学习斯坦福机器学习笔记—第三课
Logistic Regression
上一次的课程主要解决回归分析问题,这一次的课程主要为分类问题,分类问题也可看做将回归问题的连续性离散化。
1.1 Classification
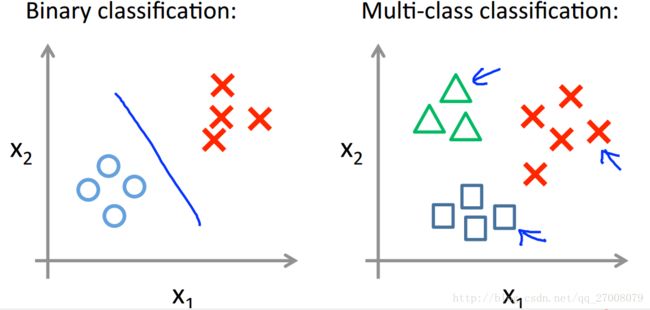
先来谈谈二分类问题。课程中先给出了几个例子。 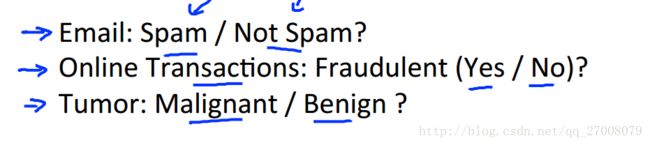
邮件是垃圾邮件还是非垃圾邮件;网上交易是的欺骗性(Y or N);肿瘤是恶性的还是良性的。
对于这些问题,我们可以通过输出值y ϵϵ {0, 1} 来表示。
通过上次的课程,我们可以想到利用假设函数y=hθ(x)y=hθ(x)来预测分类,而普通的hθ(x)hθ(x)函数存在函数值大于1和小于0的情况,于是我们要构造特殊函数使0≤hθ(x)≤10≤hθ(x)≤1。
1.2 Hypothesis Representation
Sigmoid function: hθ(x)=11+e−θTxhθ(x)=11+e−θTx 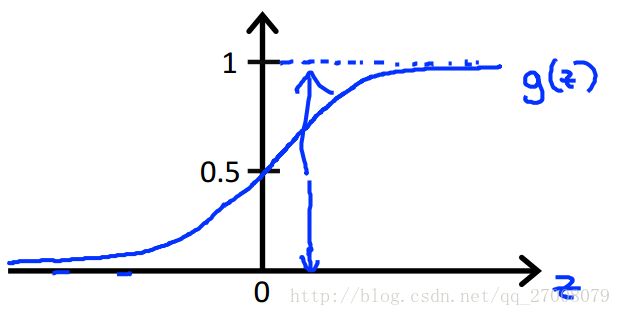
y=hθ(x)=g(θTx)y=hθ(x)=g(θTx)
g(z)=11+e−zg(z)=11+e−z
假设函数代表了一种概率含义
hθ(x)=P(y=1|x;θ)hθ(x)=P(y=1|x;θ)
P(y=1|x;θ)+P(y=0|x;θ)=1P(y=1|x;θ)+P(y=0|x;θ)=1
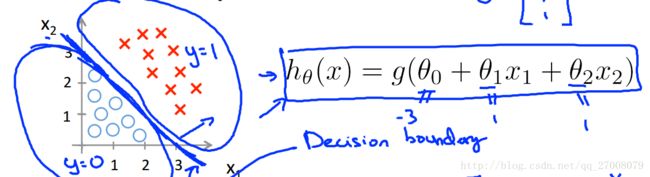
1.3 Decision boundary
y=hθ(x)=g(θTx)y=hθ(x)=g(θTx)
g(z)=11+e−zg(z)=11+e−z
- y=1 if hθ(x)≥0.5,θTx≥0y=1 if hθ(x)≥0.5,θTx≥0
- y=0 if hθ(x)≤0.5,θTx≤0y=0 if hθ(x)≤0.5,θTx≤0
2.1 Cost function
让我们先来看看线性回归中的代价函数
J(θ)=12m∑mi=1(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2J(θ)=12m∑i=1m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2
假如我们将此函数用到逻辑回归中,会有什么问题呢?
因为假设函数hθ(x)hθ(x) 的非线性,代价函数会呈现以下形状。 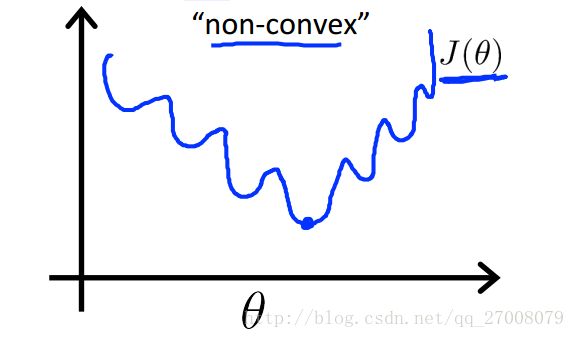
图像呈现出非凸性,也就是说,如果我们运用梯度下降法,不能保证算法收敛到全局最小值。
对于此问题,我们定义的代价函数如下所示 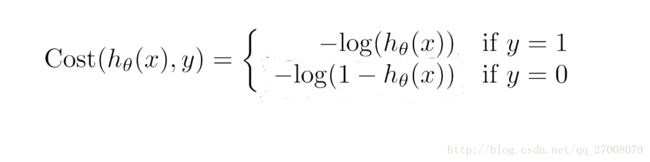
对上面的式子进行简化,总结如下。
J(θ)=12m∑mi=1Cost(hθ(x(i)),y(i))J(θ)=12m∑i=1mCost(hθ(x(i)),y(i))
Cost(hθ(x(i)),y(i))=−y(i)log(hθ(x))−(1−y(i))log(1−hθ(x(i)))Cost(hθ(x(i)),y(i))=−y(i)log(hθ(x))−(1−y(i))log(1−hθ(x(i)))
Gradient Descent
Repeat{
θj=θj−α∂∂θjJ(θ)=1m∑mi=1(hθ(x(i))−y(i))x(i)j for every jθj=θj−α∂∂θjJ(θ)=1m∑i=1m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))xj(i) for every j
}
算法看上去和线性回归保持一致
对于梯度下降法我们可以在matlab中使用如下高级函数 
其中要定义代价函数costFunction:function[jVal,gradient]=costFunction(theta)function[jVal,gradient]=costFunction(theta)
2.2 Multiclass classification: One-vs-all
对于多分类,我们可以给每一类ii训练一个分类器hiθ(x)hθi(x)
来预测y=iy=i的可能性 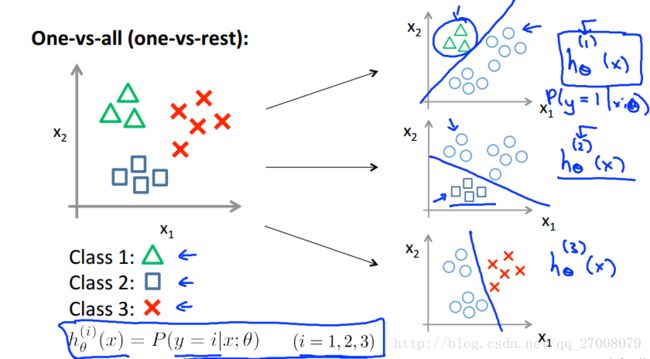
最终预测值为max(hiθ(x))max(hθi(x))
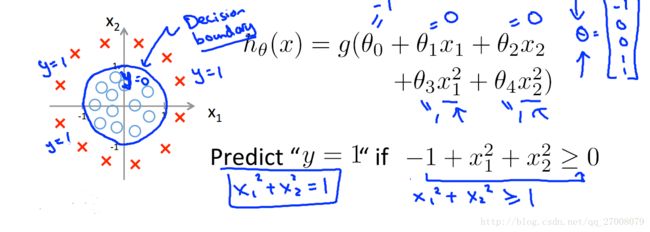
3.1 The problem of overfitting
在数据拟合中,我们来看看下面三种情况。 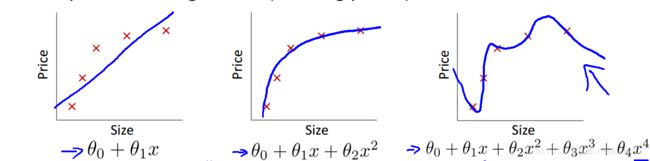
第一种称之为欠拟合,也叫高偏差,
第三种称之为过拟合,也叫高方差,在过拟合中,假设函数很好的匹配了训练集,但并不能很好的匹配测试集。
面对过拟合,我们有两种解决方式。
- 减少特征量。
- 含有所有特征量的情况下,减少θjθj
3.2 Cost function
在采取第二种方式的情况下,我们应修改我们的代价函数如下
J(θ)=12m∑mi=1(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2+λ2m∑nj=1θ2jJ(θ)=12m∑i=1m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2+λ2m∑j=1nθj2
函数中,λλ的取值过小,则抑制θθ的效果越弱,而λλ的取值过大,则会导致欠拟合现象。
这样一来修改下我们的梯度下降过程
Gradient Descent
Repeat{
θ0=1m∑mi=1(hθ(x(i))−y(i))x(i)0θ0=1m∑i=1m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))x0(i)
θj=1m∑mi=1(hθ(x(i))−y(i))x(i)j+λmθj jϵ[1,n]θj=1m∑i=1m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))xj(i)+λmθj jϵ[1,n]
}
逻辑回归时与以上情况类似。
作业代码
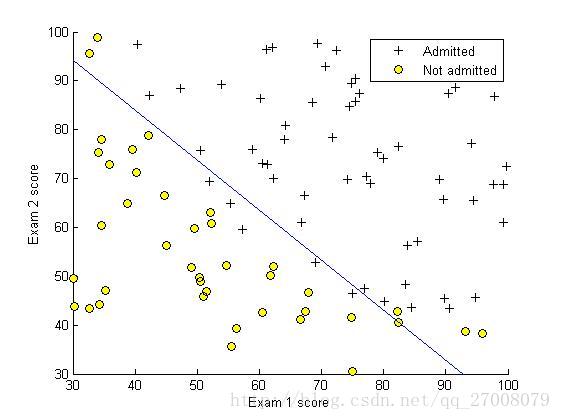
1.这次的作业任务是建立一个逻辑回归模型,判断一个学生能否被一个大学录取,给出的数据集为学生两门课的成绩和是否被录取,通过这些数据来预测一个学生能否被录取。
ex2.m
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 2: Logistic Regression
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the logistic
% regression exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% sigmoid.m
% costFunction.m
% predict.m
% costFunctionReg.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the exam scores and the third column
% contains the label.
data = load('ex2data1.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);
%% ==================== Part 1: Plotting ====================
% We start the exercise by first plotting the data to understand the
% the problem we are working with.
fprintf(['Plotting data with + indicating (y = 1) examples and o ' ...
'indicating (y = 0) examples.\n']);
plotData(X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Exam 1 score')
ylabel('Exam 2 score')
% Specified in plot order
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted')
hold off;
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============ Part 2: Compute Cost and Gradient ============
% In this part of the exercise, you will implement the cost and gradient
% for logistic regression. You neeed to complete the code in
% costFunction.m
% Setup the data matrix appropriately, and add ones for the intercept term
[m, n] = size(X);
% Add intercept term to x and X_test
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
% Compute and display initial cost and gradient
[cost, grad] = costFunction(initial_theta, X, y);
fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Expected cost (approx): 0.693\n');
fprintf('Gradient at initial theta (zeros): \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad);
fprintf('Expected gradients (approx):\n -0.1000\n -12.0092\n -11.2628\n');
% Compute and display cost and gradient with non-zero theta
test_theta = [-24; 0.2; 0.2];
[cost, grad] = costFunction(test_theta, X, y);
fprintf('\nCost at test theta: %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Expected cost (approx): 0.218\n');
fprintf('Gradient at test theta: \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad);
fprintf('Expected gradients (approx):\n 0.043\n 2.566\n 2.647\n');
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 3: Optimizing using fminunc =============
% In this exercise, you will use a built-in function (fminunc) to find the
% optimal parameters theta.
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
% Print theta to screen
fprintf('Cost at theta found by fminunc: %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Expected cost (approx): 0.203\n');
fprintf('theta: \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', theta);
fprintf('Expected theta (approx):\n');
fprintf(' -25.161\n 0.206\n 0.201\n');
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Exam 1 score')
ylabel('Exam 2 score')
% Specified in plot order
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted')
hold off;
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============== Part 4: Predict and Accuracies ==============
% After learning the parameters, you'll like to use it to predict the outcomes
% on unseen data. In this part, you will use the logistic regression model
% to predict the probability that a student with score 45 on exam 1 and
% score 85 on exam 2 will be admitted.
%
% Furthermore, you will compute the training and test set accuracies of
% our model.
%
% Your task is to complete the code in predict.m
% Predict probability for a student with score 45 on exam 1
% and score 85 on exam 2
prob = sigmoid([1 45 85] * theta);
fprintf(['For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission ' ...
'probability of %f\n'], prob);
fprintf('Expected value: 0.775 +/- 0.002\n\n');
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Expected accuracy (approx): 89.0\n');
fprintf('\n');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
sigmoid.m
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid function
% g = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.
% You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
g = 1./(1 + exp(-z));
% =============================================================
end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
costFunction.m
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
J = 1/m*(-y'*log(sigmoid(X*theta)) - (1-y)'*(log(1-sigmoid(X*theta))));
grad = 1/m * X'*(sigmoid(X*theta) - y);
% =============================================================
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
predict.m
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)
m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
p = sigmoid(X * theta)>=0.5;
% =========================================================================
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
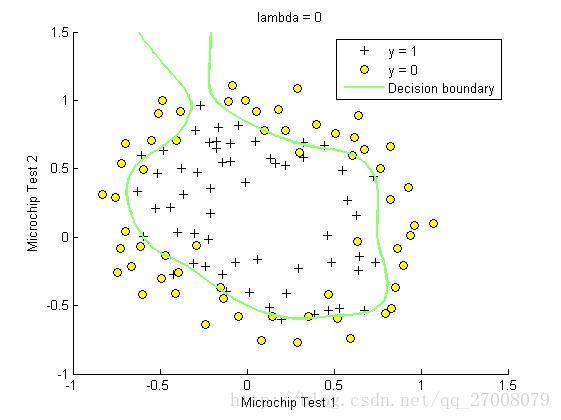
2.检测产品的质量的保证,根据训练集里每个产品经过两次检测和质量好坏,预测新产品经过两次检测后的接受与否。
ex2_reg.m
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 2: Logistic Regression
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the second part
% of the exercise which covers regularization with logistic regression.
%
% You will need to complete the following functions in this exericse:
%
% sigmoid.m
% costFunction.m
% predict.m
% costFunctionReg.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the X values and the third column
% contains the label (y).
data = load('ex2data2.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);
plotData(X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
% Specified in plot order
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0')
hold off;
%% =========== Part 1: Regularized Logistic Regression ============
% In this part, you are given a dataset with data points that are not
% linearly separable. However, you would still like to use logistic
% regression to classify the data points.
%
% To do so, you introduce more features to use -- in particular, you add
% polynomial features to our data matrix (similar to polynomial
% regression).
%
% Add Polynomial Features
% Note that mapFeature also adds a column of ones for us, so the intercept
% term is handled
X = mapFeature(X(:,1), X(:,2));
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1
lambda = 1;
% Compute and display initial cost and gradient for regularized logistic
% regression
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);
fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Expected cost (approx): 0.693\n');
fprintf('Gradient at initial theta (zeros) - first five values only:\n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad(1:5));
fprintf('Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:\n');
fprintf(' 0.0085\n 0.0188\n 0.0001\n 0.0503\n 0.0115\n');
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
% Compute and display cost and gradient
% with all-ones theta and lambda = 10
test_theta = ones(size(X,2),1);
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(test_theta, X, y, 10);
fprintf('\nCost at test theta (with lambda = 10): %f\n', cost);
fprintf('Expected cost (approx): 3.16\n');
fprintf('Gradient at test theta - first five values only:\n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad(1:5));
fprintf('Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:\n');
fprintf(' 0.3460\n 0.1614\n 0.1948\n 0.2269\n 0.0922\n');
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accuracies =============
% Optional Exercise:
% In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
% see how regularization affects the decision coundart
%
% Try the following values of lambda (0, 1, 10, 100).
%
% How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
% the training set accuracy vary?
%
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 0;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
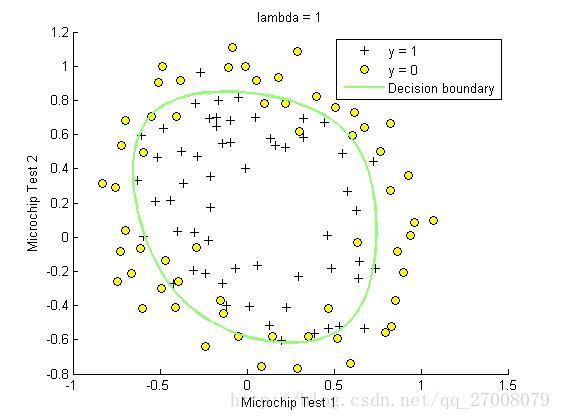
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Expected accuracy (with lambda = 1): 83.1 (approx)\n');
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 1;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Expected accuracy (with lambda = 1): 83.1 (approx)\n');
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 10;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Expected accuracy (with lambda = 1): 83.1 (approx)\n');
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 100;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Expected accuracy (with lambda = 1): 83.1 (approx)\n');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
costFunctionReg.m
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
J = 1/m * (-y' * log(sigmoid(X*theta)) - (1 - y') * log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta))) + lambda/2/m*sum(theta(2:end).^2);
grad(1,:) = 1/m * (X(:, 1)' * (sigmoid(X*theta) - y));
grad(2:size(theta), :) = 1/m * (X(:, 2:size(theta))' * (sigmoid(X*theta) - y))...
+ lambda/m*theta(2:size(theta), :);
% =============================================================
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27