排序算法总结Sorting Algo
Backto Algo Index
综述
对于一个 Sorting Algo 的评价,一般有以下几个标准
- Time Complexity:Best,Worst, Average
不仅要知道三个时间复杂度,还要知道对应的数据情形。通常对于基于比较的 Sorting Algo,Best 就是顺序排列的,Worst 就是 逆序排列的,Average 就是随机排列的。因为不同的 Algo 在不同的情形下表现可能大不同个,因为我们需要根据业务的实际情况,pick the right one. - 时间复杂度的系数,常数,低阶
当用 Big-O 分析的时候,通常忽略这些细节,但是 Big-O 针对的是数据规模很大的情况下的增长趋势。而排序算法,很多情况下是限定规模的, 比如 10, 1000, 100万,因此这些被忽略的项需要加上才能比较不同algo 的优劣。 - 比较次数和交换(或移动)的次数
尤其是对于基于比较的排序算法,核心就两步,比较–交换, 统计次数尤为重要。 - algo 的内存消耗
也就是空间复杂度啦,如果是原地排序(sorted in place),空间复杂度就是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1). - algo 的稳定性
一个sorting algo 具有稳定性指的是,排序前后相等的元素相对位置不变。否则,就是不稳定的 sorting algo。例如对于一组数据3,5,6,3,1, 排序后是1,3,3,5,6这里面两个相等的 3 相对位置是否改变了,决定了使用的algo 是否具有稳定性. 这个在实际业务中很重要, 因为我们总是需要根据多个不同的度量多层次排序, 可不希望一个层次排好了,其他层次全乱了.
经典的排序算法
| Sorting Algo | Time Complexity | Based on comparsion? | DESC |
|---|---|---|---|
| BubbleSort 冒泡排序 | O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) | Yes | 依次比较, 大的往后换 |
| InsertionSort 插入排序 | O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) | Yes | 左边已排序,右边未排序.把未排序部分依次insert到排序部分中去 |
| SelectionSort 选择排序 | O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) | Yes | 左边已排序,右边未排序.在右边select最小值,和右边第一个数swap.左边+1,右边-1. |
| QuickSort 快排 | O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn) | Yes | 在数组的头尾之间任意选取一个pivot,然后遍历数组小于pivot的放左边,大于pivot的放右边.pivot居中间.然后左右再分别QuickSort. |
| MergeSort 归并排序 | O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn) | Yes | 打散成小组,小组排好序. 再把小组结果merge成完整的排序序列. |
| BucketSort 桶排序 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | No | |
| CountingSort 计数排序 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | No | |
| RadixSort 基排序 | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | No |
BubbleSort
void Swap(int& a, int& b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//the bigger one move backward
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n) {
if(n <= 1)
return;
bool hasSorted = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { //controls bubble times
for (int j = 0; j < n-1-i; ++j) { // move the biger backward
if (a[j+1]>a[j]) {
Swap(a[j+1], a[j]);
hasSorted = false;
}
}
if (hasSorted)
break;
}
}
InsertionSort
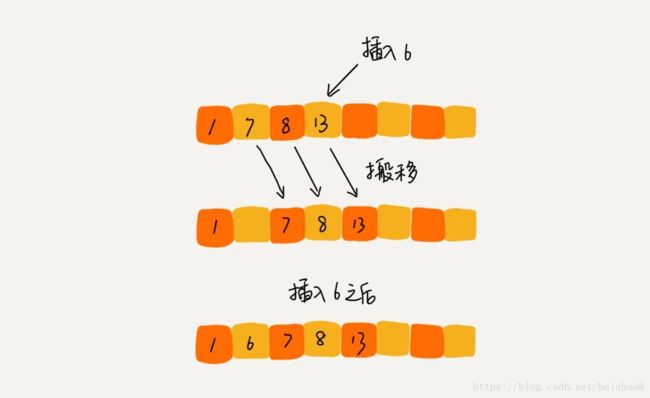
// Pick element in unsorted region and Insert it Into sorted region
void InsertionSort(int* a, int n) {
if(n <= 1)
return;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { //the 1st is in order, insert the last (n-1) elements
int value = a[i]; // value to insert
int j = i -1;
for(;j>=0;--j) { //compare with left elements to find the insertion postion
if(a[j] > value) { // greater than value
a[j+1] = a[j]; //move right-ward
} else { //less than value
break; // pos to insert is found = (j+1), stop moving
}
}
a[j+1] = value;
}
}
SelectionSort
// Select the smallest element from the unsorted region and
// append it to the tail of sorted region.
// unstable, less used
void SelectionSort(int* a, int n) {
}
MergeSort
//interface
void MergeSort(int* a, int n) {
MergeSort(a, 0, n-1);
}
//real worker
void MergeSort(int* a, int idx_head, int idx_tail) {
//terminate condition
if(idx_head >= idx_tail)
return;
//find the middle pos
int idx_mid = (idx_head + idx_tail)/2;
//divide into 2 sub-tasks with recursion
MergeSort(a, idx_head, idx_mid);
MergeSort(a, idx_mid+1, idx_tail);
//merge results
Merge(a, idx_head, idx_mid, idx_tail);
}
// Merge phase
void Merge(int* a, int idx_head, int idx_mid, int idx_tail) {
int i = idx_head; // iter over elems in the 1st part
int j = idx_mid + 1; // iter over elems in the 2nd part
int k = 0; // iter over tmp array
int* tmp = new int[idx_tail - idx_head + 1];
while(i <= idx_mid && j <= idx_tail) { // either one hits the end, stop comp
if(a[i] > a[j]) // NOT `>=`. if `=` is added, the algo is not stable anymore
tmp[k++] = a[j++];
else
tmp[k++] = a[i++];
}
//judge which array remains elems
int head = i; // 1st array remains
int end = idx_mid;
if(j <= idx_tail) { //2nd array remains
head = j;
end = idx_tail;
}
//copy remained elems
while(start <= end)
tmp[k++] = a[start++];
// copy tmp back to a
for(i=0; i <= idx_tail- idx_head; ++i)
a[i] = tmp[i];
SafeDelete(tmp);
}
QuickSort
//public interface
void QuickSort(int* a, int n) {
QuickSort(a, 0, n-1);
}
// real worker
void QuickSort(int* a, int idx_head, int idx_tail) {
if(idx_head >= idx_tail)
return;
int idx_mid = Partition(a, idx_head, idx_tail);
QuickSort(a, idx_head, idx_mid);
QuickSort(a, idx_mid+1, idx_tail);
}
//Version 1: Clear, Short,
// e.g.
// a = [5,1,4,2,3], idx_head=0, idx_tail=4
// j = 0, do nothing, 5-1-4-2-3, i = 0;
// j=1, swap(a[0], a[1]), 1-5-4-2-3, i=1;
// j=2, do nothing, 1-5-4-2-3, i=1;
// j=3, swap(a[1],a[3]), 1-2-4-5-3, i=2;
// iter over, i=2, swap(a[2],a[4]), 1-2-3-5-4, i=2
// return 2
int Partition(int* a, int idx_head, int idx_tail) {
int pivot = a[idx_tail];
int i = idx_head; //iter grows to find the mid
int j = idx_head; //iter over a to find elems less than pivot
for(; j < idx_tail; ++j) {
if(a[j] < pivot) { // find an elem less than pivot
Swap(a[i], a[j]); //swap it front
++i; //smaller elems count + 1
}
}
Swap(a[i], a[idx_tail]);
return i;
}