Python搭建神经网络
前向传播的线性函数
线性函数。神经网络的层数,3层的神经网络其隐藏层为两层。以三层神经网络为例:h1=x.dot(w1)+b1,h2=h1.dot(w2)+b2,scores=h2.dot(w3)+b3
批量归一化
批量归一化这一步骤在线性函数和激活函数之间,将h1=x.dot(w1)+b1结果拿去激活函数之前进行批量归一化。相当于每一步前向传播都运用了数据预处理的操作,使得加速收敛。
sample_mean = np.mean(x,axis=0)
sample_var = np.var(x,axis=0)
x_hat = (x - sample_mean) / (np.sqrt(sample_var + eps))
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
这四行代码代表了上面的四个公式,np.mean是求均值,np.var求标准差
正则化
损失函数需要正则化:loss += 0.5 * self.reg * np.sum(self.params["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)]**2)
dw的计算需要正则化:grads["W%d" %(ri+1,)] = dw + self.reg * self.params["W%d" %(ri+1,)] #每层的dw计算也需要正则化
反向传播
反向传播主要是为了通过最终的得分与其他得分的比较来获得梯度,从而利用梯度更新参数W和b,不断优化权值参数。
以三层神经网络为例:dh2=dscores.dot(w3.T),dw3=h2.T.dot(dscores),db3= np.sum(dscores,axis=0);
dh1=dscores.dot(w2.T),dw2=h1.T.dot(dh2),db2 = np.sum(dh2,axis=0);
dx=dscores.dot(w1.T),dw2=x.T.dot(dh1),db1 = np.sum(dh1,axis=0);
self.params["b%d" %(i+1,)] += -learning_rate * grads["b%d" %(i+1,)]
self.params["W%d" %(i+1,)] += -learning_rate * grads["W%d" %(i+1,)]
数据预处理
PCA是一种预处理形式。在这种处理中,先对数据进行零中心化处理,然后计算协方差矩阵,它展示了数据中的相关性结构。
# 假设输入数据矩阵X的尺寸为[N x D]
X -= np.mean(X, axis = 0) # 对数据进行零中心化(重要)
cov = np.dot(X.T, X) / X.shape[0] # 得到数据的协方差矩阵
数据协方差矩阵的第(i, j)个元素是数据第i个和第j个维度的协方差。具体来说,该矩阵的对角线上的元素是方差。还有,协方差矩阵是对称和半正定的。我们可以对数据协方差矩阵进行SVD(奇异值分解)运算。
U,S,V = np.linalg.svd(cov)
U的列是特征向量,S是装有奇异值的1维数组(因为cov是对称且半正定的,所以S中元素是特征值的平方)。为了去除数据相关性,将已经零中心化处理过的原始数据投影到特征基准上:
Xrot = np.dot(X,U) # 对数据去相关性
U的列是标准正交向量的集合(范式为1,列之间标准正交),所以可以把它们看做标准正交基向量。因此,投影对应x中的数据的一个旋转,旋转产生的结果就是新的特征向量。如果计算Xrot的协方差矩阵,将会看到它是对角对称的。np.linalg.svd的一个良好性质是在它的返回值U中,特征向量是按照特征值的大小排列的。我们可以利用这个性质来对数据降维,只要使用前面的小部分特征向量,丢弃掉那些包含的数据没有方差的维度。 这个操作也被称为主成分分析( Principal Component Analysis 简称PCA)降维:
Xrot_reduced = np.dot(X, U[:,:100]) # Xrot_reduced 变成 [N x 100]
经过上面的操作,将原始的数据集的大小由[N x D]降到了[N x 100],留下了数据中包含最大方差的100个维度。通常使用PCA降维过的数据训练线性分类器和神经网络会达到非常好的性能效果,同时还能节省时间和存储器空间。
全过程
http://study.163.com/course/courseLearn.htm?courseId=1003223001&from=study#/learn/text?lessonId=1051303712&courseId=1003223001
一些技巧
超参数更新
采用随机搜索,比如 lr=10**uniform[-6,1),re=10**uniform[-5,5),需要注意边界,阶段搜索从粗到细,粗搜索一个周期,然后取决于最佳结果出现在哪里,缩小范围精搜索5个周期。dropout = uniform(0,1)
参数更新
SGD+Nesterov动量
v_prev = v # 存储备份
v = mu * v - learning_rate * dx # 速度更新保持不变
x += -mu * v_prev + (1 + mu) * v # 位置更新变了形式
或者Adam
m = beta1*m + (1-beta1)*dx
v = beta2*v + (1-beta2)*(dx**2)
x += - learning_rate * m / (np.sqrt(v) + eps)
学习率退火
典型的值是每过5个周期就将学习率减少一半,或者每20个周期减少到之前的0.1。或者当验证集错误率停止下降,就乘以一个常数(比如0.5)来降低学习率。
交叉训练
比起交叉验证最好使用一个验证集,在大多数情况下,一个尺寸合理的验证集可以让代码更简单,不需要用几个数据集来交叉验证。
ANN.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
class TwoLayerNet(object):
def __init__(self,hidden_dims=[200,100],input_dim=3*32*32+1,num_calsses=10,dropout=0,use_batchnorm=False,reg=0.0,weight_scale=math.sqrt(2/3073),dtype=np.float64,seed=None,std=1e-4):
self.use_batchnorm = use_batchnorm
self.use_dropout = dropout>0
self.reg = reg
self.num_layers = 1+len(hidden_dims)
self.dtype = dtype
self.params = {}
in_dim = input_dim
for i,h_dim in enumerate(hidden_dims): #enumerate的for循环,i对应的是层数,h_dim对应的该层的值
self.params["W%d" %(i+1,)] = weight_scale * np.random.randn(in_dim,h_dim) #循环,对每一层W初始化
self.params["b%d" %(i+1,)] = np.zeros((h_dim,)) #循环,对每一层b初始化
if use_batchnorm: #判断是否归一化
self.params["gamma%d" %(i+1,)] = np.ones((h_dim,)) #初始化每一层的gamma和beta参数
self.params["beta%d" %(i+1,)] = np.zeros((h_dim,))
in_dim = h_dim
self.params["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)] = weight_scale * np.random.randn(in_dim,num_calsses) #输出层的W和b参数初始化
self.params["b%d" %(self.num_layers,)] = np.zeros((num_calsses,))
self.dropout_param = {}
if self.use_dropout: #判断随机失活
self.dropout_param = {'mode':'train','p':dropout}
if seed is not None: #随机失活的种子
self.dropout_param['seed'] = seed
self.bn_params = []
if self.use_batchnorm:
self.bn_params = [{'mode':'train'}for i in range(self.num_layers-1)] #bn_params的前num_layers-1层mode对应的参数是train
for k,v in self.params.items():
self.params[k] = v.astype(dtype)
#################################loss损失函数#######################################################################################
def loss(self, X, y=None): #损失函数,返回损失值和梯度值
X = X.astype(self.dtype) #精度转换
mode = 'test'if y is None else 'train' #若有y则为train,无y则为test
if self.dropout_param is not None:
self.dropout_param['mode'] = mode
if self.use_batchnorm:
for bn_param in self.bn_params:
bn_param['mode'] = mode
scores = None
fc_mix_cache = {}
if self.use_dropout:
dp_cache = {}
out = X
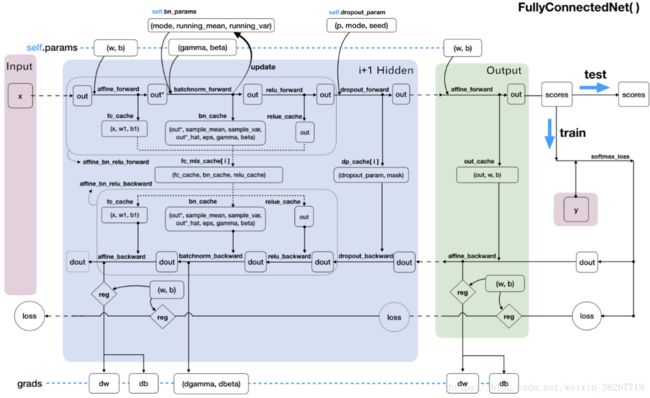
for i in range(self.num_layers-1):
w,b = self.params["W%d" %(i+1,)],self.params["b%d" %(i+1,)]
if self.use_batchnorm:
gamma = self.params["gamma%d" %(i+1,)]
beta = self.params["beta%d" %(i+1,)]
out,fc_mix_cache[i] = self.affine_bn_relu_forward(out,w,b,gamma,beta,self.bn_params[i])
#第一层的返回值是out和fc_mix_cache[1],out为batchnorm和relu激活函数之后的loss,fc_mix_cache返回值是(fc_cache,bn_cache,relu_cache)
#其中fc_cache为计算前的(x,w,b),bn_cache为batchnorm的各个参数,relu_cache为x*w+b之后的h,先x*w+b,再激活,再批量归一化
else:
out,fc_mix_cache[i] = self.affine_relu_forward(out,w,b)
if self.use_dropout:
out,dp_cache[i] = dropout_forward(out,self.dropout_param)
#最后输出层的w和b
w = self.params["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)]
b = self.params["b%d" %(self.num_layers,)]
out,out_cache = self.affine_forward(out,w,b)
#out为最终输出的scores,out_cache为隐藏层最后一层的(x,w,b),若只有一层隐藏层,那就是h1,w2,b2
scores = out
if mode == 'test': #如果是test模式loss函数就只返回scores
return scores
loss,grads = 0.0,{}
#根据最终的scores和y标签的比较,来得到损失值,和dout即dscores=probs=exp_scores / np.sum(exp_scores, axis=1, keepdims=True)
loss,dout = self.softmax_loss(scores,y)
#损失函数正则化
loss += 0.5 * self.reg * np.sum(self.params["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)]**2)
dout,dw,db = self.affine_backward(dout,out_cache)#对最后一层,通过dout和(x,w,b)来获得dx,dw,db
#dw的计算需要进行正则化,db则不需要
grads["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)] = dw + self.reg * self.params["W%d" %(self.num_layers,)]
grads["b%d" %(self.num_layers,)] = db
for i in range(self.num_layers-1): #对所有的隐藏层求dx,dw,db
ri = self.num_layers-2-i
#每一层都进行一次损失函数正则化
loss +=0.5 * self.reg * np.sum(self.params["W%d" %(ri+1,)]**2)
if self.use_dropout:
dout = dropout_backward(dout,dp_cache[ri])
if self.use_batchnorm: #判断是否进行批量归一化
#若函数中的dout为dh2,返回的dout为dh1,fc_mix_cache[ri],fc_mix_cache返回值是(fc_cache,bn_cache,relu_cache)
#其中fc_cache为计算前的(x,w,b)
dout,dw,db,dgamma,dbeta = self.affine_bn_relu_backward(dout,fc_mix_cache[ri])
grads["gamma%d" %(ri+1,)] = dgamma
grads["beta%d" %(ri+1,)] = dbeta
else:
dout,dw,db = self.affine_relu_backward(dout,fc_mix_cache[ri])
#传是传的fc_mix_cache[ri]=(fc_cache,bn_cache,relu_cache),用只用fc_cache和relu_cache
grads["W%d" %(ri+1,)] = dw + self.reg * self.params["W%d" %(ri+1,)] #每层的dw计算也需要正则化
grads["b%d" %(ri+1,)] = db
return loss,grads #返回的grads包括每层的dw,db,dgamma,dbeta
def train(self, X, y, X_val, y_val,learning_rate=1e-2, learning_rate_decay=0.95,
reg=1e-5, num_iters=1000,batch_size=200, verbose=False):
#batch_size=200,每次迭代抽取200个样本进行损失值和梯度的计算
num_train = X.shape[0]
iterations_per_epoch = max(num_train / batch_size, 1)
loss_history = []
train_acc_history = []
val_acc_history = []
for it in range(num_iters):
X_batch = None
y_batch = None
sample_index = np.random.choice(num_train, batch_size, replace=True)
X_batch = X[sample_index, :] # (batch_size,D)
y_batch = y[sample_index] # (1,batch_size)
loss, grads = self.loss(X_batch, y=y_batch)
loss_history.append(loss) #每次循环所得的loss存在一个loss_history
################对参数进行更新##############
for i in range(self.num_layers-1): #对所有的隐藏层求dx,dw,db
grads["b%d" %(i+1,)] = grads["b%d" %(i+1,)].reshape(-1)
self.params["b%d" %(i+1,)] += -learning_rate * grads["b%d" %(i+1,)]
self.params["W%d" %(i+1,)] += -learning_rate * grads["W%d" %(i+1,)]
############################################
if it % 100 == 0: #循环,每迭代一次就输出一个loss
print ('iteration %d / %d: loss %f' % (it, num_iters, loss))
if it % iterations_per_epoch == 0: #循环结束
train_acc = (self.predict(X_batch) == y_batch)
val_acc = (self.predict(X_val) == y_val)
train_acc_history.append(train_acc)
val_acc_history.append(val_acc)
learning_rate *= learning_rate_decay #学习率衰减
return loss_history
def predict(self, X):#预测是没有y,则采用test模式
y_pred = None
scores = self.loss(X,y_pred)
y_pred = np.argmax(scores, axis=1) #返回最高分数的标签list
return y_pred
#############################################################前向传播#############################################################
def affine_bn_relu_forward(self,x,w,b,gamma,beta,bn_param): #先xw+b,再relu,再bathnorm的forward
a,fc_cache = self.affine_forward(x,w,b) #xw+b,返回值a=h(i+1),fc_cache=x,w,b
a_bn,bn_cache = self.batchnorm_forward(a,gamma,beta,bn_param) #批量归一化,a_bn为归一化后的h
out,relu_cache = self.relu_forward(a_bn) #激活函数
cache = (fc_cache,bn_cache,relu_cache)
return out,cache
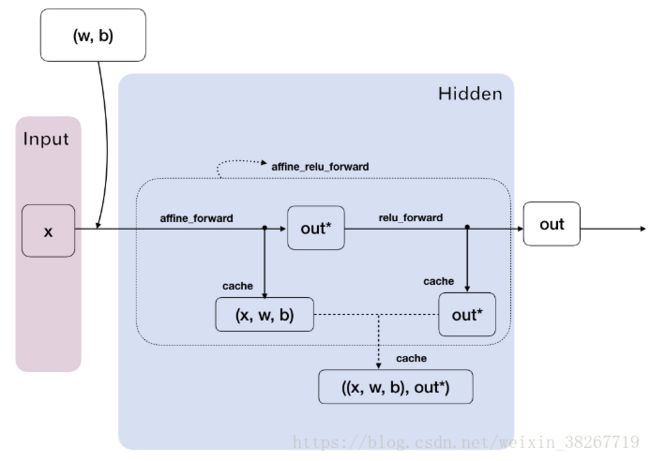
def affine_relu_forward(self,x,w,b):
a,fc_cache = self.affine_forward(x,w,b)
out,relu_cache = self.relu_forward(a)
cache = (fc_cache,relu_cache)
return out,cache
def affine_forward(self,x,w,b):
out = None
reshape_x = np.reshape(x,(x.shape[0],-1))
out = reshape_x.dot(w)+b
cache = (x,w,b)
return out,cache
def relu_forward(self,x):
out = np.maximum(0,x)
cache = x
return out,cache
##############################批量归一化####################################
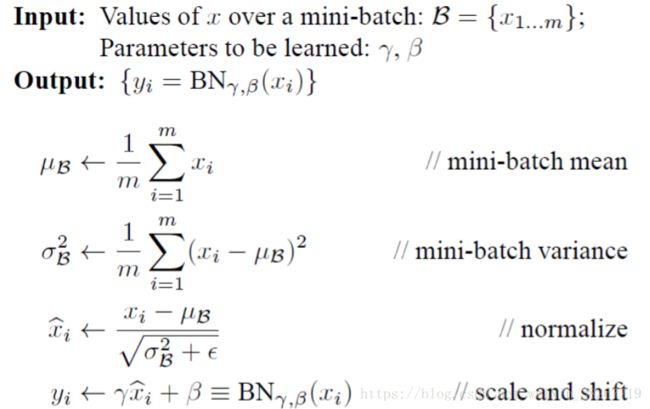
def batchnorm_forward(self,x,gamma,beta,bn_params):
mode = bn_params['mode'] #bn_params['mode']
eps = bn_params.get('eps',1e-5)
momentum = bn_params.get('momentum',0.9)
N,D = x.shape
running_mean = bn_params.get('running_mean',np.zeros(D,dtype=x.dtype))
running_var = bn_params.get('running_var',np.zeros(D,dtype=x.dtype))
out,cache = None,None
if mode == 'train': #代表1train
sample_mean = np.mean(x,axis=0)
sample_var = np.var(x,axis=0)
x_hat = (x - sample_mean) / (np.sqrt(sample_var + eps))
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
cache = (x,sample_mean,sample_var,x_hat,eps,gamma,beta)
running_mean = momentum * running_mean + (1 - momentum) * sample_mean
running_var = momentum * running_var + (1 - momentum) * sample_var
elif mode == 'test': #0代表test
out = (x - running_mean) * gamma / (np.sqrt(running_var + eps)) + beta
else:
raise ValueError('Invaild forward batchnorm mode "%s"' % mode)
bn_params['running_mean'] = running_mean
bn_params['running_var'] = running_var
return out,cache
###########################随机失活#############################3
def dropout_forward(x,dropout_param):
p,mode = dropout_param['p'],dropout_param['mode']
if 'seed' in dropout_param:
np.random.seed(dropout_param['seed'])
mask = None
out = None
if mode =='train':
keep_prob = 1-p
mask = (np.random.rand(*x.shape)0 ) * dout #与所有x中元素为正的位置处,位置对应于dout矩阵的元素保留,其他都取0
return dx
def dropout_backward(dout,cache):
dropout_param,mask = cache
mode = dropout_param['mode']
dx = None
if mode =='train':
dx = mask * dout
elif mode =='test':
dx = dout
return dx
#######################批量归一化##############################
def batchnorm_backward(self,dout,cache):
x,mean,var,x_hat,eps,gamma,beta = cache
N = x.shape[0]
dgamma = np.sum(dout*x_hat,axis=0)
dbeta = np.sum(dout*1.0,axis=0)
dx_hat = dout * gamma
dx_hat_numerator = dx_hat / np.sqrt(var + eps)
dx_hat_denominator = np.sum(dx_hat * (x - mean),axis=0)
dx_1 = dx_hat_numerator
dvar = -0.5 * ((var + eps) ** (-1.5)) * dx_hat_denominator
dmean = -1.0 * np.sum(dx_hat_numerator,axis=0) + dvar * np.mean(-2.0 * (x-mean),axis=0)
dx_var =dvar * 2.0 / N * (x - mean)
dx_mean = dmean * 1.0 / N
dx = dx_1 + dx_var + dx_mean
return dx,dgamma,dbeta
##################################################################
ANNexercise.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle as p
import numpy as np
import os
def load_CIFAR_batch(filename):
""" 载入cifar数据集的一个batch """
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
datadict = p.load(f, encoding='latin1')
X = datadict['data']
Y = datadict['labels']
X = X.reshape(10000, 3, 32, 32).transpose(0, 2, 3, 1).astype("float")
Y = np.array(Y)
return X, Y
def load_CIFAR10(ROOT):
""" 载入cifar全部数据 """
xs = []
ys = []
for b in range(1, 6):
f = os.path.join(ROOT, 'data_batch_%d' % (b,))
X, Y = load_CIFAR_batch(f)
xs.append(X) #将所有batch整合起来
ys.append(Y)
Xtr = np.concatenate(xs) #使变成行向量,最终Xtr的尺寸为(50000,32*32*3)
Ytr = np.concatenate(ys)
del X, Y
Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR_batch(os.path.join(ROOT, 'test_batch'))
return Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 载入CIFAR-10数据集
cifar10_dir = 'datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)
# 看看数据集中的一些样本:每个类别展示一些
print('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)
print('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape)
print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)
print('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)
num_train=40000
num_validation=5000
num_test=5000
num_dev=500
mask=range(num_train,num_train+num_validation)
X_val=X_train[mask]
y_val=y_train[mask]
mask=range(num_train)
X_train=X_train[mask]
y_train=y_train[mask]
mask=np.random.choice(num_train,num_dev,replace=False)
X_dev=X_train[mask]
y_dev=y_train[mask]
mask=range(num_test)
X_test=X_test[mask]
y_test=y_test[mask]
X_train=np.reshape(X_train,(X_train.shape[0],-1))
X_dev=np.reshape(X_dev,(X_dev.shape[0],-1))
X_val=np.reshape(X_val,(X_val.shape[0],-1))
X_test=np.reshape(X_test,(X_test.shape[0],-1))
print('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)
print('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape)
print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)
print('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)
#首先训练数据,计算图像的平均值
mean_image=np.mean(X_train,axis=0)#计算每一列特征的平均值,共32*32*3个特征
print(mean_image[:10]) #查看指定特征的数据
plt.figure(figsize=(4,4)) #指定画框框图的大小
plt.imshow(mean_image.reshape((32,32,3)).astype('uint8')) #将平均值可视化
#plt.show()
X_train-=mean_image #去中心化
X_dev-=mean_image
X_test-=mean_image
X_val-=mean_image
X_train=np.hstack([X_train,np.ones((X_train.shape[0],1))]) #多出了包含常量1的1个维度
X_dev=np.hstack([X_dev,np.ones((X_dev.shape[0],1))])
X_test=np.hstack([X_test,np.ones((X_test.shape[0],1))])
X_val=np.hstack([X_val,np.ones((X_val.shape[0],1))])
import ANN
learning_rates=[1e-2]
regularization_strengths = [0.6]
results={}
best_val=-1
best_ann = None
for rate in learning_rates:
for regular in regularization_strengths:
ann=ANN.TwoLayerNet()
loss_history=ann.train(X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val,learning_rate=rate, learning_rate_decay=0.95,reg=regular, num_iters=1000,batch_size=2000, verbose=False)
y_train_pred=ann.predict(X_train)
accuracy_train = np.mean(y_train==y_train_pred)
y_val_pred=ann.predict(X_val)
accuracy_val = np.mean(y_val==y_val_pred)
results[(rate,regular)] = (accuracy_train,accuracy_val)
if (best_val < accuracy_val):
best_val = accuracy_val
best_ann = ann
for lr,reg in sorted(results):
train_accuracy,val_accuracy = results[(lr,reg)]
print('lr %e reg %e train accuracy: %f val accracy: %f'%(lr,reg,train_accuracy,val_accuracy))
print('best_val_accuracy: %f'%(best_val))
y_tset_pred = best_ann.predict(X_test)
acc_test = np.mean(y_test == y_tset_pred)
print('test_accuracy: %f'%(acc_test))