netty源码分析 之九 handler
学习完前面的channel,回头来学习handler 会感觉到很简单的.
handler 这个包里面的类实现 ChannelHandlerAdapter
codec我们最后来看,先看其他
logging
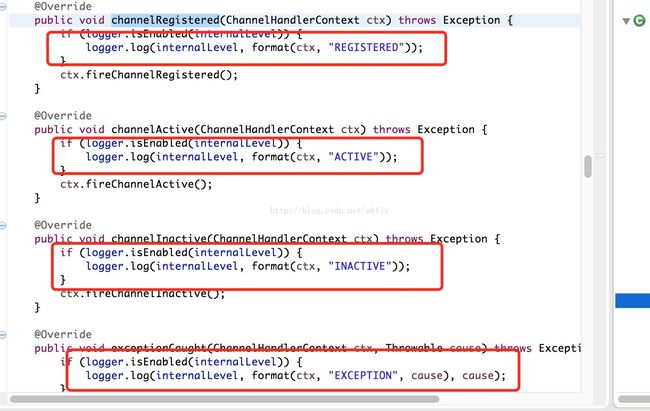
LoggingHandler 为log的输出类, 定义模板,具体实现为 InternalLogger这个接口,log4j logback之类的可以实现接口
ssl
SslHandler 这个类有点不一样,继承自 ByteToMessageDecoder,重点看decoder方法
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, Liststream
ChunkedWriteHandler chunked一般为分块的意思,又如http的chunked编码,指不知道返回的大小。
看其duflush方法
private void doFlush(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
final Channel channel = ctx.channel();
if (!channel.isActive()) {
discard(null);
return;
}
boolean needsFlush;
while (channel.isWritable()) {
if (currentWrite == null) {
currentWrite = queue.poll();
}
if (currentWrite == null) {
break;
}
needsFlush = true;
final PendingWrite currentWrite = this.currentWrite;
final Object pendingMessage = currentWrite.msg;
if (pendingMessage instanceof ChunkedInput) {
final ChunkedInput chunks = (ChunkedInput) pendingMessage;
boolean endOfInput;
boolean suspend;
Object message = null;
try {
message = chunks.readChunk(ctx);
endOfInput = chunks.isEndOfInput();
if (message == null) {
// No need to suspend when reached at the end.
suspend = !endOfInput;
} else {
suspend = false;
}
} catch (final Throwable t) {
this.currentWrite = null;
if (message != null) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(message);
}
currentWrite.fail(t);
closeInput(chunks);
break;
}
if (suspend) {
// ChunkedInput.nextChunk() returned null and it has
// not reached at the end of input. Let's wait until
// more chunks arrive. Nothing to write or notify.
break;
}
if (message == null) {
// If message is null write an empty ByteBuf.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1671
message = Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER;
}
final int amount = amount(message);
ChannelFuture f = ctx.write(message);
if (endOfInput) {
this.currentWrite = null;
// Register a listener which will close the input once the write is complete.
// This is needed because the Chunk may have some resource bound that can not
// be closed before its not written.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/303
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
currentWrite.progress(amount);
currentWrite.success();
closeInput(chunks);
}
});
} else if (channel.isWritable()) {
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
closeInput((ChunkedInput) pendingMessage);
currentWrite.fail(future.cause());
} else {
currentWrite.progress(amount);
}
}
});
} else {
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
closeInput((ChunkedInput) pendingMessage);
currentWrite.fail(future.cause());
} else {
currentWrite.progress(amount);
if (channel.isWritable()) {
resumeTransfer();
}
}
}
});
}
} else {
ctx.write(pendingMessage, currentWrite.promise);
this.currentWrite = null;
}
if (needsFlush) {
ctx.flush();
}
if (!channel.isActive()) {
discard(new ClosedChannelException());
return;
}
}
}timeout
超时handle.
IdleStateHandler 用来计算每次使用的空闲时间,来触发ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(evt); 空闲时间,让用户自己来编写处理逻辑
lastReadTime = lastWriteTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (readerIdleTimeMillis > 0) {
readerIdleTimeout = loop.schedule(
new ReaderIdleTimeoutTask(ctx),
readerIdleTimeMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
if (writerIdleTimeMillis > 0) {
writerIdleTimeout = loop.schedule(
new WriterIdleTimeoutTask(ctx),
writerIdleTimeMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
if (allIdleTimeMillis > 0) {
allIdleTimeout = loop.schedule(
new AllIdleTimeoutTask(ctx),
allIdleTimeMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}ReadTimeoutHandler 读取超时,报异常
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(ReadTimeoutException.INSTANCE);WriteTimeoutHandler 写超时,报异常
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(WriteTimeoutException.INSTANCE);traffic
单词的含义是交通灯的意思,看你代码实现主要是为了控制带宽,及读入与写出的速度
如下图代码中 getTimeToWait方法
public void write(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, final Object msg, final ChannelPromise promise)
throws Exception {
long curtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long size = calculateSize(msg);
if (size > -1 && trafficCounter != null) {
trafficCounter.bytesWriteFlowControl(size);
if (writeLimit == 0) {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
return;
}
// compute the number of ms to wait before continue with the
// channel
long wait = getTimeToWait(writeLimit,
trafficCounter.currentWrittenBytes(),
trafficCounter.lastTime(), curtime);
if (wait >= MINIMAL_WAIT) {
ctx.executor().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
}, wait, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return;
}
}
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}ipfilter
主要用来限制ip,防止误用。其实也很简单注册的时候,调用handleNewChannel ,里面有accpet,如果符合ip规则,则通过,否则直接关闭
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
handleNewChannel(ctx);
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (!handleNewChannel(ctx)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("cannot determine to accept or reject a channel: " + ctx.channel());
} else {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
}
private boolean handleNewChannel(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T remoteAddress = (T) ctx.channel().remoteAddress();
// If the remote address is not available yet, defer the decision.
if (remoteAddress == null) {
return false;
}
// No need to keep this handler in the pipeline anymore because the decision is going to be made now.
// Also, this will prevent the subsequent events from being handled by this handler.
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
if (accept(ctx, remoteAddress)) {
channelAccepted(ctx, remoteAddress);
} else {
ChannelFuture rejectedFuture = channelRejected(ctx, remoteAddress);
if (rejectedFuture != null) {
rejectedFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
} else {
ctx.close();
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* This method is called immediately after a {@link io.netty.channel.Channel} gets registered.
*
* @return Return true if connections from this IP address and port should be accepted. False otherwise.
*/
protected abstract boolean accept(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, T remoteAddress) throws Exception;