LaTeX基本命令使用教程(清晰实例)(Overleaf平台)(论文排版)
前言:本文是笔者在学习LaTeX的记录文档,主要是一些常用命令,发至博客分享给大家,笔者的感受是熟悉这些常用命令后即可上手编辑简单的论文,效率很高,体验比word好很多。希望本文能够对LaTeX的初学者有所帮助,有任何问题可以在评论区留言,笔者写的一个小实例在文末。(我使用的是Overleaf平台,具体使用哪个平台进行LaTeX排版属于个人习惯问题,但是语法是通用的)
Overleaf
Overleaf是一个使用LaTeX进行多人协同编辑的平台,可以免费注册和使用,不用下载LaTeX软件,是最为著名的LaTeX在线协作系统。主要特色是有LaTeX插件,编辑功能十分完善,有实时预览(即编即看,无需手动编译)的功能。科研工作者可以在各大期刊的网站上下载到其Overleaf模板,进行论文写作(不同模板的排版方式(比如“作者”和“地址”)的格式不同)。在注册Overleaf后会有详细的指引,在此不再赘述,平台是纯英文的,需要使用者适应,这也是科研工作者的必备素质。
Overleaf开发界面
一、文本/排版:
1、定版型:
documentclass [A] {B}
A:①字体10pt(默认值),11pt,12pt,例子:\documentclass[11pt]{article};
②纸张大小有几个,最常见的就是a4paper,letterpaper(默认值),例子:\documentclass[a4paper]{article};
③单双面oneside(article,report默认值),twoside(book默认值),例子:\documentclass[twoside]{article};
④组合实现:\documentclass[a4paper,twoside,11pt]{article}顺序随意;
B:①常用:Article(英文科研文章)/report/book;②ctex文档类(支持中文):ctexart/ctexrep/ctexbook;
2、加标题/日期/作者:
在\begin{document}之前输入:\title{标题}\author{作者}\date{日期} ; %输入空格即为空
在\begin{document}之前输入:\maketitle ; %输入后,前三者才生效
3、修改页边距:
\Usepackage{ geometry };
\Gemometry(left=2.54cm,rught=2.54cm,top=3.09cm,bottom=3.09cm); %A4版上下为 2.54厘米;左右为 3.09厘米
4、文本加粗: \textbf{ };
5、左对齐: \noindent ; %本行左对齐不缩进
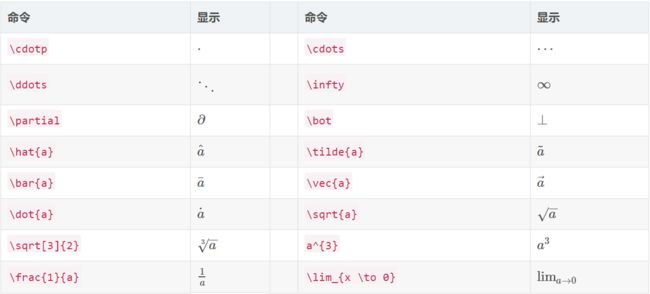
6、换行: \newline或者 \\;
7、空格: 单格\quad 双格\\quad;
8、居中/左对齐/右对齐:
①部分居中:
\centering; %小范围内(比如表格)居中后面部分内容
②全部居中/左对齐/右对齐:
\begin{center/flushleft/flushright}要居中的内容\end{center/flushleft/flushright };
二、公式编辑(2-8均是在1的条件下使用):
1、(1)行中插入公式: $公式$,例子:$\frac{L^4}{2}+\frac{L^3}{6}-\frac{4L}{3}$;
(2)行间插入公式(自动带上公式标号),\begin{equation}公式\end{equation},
例子:\begin{equation}\frac{L^4}{2}+\frac{L^3}{6}-\frac{4L}{3}\end{equation};
2、粗体(向量或矩阵):用\mathbf{}(有时\textbf{}仍然有用);
3、上标:字母^上标;下标:字母_下标;
4、括号:\left(括号内容\right) 或者直接输入();
5、分数:\frac{分子}{分母};
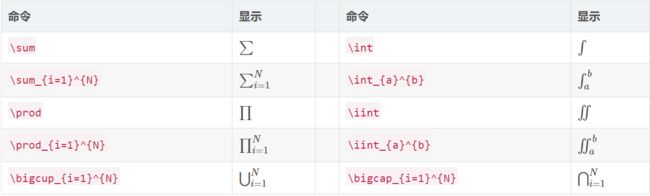
6、求和:\sum_{下标}^{上标};
7、符号(求余符号为\%):
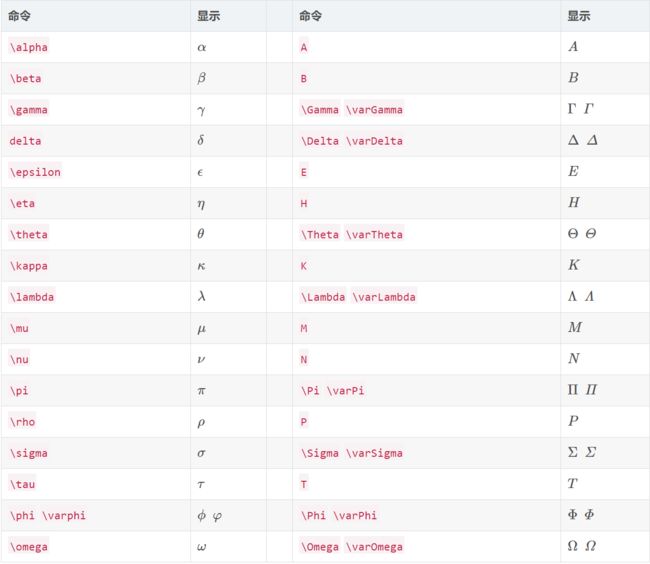
(1)希腊字母:
(2)基本运算符:
(3)积分运算符:
(4)其他符号:
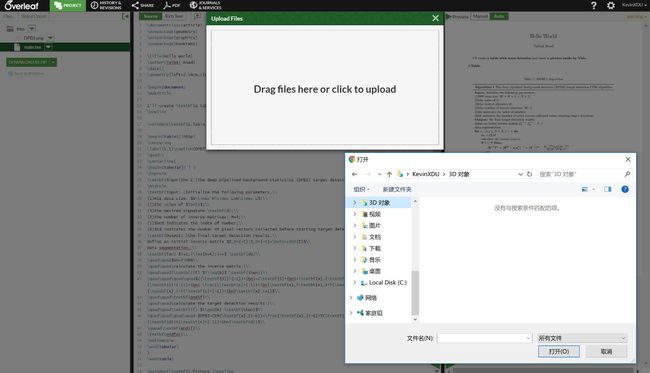
三、插入图片:
1、首先将需要插入的图片上传到当前编辑文件的云端库中;
2、其次开始编程:
\usepackage{graphicx} %加入头文件
\begin{figure}[!htpb]/[H] %[htbp]是自动排版;[H]固定位置
\centering %图片居中
\includegraphics[scale=0.3]/[width=4.5in]{DPBS.png} %设置大小和名称
\caption{DPBS}\label{1} %图片名称和图片标号
\end{figure} %结束
其中,{figure}的可选参数[!htbp]:
h代表here,将表格排在当前文字位置 ;t表示将表格放在下一页的top (页首);p表示p-page-of-its-own;
b表示将表格放在当前页的 bottom(底部);!表示忽略美观因素,尽可能按照参数指定的方式来处理图片浮动位置;
四、插入表格:
1、粗线( 表格的第一根线和最后一根线比表格中的横线更粗一些):\usepackage{booktabs}
\toprule %第一根线
\midrule %中间的线
\bottomrule %最后一根线
2、调整位置:
\begin{table}[!htbp]
\end{table}
其中,{table}有若干可选参数[!htbp]
h代表here,将表格排在当前文字位置 ;t表示将表格放在下一页的 top (页首) ;p表示p-page-of-its-own;
b表示将表格放在当前页的 bottom (底部) ;!表示忽略美观因素,尽可能按照参数指定的方式来处理表格浮动位置;
3、居中:
长度不长时\centering
长度过长时\centerline{} %把tabular的所有内容放进去
4、制表:
\begin{tabular}{|l |c | r |} %“|”表示竖线,“l/c/r”表示格内居左/中/右,
A & B & C\\ %“&”分隔不同列内的内容,“\\”表示换行
E & F & G\\
\end{tabular}
5、标签和名称:\label{label}\caption{name}
6、普通线:\hline或\cline{2-5} %后者可以画如下图这种表格:
7、行高:
\renewcommand\arraystretch{2} %表格行高设置为默认的2倍
五、参考文献:
1、格式:
(1)期刊:作者名.题目.期刊(缩写,斜体)年份(加粗),卷(斜体),页码.
(2)会议:作者名.题目.会议名称(不缩写,斜体),年份(不加粗);pp. 页码.
2、函数:
\begin{thebibliography}{}
\bibitem{ref label}
内容 %{\em要斜体的内容} {\bf要加粗的内容}
\end{thebibliography}
3、例子:
(1)效果图:
(2)代码:
\begin{thebibliography}{}
\bibitem{ref 1 }
Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image segmentation using subspace multinomial
logistic regression and Markov random fields. {\em IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.} {\bf 2012}, {\em 50}, 809-823.
\end{thebibliography}六、引用:(label是为了方便之后直接引用):
1、参考文献加label:在命令\bibitem写{ref A }
引用:\cite{ref A }
2、表格/图片加label:\label{ A }
引用:\ref{ A }
七、笔者的实例:
1、效果图:
2、代码:
\documentclass{article} %英文科研文献常用类型
\usepackage{geometry} %更改页边距所需
\usepackage{graphicx} %插入图片所需
\usepackage{booktabs} %表格线条加粗所需
\geometry{left=2.54cm,right=2.54cm,top=1.0cm,bottom=1.0cm} %更改页边距
\begin{document} %开始正文
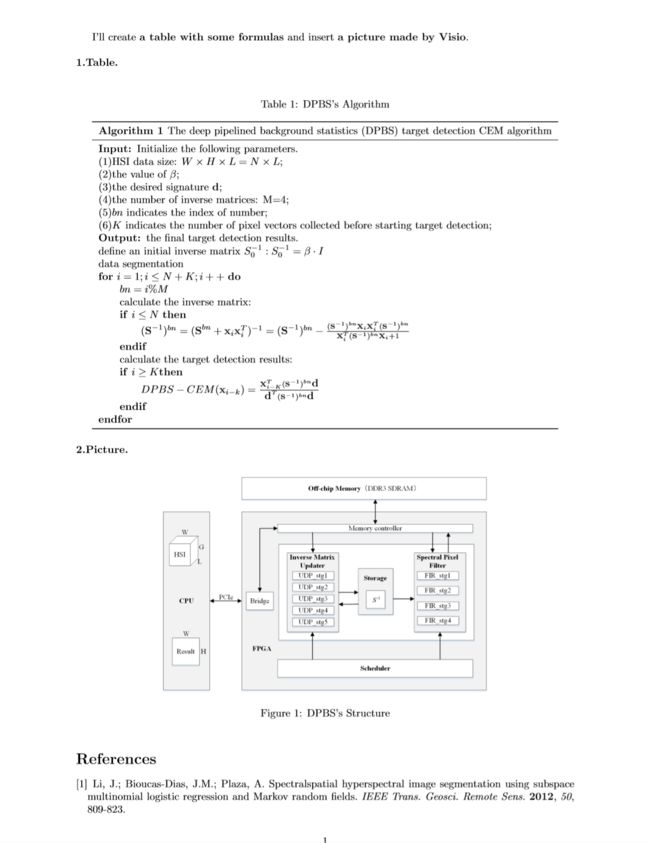
I'll create \textbf{a table with some formulas} and insert \textbf{a picture made by Visio}.
\newline\newline %换行
\noindent\textbf{1.Table.}\newline %加粗左对齐显示标题
\begin{table}[!htbp] %开始制表
\label{1.1}\caption{DPBS's Algorithm} %加标签和名称
\\ %换行
\centerline{ %表格居中开始
\begin{tabular}{ l } %构造只有一列的左对齐的表格
\toprule %第一条粗线
\textbf{Algorithm 1 }The deep pipelined background statistics (DPBS) target detection CEM algorithm\\ %第一行标题
\midrule %中间普通粗细的线
\textbf{Input: }Initialize the following parameters.\\ %以下为第二条线和第三条线之间的内容
(1)HSI data size: $W\times H\times L=N\times L$;\\
(2)the value of $\beta$;\\
(3)the desired signature \textbf{d};\\
(4)the number of inverse matrices: M=4;\\
(5)$bn$ indicates the index of number;\\
(6)$K$ indicates the number of pixel vectors collected before starting target detection;\\
\textbf{Output: }the final target detection results.\\
define an initial inverse matrix $S_0^{-1}:S_0^{-1}=\beta\cdot{I}$\\
data segmentation:\\
\textbf{for} $i=1;i\leq{N+K};i++$ \textbf{do}\\
\quad\quad$bn=i\%M$\\
\quad\quad{calculate the inverse matrix:}\\
\quad\quad{\textbf{if} $i\leq{N}$ \textbf{then}}\\
\quad\quad\quad\quad$({\textbf{S}}^{-1})^{bn}=(\textbf{S}^{bn}+\textbf{x}_i\textbf{x}_i^T)^{-1}=(\textbf{S}^{-1})^{bn}-\frac{(\textbf{s}^{-1})^{bn}\textbf{x}_i\textbf{x}_i^T(\textbf{s}^{-1})^{bn}}{\textbf{x}_i^T(\textbf{s}^{-1})^{bn}\textbf{x}_i+1}$\\
\quad\quad\textbf{endif}\\
\quad\quad{calculate the target detection results:}\\
\quad\quad\textbf{if} $i\geq{K} \textbf{then}$\\
\quad\quad\quad\quad $DPBS-CEM(\textbf{x}_{i-k})=\frac{\textbf{x}_{i-K}^T(\textbf{s}^{-1})^{bn}\textbf{d}}{\textbf{d}^T(\textbf{s}^{-1})^{bn}\textbf{d}}$\\
\qquad\textbf{endif}\\
\textbf{endfor}\\
\bottomrule %最后一条粗线
\end{tabular} %构造表格结束
} %表格居中结束
\end{table} %制表结束
\noindent\textbf{2.Picture.}\newline %加粗左对齐显示标题
\begin{figure}[!htbp] %开始插图
\centering %图片居中
\includegraphics[scale=0.55]{DPBS.png} %确定图片大小/位置
\caption{DPBS's Structure}\label{1.1} %加名称和标签
\end{figure} %结束插图
\begin{thebibliography}{} %开始编辑参考文献
\bibitem{ref1.1} %加标签
Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias,J.M.; Plaza, A. Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image segmentation usingsubspace multinomial logistic regression and Markov random fields. {\em IEEETrans. Geosci. Remote Sens.} {\bf 2012}, {\em 50}, 809-823.
\end{thebibliography} %结束编辑参考文献
\end{document} %结束正文####### 转载请注明出处 https://blog.csdn.net/gentleman_qin/article/details/79963396 ########