五:音频
5.1 音频文件
音频多媒体文件主要是存放音频数据信息,音频文件在录制的过程中把声音信号,通过音频编码,变成音频数字信号保存在某种格式文件中。在播放过程中再对音频文件解码,解码出的信号通过扬声器等设备就可以转成音波。音频文件在编码的过程中数据量很大,所以有的文件格式对于数据进行了压缩,因此音频文件可以分为:
- 无损格式,是非压缩数据格式,文件很大一般不适合移动设备,例如WAV、AU、APE等文件。
- 有损格式,对于数据进行了压缩,压缩后丢掉了一些数据,例如:MP3、(WMA)windows Media Audio等文件。
1.WAV文件
WAV文件目前是最流行的无损压缩格式。WAV文件的格式灵活,可以储存多种类型的音频数据。由于文件较大不太适合于移动设备这些存储容量小的设备。
2.MP3文件
MP3(MPEG Audio Layer3)格式现在非常流行,MP3是一种有损压缩格式,它尽可能地去掉人耳无法感觉的部分和不敏感的部分。MP3是利用MPEG Audio Layer3的技术,将数据以1:10甚至1:12的压缩率,压缩成容量较小的文件,这么高的压缩比率非常适合存储容量小的移动设备。
3.WMA文件
WMA(Windows Media Audio)格式是微软公司发布的文件格式,也是有损压缩格式。它与MP3格式不分伯仲。在低比特率渲染情况下,WMA格式显示出来比MP3更多的优点,压缩比MP3更高,音质更好。但是在高比特率渲染的情况下MP3还是占有优势。
4.CAFF文件
CAFF(Core Audio File Format)文件,是苹果公司开发的专门用于Mac OS X和iOS系统无压缩音频格式。它被设计出来替换老的WAV格式。
5.AIFF
AIFF(Audio Interchange File Format)文件,是苹果公司开发的专业音频文件格式。AIFF的压缩格式是AIFF-C(或AIFC),将数据以4:1压缩率进行压缩,专门应用于Mac OS X和iOS系统。
5.2 音频API
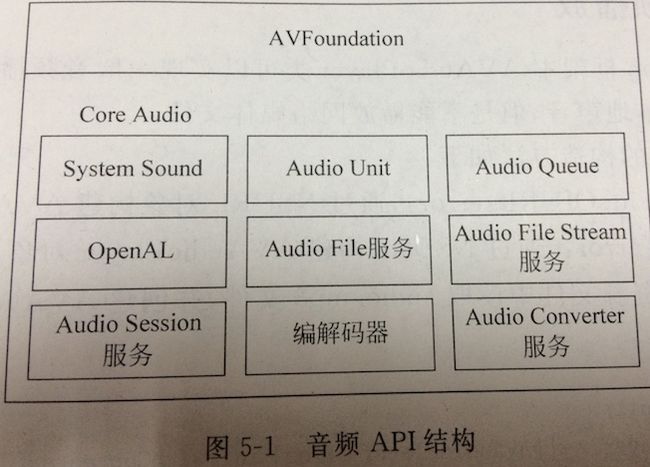
在Mac OS X和iOS系统上开发音频应用,主要有两个框架(AVFoundation和Core Audio)可以使用。AVFoundation是基于OC的高层次框架,为开发基本音频功能的开发者提供的API。而Core Audio是基于C的低层次多个框架的复合,Core Audio可以实现对于音频更加全面的控制,可以实现混合多种声音、编解码音频数据、访问声道元数据等,Core Audio还提供了一些音频处理和转化的工具。
Core Audio内容比较多使用起来也比较麻烦,它有四个主要的音频处理引擎API:System Sound、 Audio Unit、 Audio Queue、 OpenAL,其他的几个都属于辅助性的API。下面详细介绍Core Audio中的API:
- System Sound,基于C的音频API,可以播放系统声音,它播放短的声音,不超过30秒
- Audio Unit,最底层的声音生成器,它会生成原始音频样本并且将音频值放到输出缓冲区中,Audio Unit也可以实现混合多种声音
- Audio Queue,可以提供对音频的录制、播放、暂停、循环和同步处理
- OpenAL,是一个基于位置变化的3D声音的工业化标准API,它的API接口与OpenGL非常相似。主要应用于游戏音频处理
- Audio File服务,这个服务简化了处理各种不同的音频容器格式的任务,可以读写各种支持音频流,而不用考虑它们的差异
- Audio File Stream服务,是读写网络音频流数据,当从一个流读取数据时,使用该服务解析这个流并确定其格式,最终把音频数据包传递给一个音频队列或自行处理
- Audio Converter服务,实现音频数据格式的转换
- Audio Session服务,协调使用音频资源与系统之间的关系
- 编解码器,根据需要可以自定义编解码器
下面主要介绍AVFoundation框架实现音频录制和播放、使用System Sound API播放系统声音和使用OpenAL显示游戏音效处理
5.3 AVFoundation框架实现音频录制和播放
实现音频录制与播放可以使用AVFoundation框架,也可以通过Core Audio中的Audio Queue实现。
5.3.1 音频播放
在AVAudioPlayer的构造方法如下
- initWithContentsOfURL:error:,通过NSURL对象构建AVAudioPlayer;
- initWithData:error:,通过NSData构件AVAudio对象
下面的代码是从资源文件中读取audio.mp3文件,并创建AVAudioPlayer对象。其中error是NSError对象。
NSError *error =nil;
AVAudioPlayer *player = [AVAudioPlayer alloc] initWithContentOfURL:[NSURL fileURLWithPath:[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"audio" ofType:@"mp3"]] error:&error];AVAudioPlayer 中播放相关方法和属性如下:
- -(BOOL)play,开始播放音频
- -(BOOL)playAtTime:(NSTimeInterval)time,指定开始时间播放音频
- -(void)pause,暂停播放音频
- -(void)stop,停止播放音频
- -(BOOL)prepareToPlay,预处理音频播放设备,可以减少播放延迟
- playing属性,判断音频是否正在播放,布尔类型的属性
- volume属性,当前播放音频的质量,float类型的属性
- numberOfLoops属性,播放音频的次数,NSInteger类型的属性,-1表示不限次数
下面的代码实现了播放预处理和设置播放不限次数
NSError *error = nil;
AVAudioPlayer *player = [AVAudioPlayer alloc] initWithContentOfURL:[NSURL fileURLWithPath:[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"audio" ofType:@"mp3"]] error:&error];
[player prepareToPlayer];
player.numberofLoops = -1;除了上面的主要的方法和属性外AVAudioPlayer还提供了获得音频信息的方法,以及获得测试声音相关属性的方法
AVAudioPlayer还有对应的委托协议AVAudioPlayerDelegate,AVAudioPlayerDelegate协议提供的主要方法如下:
- audioPlayerDidFinishPlaying:successfully:,播放完成回调方法,successfully参数返回NO则失败,YES则成功
- audioPlayerDecodeErrorDidOccur:error:,当解码发生错误时回调的方法
- audioPlayerBeginInterruption:,当播放器被中断时候回调的方法,例如电话打入进来的时候
- audioPlayerBeginInterruption:,中断返回回调的方法
下面通过实例介绍,如图所示时一个音乐播放器的实例,在屏幕中有两个按钮,可以控制资源文件中某个音频文件的播放(或暂停)和停止
#import "ViewController.h"
#import 5.3.2 音频录制
在AVFoundation框架中AVAudioRecorder类可以实现音频录制,AVAudioRecorder的构造方法是initWithURL:setting:error:,通过NSURL对象构建AVAudioRecorder对象,其中settings是NSDictionary类型的参数,为音频录像会话提供所需要的设置。
下面的代码实现了创建AVAudioRecorder对象
NSString *filePath =
[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/rec_audio.caf", [self documentsDirectory]];
NSURL *fileUrl = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:filePath];
NSError *error = nil;
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setCategory:AVAudioSessionCategoryRecord
error:&error];
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setActive:YES error:&error];
NSMutableDictionary *settings = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
// AVFormatIDKey键是设置录制音频编码格式kAudioFormatLinearPCM代表线性PCM编码格式
// PCM(pulse code modulation)线性脉冲编码调制,它是一种非压缩格式
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithInt:kAudioFormatLinearPCM]
forKey:AVFormatIDKey];
// AVSampleRateKey设置音频采样频率
// 44100.0是音频CD、VCD、SVCD和MP3所用采样频率
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:44100.0]
forKey:AVSampleRateKey];
// AVNumberOfChannelsKey设置声道的数量,取值为NSNumber类型的1或2
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithInt:1]
forKey:AVNumberOfChannelsKey];
// AVLinearPCMBitDepthKey设置采样位数
// 取值为NSNumber类型的8、16、24或32,16是默认值
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithInt:16]
forKey:AVLinearPCMBitDepthKey];
// AVLinearPCMIsBigEndianKey设置音频解码是大字节序还是小字节序
// 大字节序设置YES 小字节序设置为NO
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithBool:NO]
forKey:AVLinearPCMIsBigEndianKey];
// AVLinearPCMIsFloatKey设置音频解码是否为浮点数
// 如果是则设置YES,否则设置为NO
[settings setValue:[NSNumber numberWithBool:NO]
forKey:AVLinearPCMIsFloatKey];
// 获得沙箱目录中Document下音频文件路径
recorder = [[AVAudioRecorder alloc]
initWithURL:fileUrl
settings:settings
error:&error];
recorder.delegate = self;注意:编码格式与文件格式不同,例如WAV是音频文件格式,它采用线性PCM音频编码
AVAudioRecorder中录制相关方法和属性如下:
- -(BOOL)record音频录制
- -(void)pause暂停录制
- -(void)stop停止录制
- -(BOOL)recordAtTime:(NSTimeInterval)time,指定开始时间录制视屏
- -(BOOL)recordForDuration:(NSTimeInterval)duration,指定持续时间录制视频
- -(BOOL)prepareToRecord,预处理音频播放设备,可以减少播放延迟
- recording属性,判断音频是否正在录制,布尔类型的属性
除了上面的主要的方法和属性外,,AVAudioPlayer还提供了获得音频信息的方法,以及获得测量声音相关属性的方法
AVAudioRecorder还有对应的委托协议AVAudioRecorderDelegate,AVAudioRecorderDelegate协议提供的主要方法:
- audioRecorderDidFinishRecording:successfully:,录制完成回调方法,successfully参数返回NO则失败,Yes则成功
- audioRecorderEncodeErrorDidOccur:error:,当编码发生错误时回调的方法
- audioRecorderBeginInterruption:,当录制过程被中断时候回调的方法,例如电话打入进来的时候
- audioRecoderEndInterruption:withOptions:,中断返回回调的方法
下面通过实例介绍。如图所示时一个录音机实例,在屏幕中有三个按钮,可以控制音频的录制、停止和播放,状态显示的视图上面的标签中。
#import "ViewController.h"
#import 注意:AVAudioSession类提供了Audio Session服务,Audio Session是指定应用与音频系统如何交互。AVAudioSession通过指定一个音频类别(Category)实现的,音频类别描述了应用使用音频的方式。下面的语句是设定音频会话类别:
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setCategory:AVAudioSessionCategoryRecord errorL&error];
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setCategory:AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayback errorL&error];AVAudioSessionCategoryRecord代表只能输入音频,即录制音频,其效果是停止其他的音频播放,开始录制音频。AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayback代表只能输出音频,即进行音频播放。常用Audio Session类别如表所示:
| 音频类别 | 获取输入硬件 | 获取输出硬件 | 与iPod混音 | 服从振铃/静音 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayback | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| AVAudioSessionCategoryRecord | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayAndRecord | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| AVAudioSessionCategoryAmbient | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| AVAudioSessionCategorySoloAmbient | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 |
注意:表中获得输入硬件,表示能使用音频输入设备。如麦克风等设备。获取输出硬件表示能够使用音频输出设备,如yangshengqi和耳机等设备。与iPod混音是只能与iPod媒体库播放的音频混音。服从震动/静音是在设备中国年设置振铃/静音后,是否影响音频类别,AVAudioSessionCategoryAmbient和AVAudioSessionCategorySlolAmbient是受到影响的类别。
还有Audio Session中还可以设置是否“活跃”,这会把后台的人和系统声音关闭,如
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setActive:YES error:&error];
[[AVAudioSession sharedInstance] setActive:YES error:&error];
5.3.3 语音合成
苹果公司在iOS7中推出了语音合成器的技术,无需网络环境也可以实现语音合成。iOS7语音合成的主要的AOI如下:
- AVSpechUtterance,是语音合成的基本单元,它封装影响语音合成需要的一些参数:语音、语调、语速和延迟等
- AVSpechSynthesisVoice,是语音合成中的Voice对像,它主要包括语音和地区两个方面
- AVSpeechSynthesisVoice,是语音合成中的voice对象,它主要包括语音合地区两个方面
- AVSpeechSynthesizer,语音合成器的管理类,通过speakUtterance:方法管理AVSpeechUtterance对象。
- AVSpeechSynthesizerDelegate,是AVSpeechSynthesizer的委托协议。
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextView *textView;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISlider *slider;
@property (nonatomic, strong) AVSpeechSynthesizer *speechSynthesizer;
- (IBAction)speakButtonWasPressed:(id)sender;
- (IBAction)speechSpeedShouldChange:(id)sender;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
//为TextView
[self.textView.layer setBorderWidth:.5f];
[self.textView.layer setBorderColor:[[UIColor grayColor] CGColor]];
[self.textView setDelegate:self];
self.speechSynthesizer = [[AVSpeechSynthesizer alloc] init];
self.speechSynthesizer.delegate = self;
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
{
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
-(BOOL)textView:(UITextView *)textView shouldChangeTextInRange:(NSRange)range replacementText:(NSString *)text{
BOOL retval = TRUE;
if([text isEqualToString:@"\n"]){
[self.textView resignFirstResponder];
retval = FALSE;
}
return retval;
}
- (IBAction)speakButtonWasPressed:(id)sender {
AVSpeechUtterance *utt = [AVSpeechUtterance speechUtteranceWithString:[self.textView text]];
utt.rate = [self.slider value];
[self.speechSynthesizer speakUtterance:utt];
}
- (IBAction)speechSpeedShouldChange:(id)sender {
UISlider *slider = (UISlider *)sender;
NSInteger val = round(slider.value);
NSLog(@"%@",[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%ld",(long)val]);
}
#pragma mark--AVSpeechSynthesizerDelegate
- (void)speechSynthesizer:(AVSpeechSynthesizer *)synthesizer
didStartSpeechUtterance:(AVSpeechUtterance *)utterance {
NSLog(@"语音合成开始。");
}
- (void)speechSynthesizer:(AVSpeechSynthesizer *)synthesizer
didFinishSpeechUtterance:(AVSpeechUtterance *)utterance {
NSLog(@"语音合成完成。");
}
@end 5.4 使用System Sound API
5.3节中介绍了AVFoundation框架,本节介绍Core Audio中的System Sound API,它属于面向C语言的低层次API,使用起来有点繁琐。使用System Sound API可以播放短的声音,不能对其暂停或停止等控制,我们可以用它来制作游戏音效(如子弹射击声音)和操作音(如按钮单击、删除操作等),以及提醒用户要做某件事情,而且它还可以发出振动提醒,但是只能是iPhone设备上。
System Sound API中的方法如下:
- AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID,创建SystemSoundID
- AudioServicesDisposeSystemSoundID,释放SystemSoundID
- AudioServicesPlayAlertSound,发出警告提示(声音+振动)
- AudioServicesPlaySystemSound,播放系统声音
- AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion,注册声音播放完成事件,指定回调函数
- AudioServicesRemoveSystemSoundCompletion,注销声音播放完成事件,指定回调函数
为了介绍System Sound API本节安排的实例,分别可以测试System Sound API的三个方面的应用

5.4.1 播放系统声音
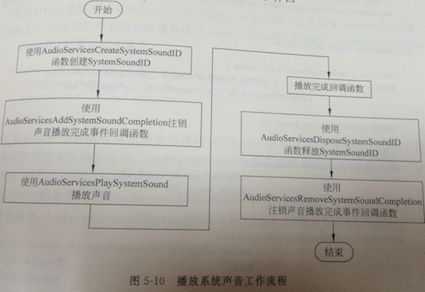
播放系统声音主要使用AudioServicesPlaySystemSound函数进行播放,主要用于游戏音效和操作声音等。它的工作流程如图
从上面的流程看,播放过程涉及5个函数,3个不同阶段:播放前的准备,播放和播放后的处理
(1)播放前的准备阶段:使用AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID函数创建SystemSoundID,然后使用AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion注销声音播放完成事件回调函数
(2)播放阶段:使用AudioServicesPlaySystemSound播放声音实现的
(3)播放后的处理阶段:释放资源、注销事件回调函数,这包括了使用AudioServicesDisPoseSoundID函数释放SystemSoundID和使用AudioServicesRemoveSystemSoundCompletion注销声音播放完成事件回调函数。
#import "ViewController.h"
#import 说明:
按照程序的流程是用户单击播放按钮,触发playSystemSound方法,NSURL* system_sound_url = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:[[NSBundle mainBundle] 该段代码是创建要播放的音频文件全路径,在System Sound API中能播放的系统声音文件必须是没有压缩的,解码必须是线性PCM或IMA-ADPCM格式,如.aif、.wav和.caf等文件。
pathForResource:@"AlertChordStroke" ofType:@"wav"]];
SystemSoundID system_sound_id;是声明一个SystemSoundID,用来管理系统声音。
AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID( 创建SystemSoundID,一旦创建成功,再往后的声音的控制都是通过SystemSoundID实现的。AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID函数的定义如下:
(CFURLRef)CFBridgingRetain(system_sound_url),
&system_sound_id
);
OSStatus AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID(
CFURLREF inFileURL,
SystemSoundID *outSystemSoundID
)函数返回值OSStatus类型的状态编码,OSStatus是SInt32类型别名。inFileURL参数是指定播放文件的全路径。outSystemSoundID是创建的SystemSoundID,使用时需要传递地址(即&system_sound_id)。
使用AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion函数注销声音播放完成事件回调函数,AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion函数的定义如下:
OSStatus AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion(
SystemSoundID outSystemSoundID,
CFRunLoopRef inRunLoop,
CGStringRef inRunLoopMode,
AudioServicesSystemSoundCompletionProc inCompletionRoutine,
void *inClientData
)inSystemSoundID参数时AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID函数中创建的SystemSoundID。inRunLoop是指定回调函数在哪个RunLoop中运行,一个RunLoop就是一个事件处理的循环,用来不停地调度工作以及处理输入事件,传递NULL是在主RunLoop运行。inRunLoopMode指定RunLoop运行模式,传递NULL是默认的RunLoop运行模式。inCompletionRoutine参数是用来指定回调函数,传递的是一个函数指针。inClientData参数是给回调函数传递的参数。
使用AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(system_sound_id)函数播放系统声音,参数system_sound_id是使用AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID函数创建SystemSoundID。
当声音播放完成之后,会回调SoundFinishedPlayingCallback,在SoundFinishedPlayingCallback函数中需要注销声音播放完成事件回调函数。
5.4.2 发出警告提醒
System Sound API可以发出警告提醒,在iPhone设备上默认情况下发出警告形式是“声音+振动”,当然可以设置其他的形式,而在iPad和iPod touch设备上不支持振动,只有声音警告了。System Sound API发出警告与播放系统声音整个工作流程一样的,只不过需要将AudioServicesPlaySystemSound换成函数AudioServicesPlayAlertSound,AudioServicesPlayAlertSound是专门用来发出警告的,事实上这两个函数在iPad和iPod touch设备上一样只能发出声音
- (IBAction)alert:(id)sender {
NSURL* system_sound_url = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:[[NSBundle mainBundle]
pathForResource:@"BeepGMC500" ofType:@"wav"]];
SystemSoundID system_sound_id;
//创建SystemSoundID
AudioServicesCreateSystemSoundID(
(CFURLRef)CFBridgingRetain(system_sound_url),
&system_sound_id
);
// 注册声音播放完成事件回调函数。
AudioServicesAddSystemSoundCompletion(
system_sound_id,
NULL,
NULL,
SoundFinishedPlayingCallback,
NULL
);
// 发出警告
AudioServicesPlayAlertSound(system_sound_id);
}上面的代码除了使用AudioServicesPlayAlertSound函数替换了AudioServicesPlaySystemSound函数,其余代码一样
5.4.3 振动
System Sound API也可以让设备振动,这样的效果也只能在iPhone设备上体会到。而在iPad和iPod touch设备上不支持振动的,在这些设备上进行Systm Sound API调用设备没有任何反应。与前面两种调用相比,振动调用非常简单,使用下面的语句就可以实现了:
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(kSystemSoundID_vibrate);
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound函数就是我们播放系统声音使用的函数,而SystemSoundID是系统定义的常量,kSystemSoundID_Vibrate代表振动调用。
(IBAction)vibrate:(id)sender {
NSString * deviceModel = [[UIDevice currentDevice] model];
NSLog(@”设备:%@”,deviceModel);if ([deviceModel isEqualToString:@”iPhone”]) {
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(kSystemSoundID_Vibrate);
} else {
UIAlertView *alertView = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@”提示”
message:@”设备不支持”
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@”Ok”
otherButtonTitles: nil];
[alertView show];
}
}
5.5 使用OpenAL API
在iOS平台上播放音效的最简单的方法是使用System Sound API。这对于发出操作音或简单UI互动之类的任务已经足够好用。但是,对于任何更复杂一点的任务,如游戏音效就力不从心了。使用System Sound API会立即开始播放音效,但若要指定的音效与游戏的特定帧相配合的话,它基本上是无法实现的。为了更好的控制音效,我们需要使用OpenAL。
OpenAL(Open Audio Library)是自由软件界的跨平台音效API。它涉及给多通道3D位置音效,其API风格模仿自OpenGL。
5.5.1 OpenAL 构成
OpenAL由三个实体构成:Listener(听众),source(声源)和buffer(缓存)
5.5.2 OpenAL与3D空间中的声音
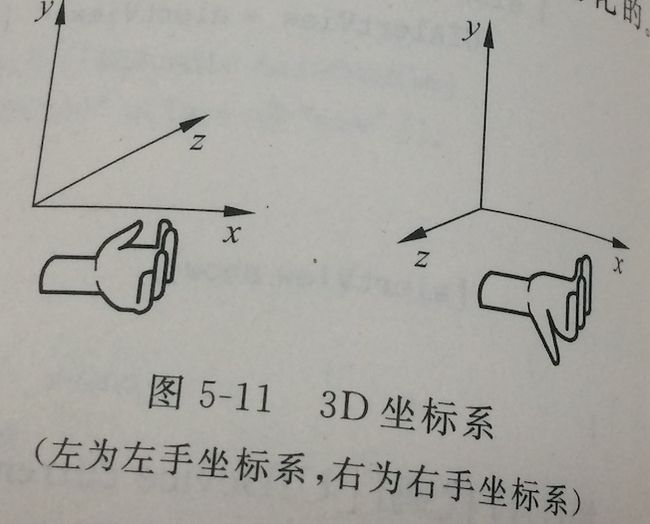
现实生活中国年,听众和声源是3D空间中的,他们之间的位置和方向是不断变化的。OpenAL能够描述这种实际的环境,因此在OpenAL中很多函数都是涉及3D空间的,3D空间采用3D笛卡尔坐标系(或3D坐标系)描述。
提示:3D坐标系分为左右坐标系,它的区别在于Z轴的方向的不同。在X轴方向向右,正Y轴方向向上。通过沿x轴方向到正Y轴方向握拳,大拇指的指向方向就是正Z轴的方向。如图,OpenAL采用右手坐标系。
5.5.3 OpenAL API
OpenAL API模仿OpenGL API,所有的函数都以“al”开头,如alSourcei()函数。OpenAL的函数都被设计为属性风格,我们对属性可以读(get)和写(set),下面的函数是取得听众某个属性:
alGetListenerf(ALenum param, ALfloat value)其中,param参数是指定属性常量,value是获得该属性需要的参数。下面代码是设置听众某个属性函数。
AlListenerf(ALenum param,ALfloat value)其中,param参数是指定属性常量,value是获得该属性需要的参数。
此外,函数名的后缀与OpenGL也是比较类似的,它们的函数后缀说明了函数参数的类型。在OpenAL中我们会看到下面几种不同的函数后缀类型:
alListenerf(ALenum param,ALfloat value);
alListener3f(ALenum param,ALfloat value1,Afloat value2,Afloat value3);
alListenerfv(ALenum param,const ALFloat *values);
alListeneri(ALenum param,ALint value);
alListener3i(ALenum param,ALint value1,ALint value2,ALint value3);
alListeneriv(ALenum param,const ALint *values);alListenerf函数后缀“f”,说明只需要传递一个float类型参数。alListener3f函数后缀“3f”,说明需要传递三个float类型的参数,如3D坐标。alListenerfv函数的后缀是“fv”,说明需要传递的数据是float的数组类型。alListeneri函数后缀“i”说明只需要传递一个证书类型参数。alListener3i函数后缀“3i”,说明需要传递三个整数类型参数。AlListeneriv函数后缀“iv”,说明需要传递一个整数类型数组参数。从上面的函数代码中我们可以归纳处理后缀的类型有:“f”、“3f”、“fv”、“i”、“3i”和“iv”等。当然也有一些函数是没有这些后缀的,这说明他们需要传递这几种类型的参数。如下面的几个函数:
alSourcePlay(ALuint sid)
alSourceStop(ALuint sid)
alSourcePause(ALuint sid)5.5.4 OpenAL应用开发流程
我们使用OpenAL开发可以播放声音、捕获声音、声音特效和声音流处理。基本上的开发流程都比较类似,我们重点介绍播放声音流程。
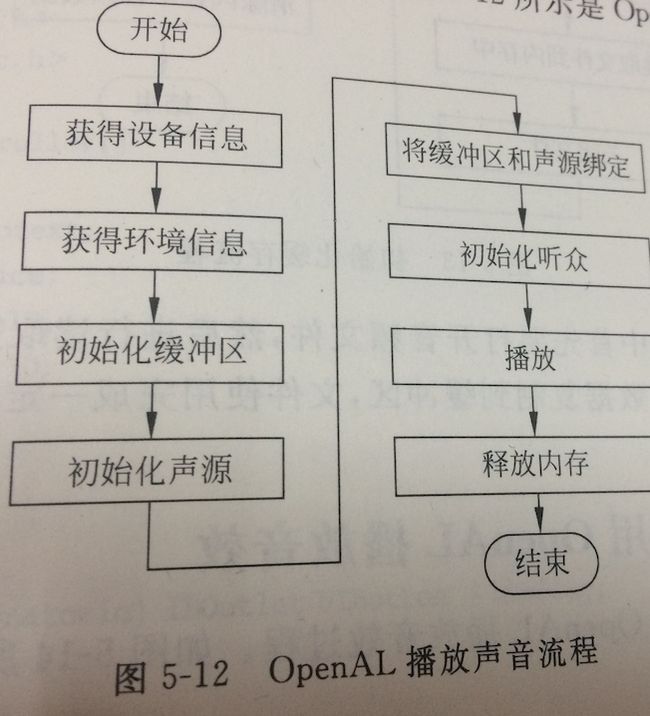
在上述六成中从获得设备信息到初始化听众都属于初始化阶段,我们可以某个类的初始化方法或者构造方法中国年处理,如视图控制器的viewDidLoad方法中的。
初始化完成之后就可以进行播放等操作了。不再使用之后一定要释放内存,包括释放声源、释放缓存、释放环境和关闭设备等处理。
//释放内存
-(void)cleanUpOpenAL
{
// 释放声源
alDeleteSources(1, &sourceID);
// 释放缓存
alDeleteBuffers(1, &bufferID);
// 释放环境
alcDestroyContext(mContext);
// 关闭设备
alcCloseDevice(mDevice);
}5.5.5 实例:使用OpenAL播放音效
#import "ViewController.h"
#import