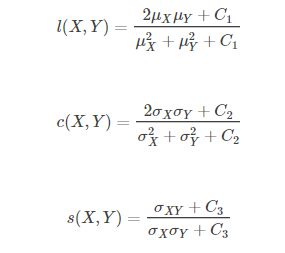图像分割_评价指标_PSNR峰值信噪比和SSIM结构相似度
PSNR
psnr是“Peak Signal to Noise Ratio”的缩写,即峰值信噪比,是一种评价图像的客观标准。
为了衡量经过处理后的影像品质,我们通常会参考PSNR值来衡量某个处理程序能否令人满意。PSNR的单位是dB,数值越大表示失真越小。n为每像素的比特数,一般的灰度图像取8,即像素灰阶数为256。它是原图像与被处理图像之间的均方误差相对于(2n-1)2的对数值(信号最大值的平方,n是每个采样值的比特数),所以PSNR值越大,就代表失真越少。
MATLAB用法的公式如下:
P S N R = 10 ∗ l o g 10 ( ( 2 n − 1 ) 2 / M S E ) PSNR=10*log10((2n-1)2/MSE) PSNR=10∗log10((2n−1)2/MSE)
其中,MSE是原图像与处理图像之间均方误差。
优缺点
PSNR是最普遍,最广泛使用的评鉴画质的客观量测法,不过许多实验结果都显示,PSNR的分数无法和人眼看到的视觉品质完全一致,有可能PSNR较高者看起来反而比PSNR较低者差。这是因为人眼的视觉对于误差的敏感度并不是绝对的,其感知结果会受到许多因素的影响而产生变化(例如:人眼对空间频率较低的对比差异敏感度较高,人眼对亮度对比差异的敏感度较色度高,人眼对一个区域的感知结果会受到其周围邻近区域的影响)。
Matlab代码
function [PSNR, MSE] = psnr(X, Y)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%
% 计算峰值信噪比PSNR
% 将RGB转成YCbCr格式进行计算
% 如果直接计算会比转后计算值要小2dB左右(当然是个别测试)
%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if size(X,3)~=1 %判断图像时不是彩色图,如果是,结果为3,否则为1
org=rgb2ycbcr(X);
test=rgb2ycbcr(Y);
Y1=org(:,:,1);
Y2=test(:,:,1);
Y1=double(Y1); %计算平方时候需要转成double类型,否则uchar类型会丢失数据
Y2=double(Y2);
else %灰度图像,不用转换
Y1=double(X);
Y2=double(Y);
end
if nargin<2
D = Y1;
else
if any(size(Y1)~=size(Y2))
error('The input size is not equal to each other!');
end
D = Y1 - Y2;
end
MSE = sum(D(:).*D(:)) / numel(Y1);
PSNR = 10*log10(255^2 / MSE);
SSIM
SSIM(structural similarity index),结构相似性,是一种衡量两幅图像相似度的指标。该指标首先由德州大学奥斯丁分校的图像和视频工程实验室(Laboratory for Image and Video Engineering)提出。SSIM使用的两张图像中,一张为未经压缩的无失真图像,另一张为失真后的图像。
给定两个图像 x和y , 两张图像的结构相似性可按照以下方式求出
其中, μ X μ_X μX、 μ Y μ_Y μY分别表示图像 X X X和 Y Y Y的均值, σ X σ_X σX、 σ Y σ_Y σY分别表示图像 X X X和 Y Y Y的方差, σ X Y σ_XY σXY表示图像 X X X和 Y Y Y的协方差。
C 1 C1 C1、 C 2 C2 C2、 C 3 C3 C3为常数,为了避免分母为0的情况,通常取 C 1 = ( K 1 ∗ L ) 2 C1=(K1∗L)2 C1=(K1∗L)2,$ C2=(K2∗L)2$, C 3 = C 22 C3=C22 C3=C22, 一般地K1=0.01, K2=0.03, L=255 则,
Matlab公式
function [ssimval, ssimmap] = ssim(varargin)
%SSIM Structural Similarity Index for measuring image quality
% SSIMVAL = SSIM(A, REF) calculates the Structural Similarity Index
% (SSIM) value for image A, with the image REF as the reference. A and
% REF can be 2D grayscale or 3D volume images, and must be of the same
% size and class.
%
% [SSIMVAL, SSIMMAP] = SSIM(A, REF) also returns the local SSIM value for
% each pixel in SSIMMAP. SSIMMAP has the same size as A.
%
% [SSIMVAL, SSIMMAP] = SSIM(A, REF, NAME1, VAL1,...) calculates the SSIM
% value using name-value pairs to control aspects of the computation.
% Parameter names can be abbreviated.
%
% Parameters include:
%
% 'Radius' - Specifies the standard deviation of
% isotropic Gaussian function used for
% weighting the neighborhood pixels around a
% pixel for estimating local statistics. This
% weighting is used to avoid blocking
% artifacts in estimating local statistics.
% The default value is 1.5.
%
% 'DynamicRange' - Positive scalar, L, that specifies the
% dynamic range of the input image. By
% default, L is chosen based on the class of
% the input image A, as L =
% diff(getrangefromclass(A)). Note that when
% class of A is single or double, L = 1 by
% default.
%
% 'RegularizationConstants'- Three-element vector, [C1 C2 C3], of
% non-negative real numbers that specifies the
% regularization constants for the luminance,
% contrast, and structural terms (see [1]),
% respectively. The regularization constants
% are used to avoid instability for image
% regions where the local mean or standard
% deviation is close to zero. Therefore, small
% non-zero values should be used for these
% constants. By default, C1 = (0.01*L).^2, C2
% = (0.03*L).^2, and C3 = C2/2, where L is the
% specified 'DynamicRange' value. If a value
% of 'DynamicRange' is not specified, the
% default value is used (see name-value pair
% 'DynamicRange').
%
% 'Exponents' - Three-element vector [alpha beta gamma],
% of non-negative real numbers that specifies
% the exponents for the luminance, contrast,
% and structural terms (see [1]),
% respectively. By default, all the three
% exponents are 1, i.e. the vector is [1 1
% 1].
%
% Notes
% -----
% 1. A and REF can be arrays of upto three dimensions. All 3D arrays
% are considered 3D volumetric images. RGB images will also be
% processed as 3D volumetric images.
%
% 2. Input image A and reference image REF are converted to
% floating-point type for internal computation.
%
% 3. For signed-integer images (int16), an offset is applied to bring the
% gray values in the non-negative range before computing the SSIM
% index.
%
% Example
% ---------
% This example shows how to compute SSIM value for a blurred image given
% the original reference image.
%
% ref = imread('pout.tif');
% H = fspecial('Gaussian',[11 11],1.5);
% A = imfilter(ref,H,'replicate');
%
% subplot(1,2,1); imshow(ref); title('Reference Image');
% subplot(1,2,2); imshow(A); title('Blurred Image');
%
% [ssimval, ssimmap] = ssim(A,ref);
%
% fprintf('The SSIM value is %0.4f.\n',ssimval);
%
% figure, imshow(ssimmap,[]);
% title(sprintf('SSIM Index Map - Mean SSIM Value is %0.4f',ssimval));
% Class Support
% -------------
% Input arrays A and REF must be one of the following classes: uint8,
% int16, uint16, single, or double. Both A and REF must be of the same
% class. They must be nonsparse. SSIMVAL is a scalar and SSIMMAP is an
% array of the same size as A. Both SSIMVAL and SSIMMAP are of class
% double, unless A and REF are of class single in which case SSIMVAL and
% SSIMMAP are of class single.
%
% References:
% -----------
% [1] Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, "Image
% Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural
% Similarity," IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Volume 13,
% Issue 4, pp. 600- 612, 2004.
%
% See also IMMSE, MEAN, MEDIAN, PSNR, SUM, VAR.
% Copyright 2013-2014 The MathWorks, Inc.
narginchk(2,10);
[A, ref, C, exponents, radius] = parse_inputs(varargin{:});
if isempty(A)
ssimval = zeros(0, 'like', A);
ssimmap = A;
return;
end
if isa(A,'int16') % int16 is the only allowed signed-integer type for A and ref.
% Add offset for signed-integer types to bring values in the
% non-negative range.
A = double(A) - double(intmin('int16'));
ref = double(ref) - double(intmin('int16'));
elseif isinteger(A)
A = double(A);
ref = double(ref);
end
% Gaussian weighting function
gaussFilt = getGaussianWeightingFilter(radius,ndims(A));
% Weighted-mean and weighted-variance computations
mux2 = imfilter(A, gaussFilt,'conv','replicate');
muy2 = imfilter(ref, gaussFilt,'conv','replicate');
muxy = mux2.*muy2;
mux2 = mux2.^2;
muy2 = muy2.^2;
sigmax2 = imfilter(A.^2,gaussFilt,'conv','replicate') - mux2;
sigmay2 = imfilter(ref.^2,gaussFilt,'conv','replicate') - muy2;
sigmaxy = imfilter(A.*ref,gaussFilt,'conv','replicate') - muxy;
% Compute SSIM index
if (C(3) == C(2)/2) && isequal(exponents(:),ones(3,1))
% Special case: Equation 13 from [1]
num = (2*muxy + C(1)).*(2*sigmaxy + C(2));
den = (mux2 + muy2 + C(1)).*(sigmax2 + sigmay2 + C(2));
if (C(1) > 0) && (C(2) > 0)
ssimmap = num./den;
else
% Need to guard against divide-by-zero if either C(1) or C(2) is 0.
isDenNonZero = (den ~= 0);
ssimmap = ones(size(A));
ssimmap(isDenNonZero) = num(isDenNonZero)./den(isDenNonZero);
end
else
% General case: Equation 12 from [1]
% Luminance term
if (exponents(1) > 0)
num = 2*muxy + C(1);
den = mux2 + muy2 + C(1);
ssimmap = guardedDivideAndExponent(num,den,C(1),exponents(1));
else
ssimmap = ones(size(A), 'like', A);
end
% Contrast term
sigmaxsigmay = [];
if (exponents(2) > 0)
sigmaxsigmay = sqrt(sigmax2.*sigmay2);
num = 2*sigmaxsigmay + C(2);
den = sigmax2 + sigmay2 + C(2);
ssimmap = ssimmap.*guardedDivideAndExponent(num,den,C(2),exponents(2));
end
% Structure term
if (exponents(3) > 0)
num = sigmaxy + C(3);
if isempty(sigmaxsigmay)
sigmaxsigmay = sqrt(sigmax2.*sigmay2);
end
den = sigmaxsigmay + C(3);
ssimmap = ssimmap.*guardedDivideAndExponent(num,den,C(3),exponents(3));
end
end
ssimval = mean(ssimmap(:));
end
% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
function component = guardedDivideAndExponent(num, den, C, exponent)
if C > 0
component = num./den;
else
component = ones(size(num),'like',num);
isDenNonZero = (den ~= 0);
component(isDenNonZero) = num(isDenNonZero)./den(isDenNonZero);
end
if (exponent ~= 1)
component = component.^exponent;
end
end
function gaussFilt = getGaussianWeightingFilter(radius,N)
% Get 2D or 3D Gaussian weighting filter
filtRadius = ceil(radius*3); % 3 Standard deviations include >99% of the area.
filtSize = 2*filtRadius + 1;
if (N < 3)
% 2D Gaussian mask can be used for filtering even one-dimensional
% signals using imfilter.
gaussFilt = fspecial('gaussian',[filtSize filtSize],radius);
else
% 3D Gaussian mask
[x,y,z] = ndgrid(-filtRadius:filtRadius,-filtRadius:filtRadius, ...
-filtRadius:filtRadius);
arg = -(x.*x + y.*y + z.*z)/(2*radius*radius);
gaussFilt = exp(arg);
gaussFilt(gaussFilt 3)
error(message('images:validate:tooManyDimensions','A and REF',3));
end
% Default values for parameters
dynmRange = diff(getrangefromclass(A));
C = [];
exponents = [1 1 1];
radius = 1.5;
args_names = {'dynamicrange', 'regularizationconstants','exponents',...
'radius'};
for i = 3:2:nargin
arg = varargin{i};
if ischar(arg)
idx = find(strncmpi(arg, args_names, numel(arg)));
if isempty(idx)
error(message('images:validate:unknownInputString', arg))
elseif numel(idx) > 1
error(message('images:validate:ambiguousInputString', arg))
elseif numel(idx) == 1
if (i+1 > nargin)
error(message('images:validate:missingParameterValue'));
end
if idx == 1
dynmRange = varargin{i+1};
validateattributes(dynmRange,{'numeric'},{'positive', ...
'finite', 'real', 'nonempty','scalar'}, mfilename, ...
'DynamicRange',i);
dynmRange = double(dynmRange);
elseif idx == 2
C = varargin{i+1};
validateattributes(C,{'numeric'},{'nonnegative','finite', ...
'real','nonempty','vector', 'numel', 3}, mfilename, ...
'RegularizationConstants',i);
C = double(C);
elseif idx == 3
exponents = varargin{i+1};
validateattributes(exponents,{'numeric'},{'nonnegative', ...
'finite', 'real', 'nonempty','vector', 'numel', 3}, ...
mfilename,'Exponents',i);
exponents = double(exponents);
elseif idx == 4
radius = varargin{i+1};
validateattributes(radius,{'numeric'},{'positive','finite', ...
'real', 'nonempty','scalar'}, mfilename,'Radius',i);
radius = double(radius);
end
end
else
error(message('images:validate:mustBeString'));
end
end
% If 'RegularizationConstants' is not specified, choose default C.
if isempty(C)
C = [(0.01*dynmRange).^2 (0.03*dynmRange).^2 ((0.03*dynmRange).^2)/2];
end
end
参考文章1
参考文章2