爬虫数据提取方法详解(一)
爬虫中数据的分类:结构化数据(json,xml等)处理方式是直接转化为python类型,jsonpath,xpath,bs4等.
非结构化数据(HTML)处理方式是正则表达式,xpath,bs4等.
数据提取之json: json是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,他使得人们很容易的进行阅读和编写,同时也方便了机器进行解析和生成。适用于进行数据交互的场景,比如网站前台与后台直接的数据交互。以下举例。
import json
mydict = {
"store":{
"book":[
{"category":"reference",
"author":"Nigel Rees",
"title":"Saying of the Century",
"price":8.95
},
{"category":"fiction",
"author":"Evelyn Waugh",
"title":"Sword of Honour",
"price":12.09
},
],
}
}
# json.dumps 实现python类型转化为json字符串
# indent实现换行和换格
# ensure_ascii = Flase 实现让中文写入的时候保持为中文
json_str = json.dumps(mydict,indent=2,ensure_ascii=False)
print('json.dumps python_type-->json_str: {}'.format(type(json_str)))
# json.loads 实现json字符串转化为python的数据类型
my_dict = json.loads(json_str)
print('json.loads json_str-->python_type: {}'.format(type(my_dict)))
# json.dump 实现把python类型写入类文件对象
with open("json模块示例文件.txt", "w") as f:
json.dump(mydict, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
input('json.dump 已成功写入文件')
# json.load 实现类文件对象中的json字符串转化为python类型
with open("json模块示例文件.txt", "r") as f:
my_dict = json.load(f)
print('json.load 读取文件--> {}: {}'.format(type(my_dict), my_dict))jsonpath介绍: 用来解析多层嵌套的json数据;JsonPath 是一种信息抽取类库,是从JSON文档中抽取指定信息的工具,提供多种语言实现版本,包括:Javascript, Python, PHP 和 Java。
jsonpath 对于 JSON 来说,相当于 XPath 对于 XML。
我们以拉勾网城市JSON文件 http://www.lagou.com/lbs/getAllCitySearchLabels.json 为例,获取所有城市的名字的列表,并写入文件。
import requests
import jsonpath
import json
# 获取拉勾网城市json字符串
url = 'http://www.lagou.com/lbs/getAllCitySearchLabels.json'
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0)"}
response =requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html_str = response.content.decode()
# 把json格式字符串转换成python对象
jsonobj = json.loads(html_str)
# 从根节点开始,获取所有key为name的值
citylist = jsonpath.jsonpath(jsonobj,'$..name')
# 写入文件
with open('city_name.txt','w') as f:
content = json.dumps(citylist, ensure_ascii=False)
f.write(content)数据提取之正则
正则:用事先定义好的一些特定字符、及这些特定字符的组合,组成一个规则字符串,这个规则字符串用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。
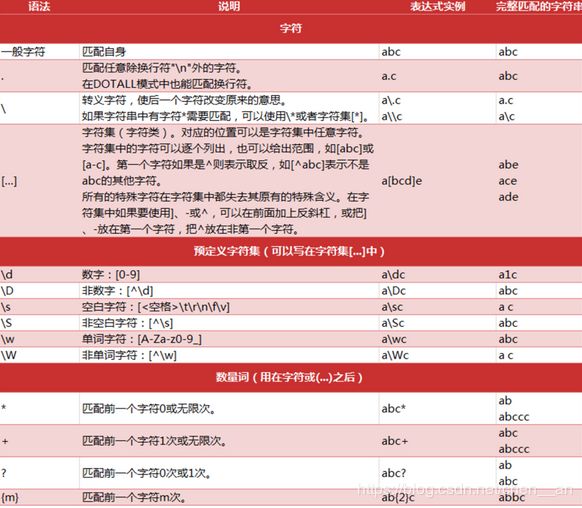
正则表达式常见用法:
re模块常见方法:
- re.match(从头找一个)
- re.search(找一个)
- re.findall(找所有)
- 返回一个列表,没有就是空列表
re.findall("\d","chuan1zhi2") >> ["1","2"]
-
re.sub(替换)
re.sub("\d","_","chuan1zhi2") >> ["chuan_zhi_"]
-
re.compile(编译,提升匹配速度)
- 返回一个模型P,具有和re一样的方法,但是传递的参数不同
-
匹配模式需要传到compile中
p = re.compile("\d",re.S) p.findall("chuan1zhi2")