aiohttpdemo_polls 小结
小引
廖雪峰老师的python3实战部分(个人博客),是基于aiohttp的,之前跟着廖老师写的时候,有许多问题很困惑,最近打算重写一遍。重写之前,发现aiohttp的在线文档中有多个project_demos,遂选择了一个polls练手,重新熟悉一下用法。
另外一个demo_chat涉及websocket编程,以后再做。
Requirements
- aiohttp
- aiohttp_jinja2
- jinja2
- aiopg (for accessing a PostgreSQL database from the asyncio)
另外,数据库选用的是PostgreSQL。
Structures
aiohttpdemo_polls/
- static/
- templates/
- settings.py
- db.py
- routes.py
- middlewares.py
- views.py
- main.py
config/
init_db.py
Pipfiles
main.py
- 建立app
app = web.Application() - init_app()涉及多种设定,包括:
- 载入app的配置
app['config'] = get_config(argv),get_config() 由 settings.py定义。 - 设定模板的aiohttp_jinja2.setup():
aiohttp_jinja2.setup(app, loader=jinja2.FileSystemLoader(_templates_path)) - 建立/关闭数据库connection的init_pg 和 close_pg (db.py定义),通过
app.on_startup.append(init_pg) 和 app.on_cleanup.append(close_pg)完成。 - 设定路由
setup_routes(app),routes.py定义。routes direct to handlers, 即本项目中的views.py。 - 设定中间件,
setup_middlewares(app),middlewares.py定义。
- 载入app的配置
- init_app完成初始设定,返回app, 然后main()载入配置执行(注:port设定了8080,与postgres的5432不同)。
settings.py
- 定义 get_confgi(argv),return需要的配置(config/polls.yaml中定义的配置;yaml比xml更易构建传播)。
- trafaret,validation library with support to convert data structures.
- Trafaret-config , 封装了用于检查配置的
trafaret,并可以载入yaml格式,并能定位真实文件的错误(Trafaret-config is a wrapper that loads yaml and checks config using trafaret while keeping track of actual lines of file where error has happened.) - 以上两个lib,有时间再研究一下。
db.py
- 利用SQLAlchemy的ORM,建立 两个类:Table question 和 Table choice。其中Table question 的 字段
pub_date用的default=sqlalchemy.sql.func.now()·。Table choice 设置外键question_id,并采用ondelete='CASCADE', when PrimaryKey item deleted, ForeignKey item also deleted. - RecordNotFound 类,”“”Requested record in database was not found”“”。
- init_pg(app),建立数据库连接,
engine = await aiopg.sa.create_engine(conf),采用sqlalchemy的异步驱动aiopg.sa建立engine,其中conf = app['config']['postgres']。(app['config'] = get_config(argv),在settings.py定义)。 然后获得app['db'] = engine, 用以后建立连接,即app[‘db’].connect()。 - close_pg(app),关闭数据库连接,
await app['db'].wait_closed()。 - 封装的用于查询的函数,
async def get_question(conn, question_id),基于conn 和 question_id,查询到的记录(question_record, choice_records)。因为基于某个question_id,只查到一个question_text相关的内容,所有是question_record,而对应的choice内容是多条,用choice_records。 - 查询语法举例:
result = await conn.execute(question.select().where(question.c.id==question_id)),直接用table_name.select(),然后叠加.where(),其中c是 sqlalchemy的expression language语法,是column的意思。 - 封装
async def vote(conn, question_id, choice_id),其中的更新语法类似,但涉及一个returning用法,即choice.update().returning(*choice.c).where().where().values(),表示更新后返回的是choice的所有columns;另外可以多重.where()限定条件;最后的.values(votes = choice.c.votes+1),直接用字段 votes 操作。 - 注意,所有涉及I/O操作的部分,都需要
await。一旦决定采用异步的方式,都必须保持一致。
routes.py
setup_routes() 建立四类不同的url与相应的handler的映射,方法是:
router.add_route(method, path, handler, *, name=None, expect_handler=None)而
router.add_get(path, handler, *, name=None, allowe_head=True, **kwargs)其实是明确了method的router.add_route(); router.add_post()类似。
但注意:router.add_get(path, handler, name=’route’) adds two routes: first for GET with name ‘route’ and second for HEAD with name ‘route-head’.
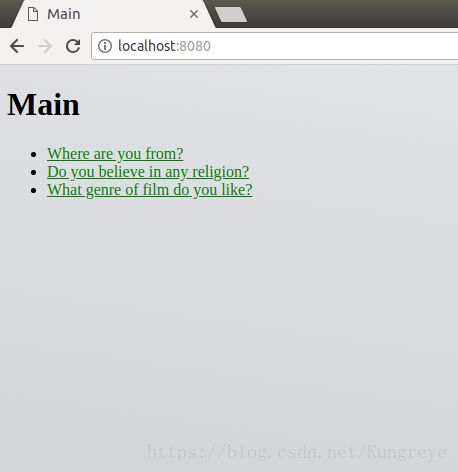
app.router.add_get('/', index, name='index'), 索引页即polls的questions列表首页。app.router.add_get('/poll/{question_id}', poll, name='poll'), 某question_id的poll选项app.router.add_get('/poll/{question_id}/results', results, name='results')某question_id的poll 结果app.router.add_post('/poll/{question_id}/vote', vote, name='vote'),无独立页面展示,作为过渡url,从poll/question_id 页面的form提交—-> /poll/question_id/vote —> /poll/question_id/results。setup_static_routes(app),语法: add_static(prefix, path, *, name=None, expect_handler=None,….), 本项目为app.router.add_static('/static/', path=PROJECT_ROOT / 'static', name='static')。
注: add_static() 只用于开发. 生产中,静态文件由web服务器处理(如 nginx or apache.)
views.py
- views.py 即是 handlers.py, 定义了routes.py中出现的四类url的处理函数。收到某个request,经服务器解析后, 按照定义的路由(app.router.add_route()),到达对应的handler,handler根据match_info,利用相关函数(已有的或自己封装实现,如db.py中的 get_question() 及vote()) 成对数据库的数据操作。
- 每个handler,均经过 @aiohttp_jinja2.template()修饰,参数为 main.py中
aiohttp_jinja2.setup(app, loader=jinja2.FileSystemLoader(_templates_path))定义的loader中的相关模板 *.html 。
- index(request)
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('index.html')
async def index(request):
async with request.app['db'].acquire() as conn: # aiopg.sa.create_engine(URL)
cursor = await conn.execute(db.question.select())
records = await cursor.fetchall()
questions = [dict(row) for row in records]
return {'questions': questions}注意: 通常的fetchall() 返回a list of tuples,但这里的fetchall(), like aiopg.Cursor.fetchall(), but 。而RowProxy,是 a collections.abc.Mapping for representing a row in query result; Keys are column names, values are result values.
returns a list of RowProxy.
所以上面代码中的records,就是 a list of RowProxy 或者 a list of collections.abc.Mapping。用dict(row)处理(??),得到 a list of dicts 形如 [{‘id’: xx, ‘question_text’:xx}, {…}, {…}], 最终传给模板变量questions进行渲染。
对应:index.html:
<li><a href="{{ url('poll', question_id=question.id) }}">{{ question.question_text }}a>li>其中 ‘poll’ 指的是,对应此链接url的路由为routes.py定义的路由‘poll’,变量question_id则不言而喻。
相当于单击polls主页 (/) 的某个question 时,会进入某个question的详情页(/poll/question_id/)。
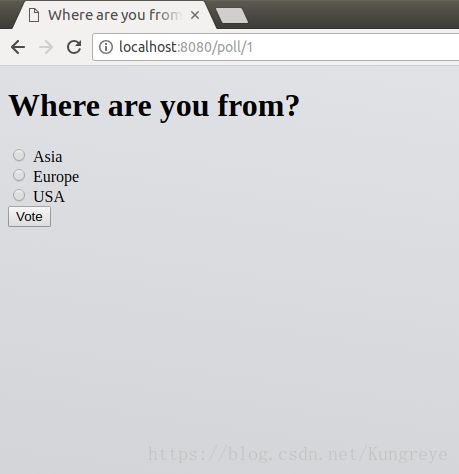
- poll(request)
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('detail.html')
async def poll(request):
async with request.app['db'].acquire() as conn:
question_id = request.match_info['question_id']
try:
question, choices = await db.get_question(conn, question_id) # get_question() defined in db.py
except db.RecordNotFound as e: # class RecordNotFound defined in db.py
raise web.HTTPNotFound(text=str(e))
return {
'question': question,
'choices': choices
}对应: detail.html
<form action="{{ url('vote', question_id=question.id) }}" method="post">
{% for choice in choices %}
<input type="radio" name="choice" id="choice{{ loop.index }}" value="{{ choice.id }}" />
<label for="choice{{ loop.index }}">{{ choice.choice_text }}label><br/>
{% endfor %}
<input type="submit" value="Vote">
form>form: action,对应的 method 为 post,对应的url的路由为’vote’。
input:“radio”表示type为单选按钮,提交form时,input 的 name为‘choice’,value为choice.id。
- vote(request)
上面的 poll(request) 提交 form 后,跳转到本路由。
‘vote’ 路由,无对应的独立 html 页面,
async def vote(request):
async with request.app['db'].acquire() as conn:
question_id = int(request.match_info['question_id']) # why int()
data = await request.post() # see detail.html --> the post of
try:
choice_id = int(data['choice']) # 'choice' is the name of
except (KeyError, TypeError, ValueError) as e:
raise web.HTTPBadRequest(text='You have not specified choice value') from e
try:
await db.vote(conn, question_id, choice_id)
except db.RecordNotFound as e:
raise web.HTTPNotFound(text=str(e))
router = request.app.router # get router info of app
url = router['results'].url_for(question_id=str(question_id))
# router['results']: router.add_get('/poll/{question_id}/results', results, name='results')
return web.HTTPFound(location=url)最后利用 router[‘results’].url_for() 方法,跳转到 /poll/{question_id}/results页面
- results(request)
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('results.html')
async def results(request):
async with request.app['db'].acquire() as conn:
question_id = request.match_info['question_id']
try:
question, choices = await db.get_question(conn, question_id)
except db.RecordNotFound as e:
raise web.HTTPNotFound(text=str(e))
return {
'question': question,
'choices': choices
}和 poll(request) 代码相同,只是对应的html模板不同。
对应:results.html
{% block content %}
<ul>
{% for choice in choices %}
<li>{{ choice.choice_text }} -- {{ choice.votes }} vote(s) li>
{% endfor %}
ul>
<a href="{{ url('poll', question_id=question.id) }}">Vote again?a>
{% endblock %}链接的 url 路由为 ‘poll’, 即点击 ‘Vote again?’, 会跳转到 /poll/question_id 页面。
middlewares.py
封装了两个异常处理函数 handle_404(request) 和 handle_500(request)。
注意: create_error_middleware(overrides),其实是个带参数的decorator,并且内部还调用了@web.middleware来修饰 error_middleware(request, handler)。
def create_error_middleware(overrides):
@web.middleware
async def error_middleware(request, handler):
try:
response = await handler(request)
override = overrides.get(response.status)
if override:
return await override(request)
return response
except web.HTTPException as ex:
override = overrides.get(ex.status)
if override:
return await override(request)
raise
return error_middlewareinit_db.py
- 定义
DSN = "postgresql://{user}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}" - 利用 ADMIN,USER, TESTER 的 CONFIG_PATH,得到对应的CONFIG
- 然后DSN.format(CONFIG) 出对应的URI
- sqlalchemy.create_engine(URL) 。初始化database,无需异步的aiopg.sa,直接sqlalchemy.create_engine()即可。
def setup_db(config):
db_name = config['database']
db_user = config['user']
db_password = config['password']
conn = admin_engine.connect()
conn.execute("DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS %s" % db_name)
# conn.execute("CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS %s WITH PASSWORD '%s'" % (db_user, db_password))
conn.execute("CREATE DATABASE %s ENCODING 'UTF8'" % db_name)
conn.execute("GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE %s TO %s" % (db_name,db_user))
conn.close()- 从sqlalchemy引入MetaData,创建表格:
def create_tables(engine=test_engine):
meta = MetaData()
meta.create_all(bind=engine, tables=[question, choice])
def drop_tables(engine=test_engine):
meta = MetaData()
meta.drop_all(bind=engine, tables=[question, choice])demo_images