比特币中的默克尔树Merkle
比特币中的默克尔树Merkle
简介
Merkle Tree,通常也被称作Hash Tree,顾名思义,就是存储hash值的一棵树。Merkle树的叶子是数据块(例如,文件或者文件的集合)的hash值。非叶节点是其对应子节点串联字符串的hash。
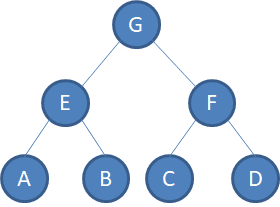
比特币中对应的默克尔树
比特币中区块的定义结构
//
// Nodes collect new transactions into a block, hash them into a hash tree,
// and scan through nonce values to make the block's hash satisfy proof-of-work
// requirements. When they solve the proof-of-work, they broadcast the block
// to everyone and the block is added to the block chain. The first transaction
// in the block is a special one that creates a new coin owned by the creator
// of the block.
//
// Blocks are appended to blk0001.dat files on disk. Their location on disk
// is indexed by CBlockIndex objects in memory.
//
class CBlock
{
public:
// header
int nVersion;
uint256 hashPrevBlock;
uint256 hashMerkleRoot;
unsigned int nTime;
unsigned int nBits; // 记录本区块难度
unsigned int nNonce;
// network and disk
vector vtx;
// memory only
mutable vector vMerkleTree;
// 对应的方法省略,后面用到会单独讲解
};
- 构建块中交易对应的默克尔树
对应的代码如下:
uint256 CBlock::BuildMerkleTree() const
{
vMerkleTree.clear();
foreach(const CTransaction& tx, vtx)
vMerkleTree.push_back(tx.GetHash());
int j = 0;
for (int nSize = vtx.size(); nSize > 1; nSize = (nSize + 1) / 2)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; i += 2)
{
int i2 = min(i+1, nSize-1);
vMerkleTree.push_back(Hash(BEGIN(vMerkleTree[j+i]), END(vMerkleTree[j+i]),
BEGIN(vMerkleTree[j+i2]), END(vMerkleTree[j+i2])));
}
j += nSize;
}
return (vMerkleTree.empty() ? 0 : vMerkleTree.back());
}
举一个例子,假设对应的block中有A,B,C,D四个交易记录(这些交易记录保存在block中的vector
则使用上述构建默克尔树的方法BuildMerkleTree,则使得block中对应的默克尔树结构体vector
- 根据交易在块中的索引查询其对应的默克尔树分支
获取对应的默克尔树的分支在CBlock中对应的方法GetMerkleBranch代码如下:
vector CBolck::GetMerkleBranch(int nIndex) const
{
if (vMerkleTree.empty())
BuildMerkleTree();
vector vMerkleBranch;
int j = 0;
for (int nSize = vtx.size(); nSize > 1; nSize = (nSize + 1) / 2)
{
int i = min(nIndex^1, nSize-1);
vMerkleBranch.push_back(vMerkleTree[j+i]);
nIndex >>= 1;
j += nSize;
}
return vMerkleBranch;
}
- 验证对应的交易是否在默克尔树中
验证某个节点是否在默克尔树中,在CBlock中对应的方法代码如下:
static uint256 CBlock::CheckMerkleBranch(uint256 hash, const vector& vMerkleBranch, int nIndex)
{
if (nIndex == -1)
return 0;
foreach(const uint256& otherside, vMerkleBranch)
{
if (nIndex & 1)
hash = Hash(BEGIN(otherside), END(otherside), BEGIN(hash), END(hash));
else
hash = Hash(BEGIN(hash), END(hash), BEGIN(otherside), END(otherside));
nIndex >>= 1;
}
return hash;
}
验证CheckMerkleBranch方法返回的结果是否和CBlock中对应的默克尔树中对应根的值一样,即如下面代码所示:
if (CBlock::CheckMerkleBranch(GetHash(), vMerkleBranch, nIndex) != pBlock->hashMerkleRoot)
return 0;
对应上面的例子对应的验证过程如下图所示:
比特币交易对应的数据结构
对应的代码如下:
//
// The basic transaction that is broadcasted on the network and contained in
// blocks. A transaction can contain multiple inputs and outputs.
//
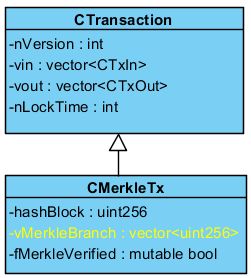
class CTransaction
{
public:
int nVersion;
vector vin;
vector vout;
int nLockTime;
// 方法省略
};
//
// A transaction with a merkle branch linking it to the block chain
//
class CMerkleTx : public CTransaction
{
public:
uint256 hashBlock;
vector vMerkleBranch;
int nIndex;
// memory only
mutable bool fMerkleVerified;
// 方法省略
};
从类图或代码中可以看到CMerkleTx 中有一个属性是vMerkleBranch,表示的是对应的每一个默克尔交易都对应一个默克尔树分支,因此对应默克尔交易可以很快的验证这个交易是否在某个CBlock中。