吃饭【网络流】
题目大意:
有 n n 头牛,每头牛有自己喜欢的食物和饮料,每种食物或饮料只有一个。求最多能让多少头牛吃到食物并喝到饮料。
Input I n p u t
4 3 3
2 2 1 2 3 1
2 2 2 3 1 2
2 2 1 3 1 2
2 1 1 3 3Output O u t p u t
3思路:
很明显的最大流题目。这道题匈牙利会超时,正解是 Dinic D i n i c 。
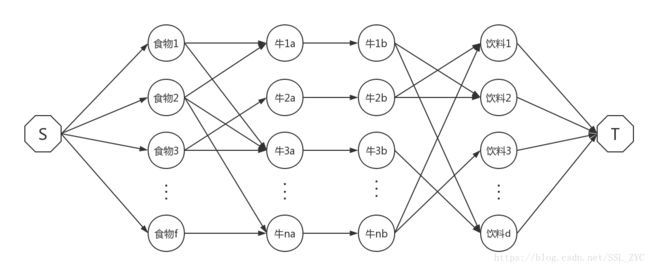
这道题最难的也就是考点是建图。很容易想到这样的建法(权值均为1):

但是这样的话,就有可能一头牛吃多个食物及饮料,例如上图中牛 1 1 可以既吃食物 1 1 ,饮料 2 2 组成的套餐,又可以吃食物 2 2 ,饮料 d d 组成的套餐。
所以,这里就要拆点。将一头牛拆成两头,中间连一条权值为 1 1 的线,就可以保证不会有一头牛吃多组套餐的情况。
代码:
#include int dfs(int u,int low)
{
int lows=0;
if (u==t) return low;
for (int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].next)
{
int v=e[i].to;
if (dep[v]==dep[u]+1&&e[i].c)
{
lows=dfs(v,min(low,e[i].c)); //继续找增广路
if (!lows) continue;
e[i].c-=lows; //正向边
e[(i+1)^1-1].c+=lows; //反向边
return lows;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//建图时牛a编号为1~n,牛b编号为n+1~2n,食物编号为2n+1~2n+f,饮料编号为2n+f+1~2n+f+d
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&f,&d);
s=0;
t=n+n+f+d+1;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&fnum,&dnum);
for (int j=1;j<=fnum;j++) //食物连向牛a
{
scanf("%d",&x);
add(n+n+x,i,1);
add(i,n+n+x,0);
}
for (int j=1;j<=dnum;j++) //牛b连向饮料
{
scanf("%d",&x);
add(n+i,n+n+f+x,1);
add(n+n+f+x,n+i,0);
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) //牛a连向牛b
{
add(i,n+i,1);
add(n+i,i,0);
}
for (int i=1;i<=f;i++) //S连向食物
{
add(s,n+n+i,1);
add(n+n+i,s,0);
}
for (int i=1;i<=d;i++) //饮料连向T
{
add(n+n+f+i,t,1);
add(t,n+n+f+i,0);
}
while (bfs())
{
while (sum=dfs(s,INF))
ans+=sum;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}