能与功能的全面升级引言2023年,树莓派基金会正式发布了备受期待的树莓派5(RaspberryPi5)。作为树莓派系列的最新一代产品,树莓派5在处理性能、连接性和功能扩展方面都有了显著的提升,为开发者、教育者和科技爱好者带来了更强大的工具。本文将详细介绍树莓派5的特性、规格和应用场景。一、产品概述树莓派5是基于ARM架构的单板计算机,延续了树莓派系列低成本、高性能的设计理念。它
- 避免 PyCharm 将该 Python 脚本作为测试运行
MonkeyKing.sun
pythonpycharmide
为了避免PyCharm将该Python脚本作为测试运行(即pytest自动捕获),你可以做以下几步来确保该脚本作为普通的Python程序执行,而不是作为pytest运行。解决方案:1.确保文件名不以test_开头:Pytest会自动检测以test_开头的文件,并尝试将其作为测试运行。如果你的文件名是test_milvus.py,pytest会尝试收集并运行它。可以重命名文件为不包含test_的前缀
- PyCharm配置及使用Git教程_pycharm配置git(2)
2401_84182146
程序员pycharmgitelasticsearch
文章目录1.安装PyCharm2.安装Git3.在PyCharm中配置Git插件4.连接远程仓库5.Clone项目代码6.将本地文件提交到远程仓库6.1gitadd6.2gitcommit6.3gitpush6.4gitpull7.代码回滚8.分支操作8.1新建分支8.2切换分支8.3合并分支
- python做窗口软件界面绑定py程序_PyCharm GUI界面开发和exe文件生成的实现
weixin_39948442
一、安装Python二、安装PyQt5推荐使用pip安装:win+R调出cmd命令窗口pipinstallPyQt5等待片刻,继续安装PyQt5-toolspipinstallPyQt5-tools如果直接pip不成功的话,建议在python库这个网站上搜索相关库,下载相应的.whl文件,然后用以下方法进行安装:①pipwhl文件所在路径whl文件名②在cmd命令窗口先执行cdwhl文件所在路径到
- Kotlin 代替Java接口回调,就这么简单
深海呐
Android#Kotlinjavakotlin开发语言
假如你使用旧的接口回调:通常三步:1定义接口和方法;2使用接口中方法;3继承接口并实现方法;例:classXXXAdapter{publicvarmClickCollBack:clickCollBack?=null//1定义interfaceclickCollBack{//1定义funclick(int:Int)//1定义}itemView.setOnClickListener{mClickCol
- python基于django/flask的NBA球员大数据分析与可视化python+java+node.js
QQ_511008285
pythondjangoflaskjavaspringboot数据分析
前端开发框架:vue.js数据库mysql版本不限后端语言框架支持:1java(SSM/springboot)-idea/eclipse2.Nodejs+Vue.js-vscode3.python(flask/django)--pycharm/vscode4.php(thinkphp/laravel)-hbuilderx数据库工具:Navicat/SQLyog等都可以本文针对NBA球员的大数据进行
- Java基于spring boot的国产电影数据分析与可视化python+java+node.js
QQ_511008285
javaspringboot数据分析pythondjangovue.jsflask
前端开发框架:vue.js数据库mysql版本不限后端语言框架支持:1java(SSM/springboot)-idea/eclipse2.Nodejs+Vue.js-vscode3.python(flask/django)--pycharm/vscode4.php(thinkphp/laravel)-hbuilderx数据库工具:Navicat/SQLyog等都可以 该系统使用进行大数据处理和
- pycharm 运行celery_python远程调试及celery调试
夏小龙
pycharm运行celery
部分来自from:https://www.xncoding.com/2016/05/26/python/pycharm-remote.html你是否经常要在Windows7或MACOSX上面开发Python或Web应用程序,但是它们最后需要在linux上面来运行呢?我们经常会碰到开发时没有问题但是到了正式的Linux环境下面却出现问题。那么怎样保证开发环境跟运行环境的一致呢?通常有两种方法解决。一
- [HarmonyOS Next示例代码] 鸿蒙UI开发 - 组件动态创建
xiaohai_09
HarmonyOSNextUI开发harmonyos鸿蒙
鸿蒙UI开发-组件动态创建源码下载地址介绍本示例介绍了在声明式UI中实现组件动态创建的方法效果图预览主页面广告关闭弹窗使用说明进入应用后,广告组件随即被动态创建。其分为两种,分别为图片广告与视频广告。实现思路构建广告组件。源码参考AdBuilder.ets。模拟从云端初始化卡片列表,根据云端数据生成普通卡片对象和广告卡片对象。源码参考代码可参考MainPage.ets中的aboutToAppear
- ztree异步加载
3213213333332132
JavaScriptAjaxjsonWebztree
相信新手用ztree的时候,对异步加载会有些困惑,我开始的时候也是看了API花了些时间才搞定了异步加载,在这里分享给大家。
我后台代码生成的是json格式的数据,数据大家按各自的需求生成,这里只给出前端的代码。
设置setting,这里只关注async属性的配置
var setting = {
//异步加载配置
- thirft rpc 具体调用流程
BlueSkator
中间件rpcthrift
Thrift调用过程中,Thrift客户端和服务器之间主要用到传输层类、协议层类和处理类三个主要的核心类,这三个类的相互协作共同完成rpc的整个调用过程。在调用过程中将按照以下顺序进行协同工作:
(1) 将客户端程序调用的函数名和参数传递给协议层(TProtocol),协议
- 异或运算推导, 交换数据
dcj3sjt126com
PHP异或^
/*
* 5 0101
* 9 1010
*
* 5 ^ 5
* 0101
* 0101
* -----
* 0000
* 得出第一个规律: 相同的数进行异或, 结果是0
*
* 9 ^ 5 ^ 6
* 1010
* 0101
* ----
* 1111
*
* 1111
* 0110
* ----
* 1001
- 事件源对象
周华华
JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml&q
- MySql配置及相关命令
g21121
mysql
MySQL安装完毕后我们需要对它进行一些设置及性能优化,主要包括字符集设置,启动设置,连接优化,表优化,分区优化等等。
一 修改MySQL密码及用户
- [简单]poi删除excel 2007超链接
53873039oycg
Excel
采用解析sheet.xml方式删除超链接,缺点是要打开文件2次,代码如下:
public void removeExcel2007AllHyperLink(String filePath) throws Exception {
OPCPackage ocPkg = OPCPac
- Struts2添加 open flash chart
云端月影
准备以下开源项目:
1. Struts 2.1.6
2. Open Flash Chart 2 Version 2 Lug Wyrm Charmer (28th, July 2009)
3. jofc2,这东西不知道是没做好还是什么意思,好像和ofc2不怎么匹配,最好下源码,有什么问题直接改。
4. log4j
用eclipse新建动态网站,取名OFC2Demo,将Struts2 l
- spring包详解
aijuans
spring
下载的spring包中文件及各种包众多,在项目中往往只有部分是我们必须的,如果不清楚什么时候需要什么包的话,看看下面就知道了。 aspectj目录下是在Spring框架下使用aspectj的源代码和测试程序文件。Aspectj是java最早的提供AOP的应用框架。 dist 目录下是Spring 的发布包,关于发布包下面会详细进行说明。 docs&nb
- 网站推广之seo概念
antonyup_2006
算法Web应用服务器搜索引擎Google
持续开发一年多的b2c网站终于在08年10月23日上线了。作为开发人员的我在修改bug的同时,准备了解下网站的推广分析策略。
所谓网站推广,目的在于让尽可能多的潜在用户了解并访问网站,通过网站获得有关产品和服务等信息,为最终形成购买决策提供支持。
网站推广策略有很多,seo,email,adv
- 单例模式,sql注入,序列
百合不是茶
单例模式序列sql注入预编译
序列在前面写过有关的博客,也有过总结,但是今天在做一个JDBC操作数据库的相关内容时 需要使用序列创建一个自增长的字段 居然不会了,所以将序列写在本篇的前面
1,序列是一个保存数据连续的增长的一种方式;
序列的创建;
CREATE SEQUENCE seq_pro
2 INCREMENT BY 1 -- 每次加几个
3
- Mockito单元测试实例
bijian1013
单元测试mockito
Mockito单元测试实例:
public class SettingServiceTest {
private List<PersonDTO> personList = new ArrayList<PersonDTO>();
@InjectMocks
private SettingPojoService settin
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(9)使用游标
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*使用游标
*/
--显示游标
--在显式游标中使用FETCH...INTO语句
DECLARE
CURSOR emp_cursor is
select ename,sal from emp where deptno=1;
v_ename emp.ename%TYPE;
v_sal emp.sal%TYPE;
begin
ope
- 【Java语言】动态代理
bit1129
java语言
JDK接口动态代理
JDK自带的动态代理通过动态的根据接口生成字节码(实现接口的一个具体类)的方式,为接口的实现类提供代理。被代理的对象和代理对象通过InvocationHandler建立关联
package com.tom;
import com.tom.model.User;
import com.tom.service.IUserService;
- Java通信之URL通信基础
白糖_
javajdkwebservice网络协议ITeye
java对网络通信以及提供了比较全面的jdk支持,java.net包能让程序员直接在程序中实现网络通信。
在技术日新月异的现在,我们能通过很多方式实现数据通信,比如webservice、url通信、socket通信等等,今天简单介绍下URL通信。
学习准备:建议首先学习java的IO基础知识
URL是统一资源定位器的简写,URL可以访问Internet和www,可以通过url
- 博弈Java讲义 - Java线程同步 (1)
boyitech
java多线程同步锁
在并发编程中经常会碰到多个执行线程共享资源的问题。例如多个线程同时读写文件,共用数据库连接,全局的计数器等。如果不处理好多线程之间的同步问题很容易引起状态不一致或者其他的错误。
同步不仅可以阻止一个线程看到对象处于不一致的状态,它还可以保证进入同步方法或者块的每个线程,都看到由同一锁保护的之前所有的修改结果。处理同步的关键就是要正确的识别临界条件(cri
- java-给定字符串,删除开始和结尾处的空格,并将中间的多个连续的空格合并成一个。
bylijinnan
java
public class DeleteExtraSpace {
/**
* 题目:给定字符串,删除开始和结尾处的空格,并将中间的多个连续的空格合并成一个。
* 方法1.用已有的String类的trim和replaceAll方法
* 方法2.全部用正则表达式,这个我不熟
* 方法3.“重新发明轮子”,从头遍历一次
*/
public static v
- An error has occurred.See the log file错误解决!
Kai_Ge
MyEclipse
今天早上打开MyEclipse时,自动关闭!弹出An error has occurred.See the log file错误提示!
很郁闷昨天启动和关闭还好着!!!打开几次依然报此错误,确定不是眼花了!
打开日志文件!找到当日错误文件内容:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- [矿业与工业]修建一个空间矿床开采站要多少钱?
comsci
地球上的钛金属矿藏已经接近枯竭...........
我们在冥王星的一颗卫星上面发现一些具有开采价值的矿床.....
那么,现在要编制一个预算,提交给财政部门..
- 解析Google Map Routes
dai_lm
google api
为了获得从A点到B点的路劲,经常会使用Google提供的API,例如
[url]
http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/directions/json?origin=40.7144,-74.0060&destination=47.6063,-122.3204&sensor=false
[/url]
从返回的结果上,大致可以了解应该怎么走,但
- SQL还有多少“理所应当”?
datamachine
sql
转贴存档,原帖地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-29242841-id-3968998.html、http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-29242841-id-3971046.html!
------------------------------------华丽的分割线--------------------------------
- Yii使用Ajax验证时,如何设置某些字段不需要验证
dcj3sjt126com
Ajaxyii
经常像你注册页面,你可能非常希望只需要Ajax去验证用户名和Email,而不需要使用Ajax再去验证密码,默认如果你使用Yii 内置的ajax验证Form,例如:
$form=$this->beginWidget('CActiveForm', array( 'id'=>'usuario-form',&
- 使用git同步网站代码
dcj3sjt126com
crontabgit
转自:http://ued.ctrip.com/blog/?p=3646?tn=gongxinjun.com
管理一网站,最开始使用的虚拟空间,采用提供商支持的ftp上传网站文件,后换用vps,vps可以自己搭建ftp的,但是懒得搞,直接使用scp传输文件到服务器,现在需要更新文件到服务器,使用scp真的很烦。发现本人就职的公司,采用的git+rsync的方式来管理、同步代码,遂
- sql基本操作
蕃薯耀
sqlsql基本操作sql常用操作
sql基本操作
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年6月1日 17:30:33 星期一
&
- Spring4+Hibernate4+Atomikos3.3多数据源事务管理
hanqunfeng
Hibernate4
Spring3+后不再对JTOM提供支持,所以可以改用Atomikos管理多数据源事务。Spring2.5+Hibernate3+JTOM参考:http://hanqunfeng.iteye.com/blog/1554251Atomikos官网网站:http://www.atomikos.com/ 一.pom.xml
<dependency>
<
- jquery中两个值得注意的方法one()和trigger()方法
jackyrong
trigger
在jquery中,有两个值得注意但容易忽视的方法,分别是one()方法和trigger()方法,这是从国内作者<<jquery权威指南》一书中看到不错的介绍
1) one方法
one方法的功能是让所选定的元素绑定一个仅触发一次的处理函数,格式为
one(type,${data},fn)
&nb
- 拿工资不仅仅是让你写代码的
lampcy
工作面试咨询
这是我对团队每个新进员工说的第一件事情。这句话的意思是,我并不关心你是如何快速完成任务的,哪怕代码很差,只要它像救生艇通气门一样管用就行。这句话也是我最喜欢的座右铭之一。
这个说法其实很合理:我们的工作是思考客户提出的问题,然后制定解决方案。思考第一,代码第二,公司请我们的最终目的不是写代码,而是想出解决方案。
话粗理不粗。
付你薪水不是让你来思考的,也不是让你来写代码的,你的目的是交付产品
- 架构师之对象操作----------对象的效率复制和判断是否全为空
nannan408
架构师
1.前言。
如题。
2.代码。
(1)对象的复制,比spring的beanCopier在大并发下效率要高,利用net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanCopier
Src src=new Src();
BeanCopier beanCopier = BeanCopier.create(Src.class, Des.class, false);
- ajax 被缓存的解决方案
Rainbow702
JavaScriptjqueryAjaxcache缓存
使用jquery的ajax来发送请求进行局部刷新画面,各位可能都做过。
今天碰到一个奇怪的现象,就是,同一个ajax请求,在chrome中,不论发送多少次,都可以发送至服务器端,而不会被缓存。但是,换成在IE下的时候,发现,同一个ajax请求,会发生被缓存的情况,只有第一次才会被发送至服务器端,之后的不会再被发送。郁闷。
解决方法如下:
① 直接使用 JQuery提供的 “cache”参数,
- 修改date.toLocaleString()的警告
tntxia
String
我们在写程序的时候,经常要查看时间,所以我们经常会用到date.toLocaleString(),但是date.toLocaleString()是一个过时 的API,代替的方法如下:
package com.tntxia.htmlmaker.util;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.
- 项目完成后的小总结
xiaomiya
js总结项目
项目完成了,突然想做个总结但是有点无从下手了。
做之前对于客户端给的接口很模式。然而定义好了格式要求就如此的愉快了。
先说说项目主要实现的功能吧
1,按键精灵
2,获取行情数据
3,各种input输入条件判断
4,发送数据(有json格式和string格式)
5,获取预警条件列表和预警结果列表,
6,排序,
7,预警结果分页获取
8,导出文件(excel,text等)
9,修