南邮 | 算法分析与设计实验一:分治策略
题目:用分治法实现一组无序序列的两路合并排序和快速排序以及其它排序算法。
程序代码
#include
}
void Menu(){
//system("cls");
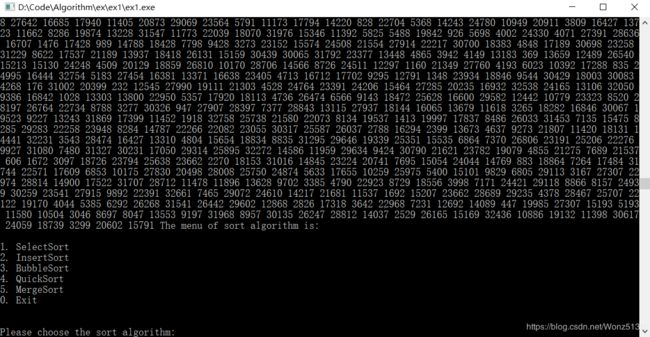
printf("\n\nThe menu of sort algorithm is:\n\n");
printf("1. SelectSort\n");
printf("2. InsertSort\n");
printf("3. BubbleSort\n");
printf("4. QuickSort\n");
printf("5. MergeSort\n");
printf("0. Exit\n");
printf("\n\nPlease choose the sort algorithm:");
}
int main()
{
int *a,*b,*c,*d,*e,*f,*g,choose;
//long long NUM;
//printf("Please enter the size of List:");
//scanf("%lld",&NUM);
a = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
b = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
c = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
d = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
e = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
f = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
g = (int*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(int));
/*
//不用malloc的话,随机生成100000个数时,会出现停止运行
int a[NUM];//乱序
int b[NUM];
int c[NUM];
int d[NUM];//乱序
int e[NUM];
int f[NUM];
int g[NUM];//乱序
*/
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
memset(e,0,sizeof(e));
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
srand((int)time(0));
for(int x = 0;x < NUM;x ++){
a[x]=random(NUM);
b[x]=a[x];
c[x]=a[x];
d[x]=a[x];
e[x]=a[x];
f[x]=a[x];
g[x]=a[x];
//cout<
}
//Output
printf("\nThe initial List is:\n");
Output(a,NUM);
Menu();
scanf("%d",&choose);
switch(choose){
case 1:
//SelectSort(a,NUM);
//Output(a,NUM);
start = clock();
SelectSort(a,NUM);
stop = clock();
Output(a,NUM);
//printf("\nThe List after SelectSort is:\n");
//Output(a,NUM);
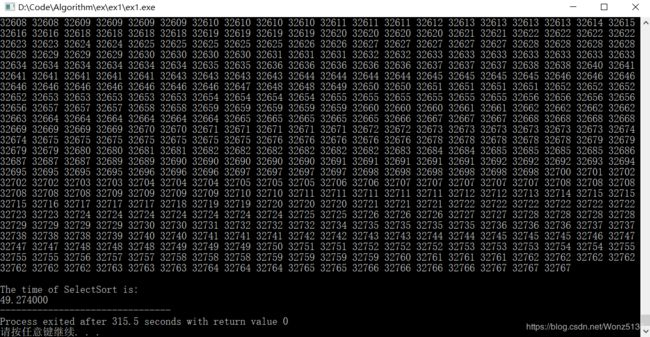
printf("\n\nThe time of SelectSort is:\n");
duration = (double)(stop-start)/(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("%f",duration);
break;
case 2:
InsertSort(a,NUM);
Output(a,NUM);
start = clock();
InsertSort(b,NUM);
stop = clock();
//printf("\nThe List after SelectSort is:\n");
//Output(a,NUM);
printf("\n\nThe time of InsertSort is:\n");
duration = (double)(stop-start)/(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("%f",duration);
break;
case 3:
BubbleSort(a,NUM);
Output(a,NUM);
start = clock();
BubbleSort(c,NUM);
stop = clock();
//printf("\nThe List after SelectSort is:\n");
//Output(a,NUM);
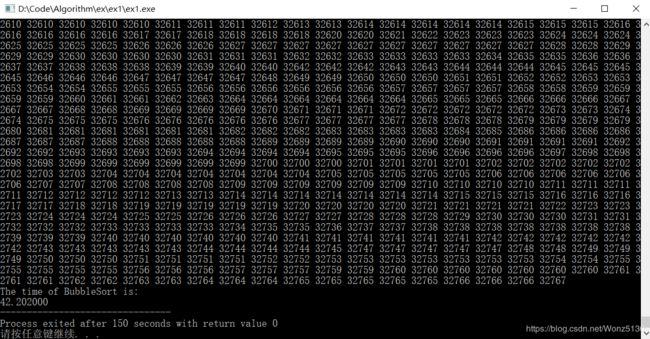
printf("\nThe time of BubbleSort is:\n");
duration = (double)(stop-start)/(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("%f",duration);
break;
case 4:
QuickSort(a,NUM);
Output(a,NUM);
start = clock();
QuickSort(d,NUM);
stop = clock();
//printf("\nThe List after SelectSort is:\n");
//Output(a,NUM);
printf("\nThe time of QuickSort is:\n");
duration = (double)(stop-start)/(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("%f",duration);
break;
case 5:
MergeSort(a,NUM);
Output(a,NUM);
start = clock();
MergeSort(f,NUM);
stop = clock();
//printf("\nThe List after SelectSort is:\n");
//Output(a,NUM);
printf("\nThe time of MergeSort is:\n");
duration = (double)(stop-start)/(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("%f",duration);
break;
case 0:printf("Wrong Input\n");break;
}
return 0;
}
实验结果
测试数据:随机生成100000个数据。
运行结果: