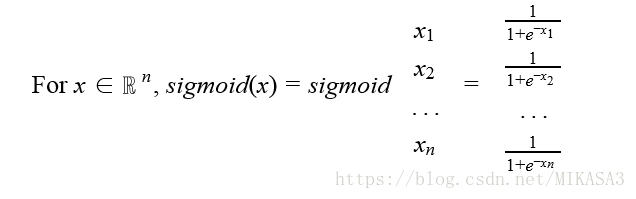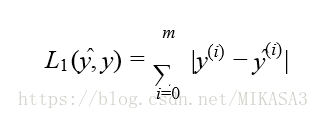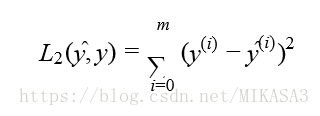
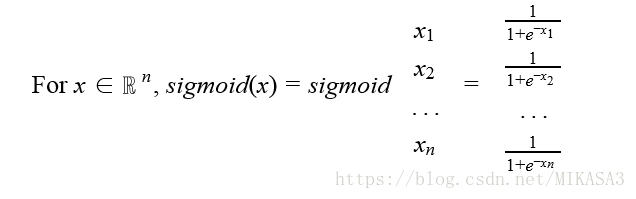



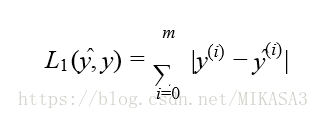
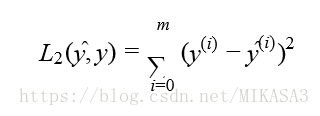
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
from lr_utils import load_dataset
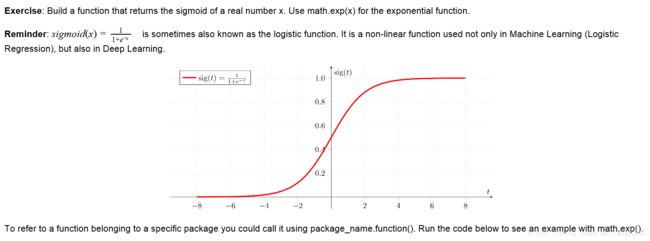
def sigmoid(x):#激活函数
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1 / (1+np.exp(-x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
# GRADED FUNCTION: sigmoid_derivative
def sigmoid_derivative(x):#激活函数的导数
"""
Compute the gradient (also called the slope or derivative) of the sigmoid function with respect to its input x.
You can store the output of the sigmoid function into variables and then use it to calculate the gradient.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array
Return:
ds -- Your computed gradient.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
ds = s*(1-s)
### END CODE HERE ###
return ds
# GRADED FUNCTION: image2vector
def image2vector(image):#图片像素矩阵转置成一个列向量
"""
Argument:
image -- a numpy array of shape (length, height, depth)
Returns:
v -- a vector of shape (length*height*depth, 1)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
v = image.reshape((image.shape[0]*image.shape[1], image.shape[2])) # v.shape[0] = a ; v.shape[1] = b ; v.shape[2] = c
### END CODE HERE ###
return v
# GRADED FUNCTION: normalizeRows
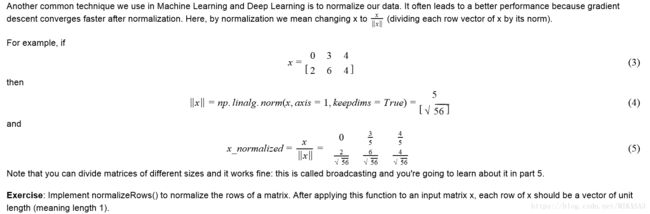
def normalizeRows(x):#正则化,使用第二范数
"""
Implement a function that normalizes each row of the matrix x (to have unit length).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n, m)
Returns:
x -- The normalized (by row) numpy matrix. You are allowed to modify x.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
# Compute x_norm as the norm 2 of x. Use np.linalg.norm(..., ord = 2, axis = ..., keepdims = True)
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x, ord = 2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
# Divide x by its norm.
x = x / x_norm
### END CODE HERE ###
return x
# GRADED FUNCTION: softmax
def softmax(x):#计算softmax函数值
"""Calculates the softmax for each row of the input x.
Your code should work for a row vector and also for matrices of shape (n, m).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n,m)
Returns:
s -- A numpy matrix equal to the softmax of x, of shape (n,m)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
# Apply exp() element-wise to x. Use np.exp(...).
x_exp = np.exp(x)
# Create a vector x_sum that sums each row of x_exp. Use np.sum(..., axis = 1, keepdims = True).
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
# Compute softmax(x) by dividing x_exp by x_sum. It should automatically use numpy broadcasting.
s = x_exp / x_sum
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
# GRADED FUNCTION: L1
def L1(yhat, y):#计算L1损失函数
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L1 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
loss = np.sum(np.abs(y-yhat))
### END CODE HERE ###
return loss
# GRADED FUNCTION: L2
def L2(yhat, y):#计算L2损失函数
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L2 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
loss = np.sum((y-yhat) * (y-yhat))
### END CODE HERE ###
return loss
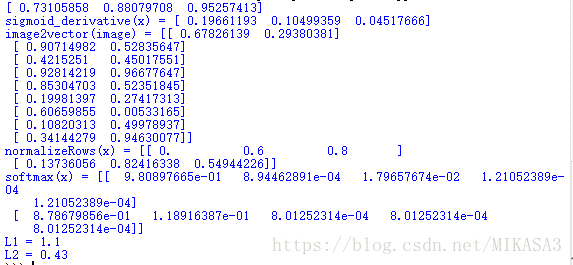
if __name__=='__main__':#测试用例
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print sigmoid(x)
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print ("sigmoid_derivative(x) = " + str(sigmoid_derivative(x)))
# This is a 3 by 3 by 2 array, typically images will be (num_px_x, num_px_y,3) where 3 represents the RGB values
image = np.array([[[ 0.67826139, 0.29380381],
[ 0.90714982, 0.52835647],
[ 0.4215251 , 0.45017551]],
[[ 0.92814219, 0.96677647],
[ 0.85304703, 0.52351845],
[ 0.19981397, 0.27417313]],
[[ 0.60659855, 0.00533165],
[ 0.10820313, 0.49978937],
[ 0.34144279, 0.94630077]]])
print ("image2vector(image) = " + str(image2vector(image)))
x = np.array([
[0, 3, 4],
[1, 6, 4]])
print("normalizeRows(x) = " + str(normalizeRows(x)))
x = np.array([
[9, 2, 5, 0, 0],
[7, 5, 0, 0 ,0]])
print("softmax(x) = " + str(softmax(x)))
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L1 = " + str(L1(yhat,y)))
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L2 = " + str(L2(yhat,y)))